Anesthesia
Pharmacology: Gastrointestinal Pharmacology Practice Questions
Choose the correct answer for each question.
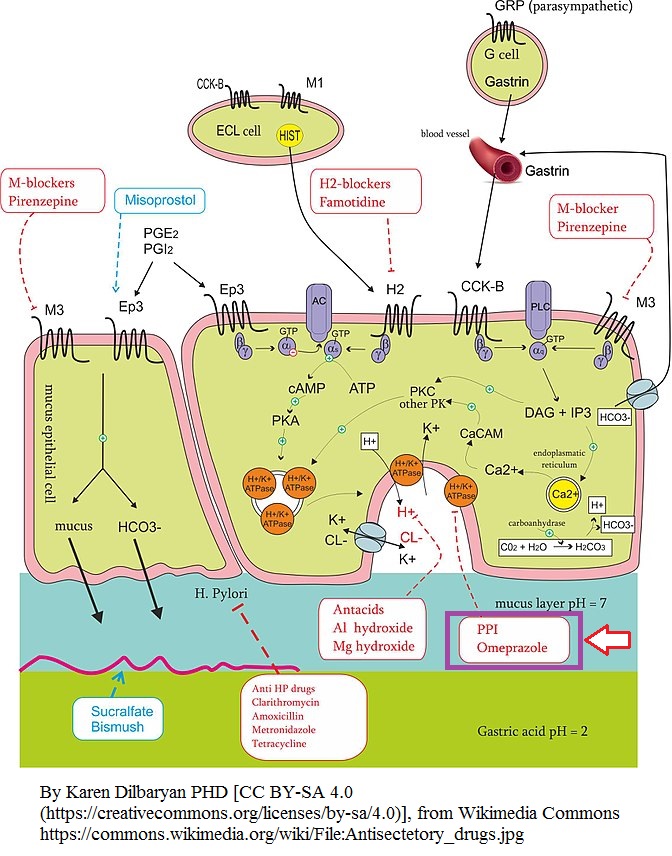
Concerning gastrointestinal mucosal defenses:
- Mucosal defense depends in part on prostaglandins and nitric oxide, locally synthesized.
- Damage to the gastric mucosa in absence of appropriate defense mechanisms can be mediated by gastric acid and pepsin
- Both
- Neither
Gastric acid-mediated mucosal damage may be managed or prevented by which one(s) of the following?
- Reducing gastric pH (acidity)
- Increasing mucosal defense systems
- Both
- Neither
This infectious agent is thought to play a central role in asset-peptic disease pathologies:
- Spirochetes (especially Borrelia burgdorferi)
- Helicobacter pylori
- Acidobacterium capsulatum
Most effective drugs that reduce gastric acid secretion inhibit gastric H+, K+--ATPase (proton pump).
- True
- False
Typically, proton pump inhibitors are pro-drugs which undergo activation to a sulfenamide derivative.
- True
- False
Omeprazole (Prilosec and others) and esomeprazole (Nexium):
- Esomeprazole is the S-isomer of omeprazole.
- Omeprazole turns out to be about twice as potent as its S-isomer, esomeprazole.
- True
- False
Which one(s) of the following agents are classified as proton pump inhibitor(s)?
- Lansoprazole (Prevacid)
- Rabeprazole (AcipoHex)
- Both
- Neither
After administration, proton pump prodrugs reach stomach parietal cells and concentrate in acidic secretory canaliculi.
- True
- False
Proton pump inhibitors interact with H+, K+-ATPase (the proton pump) anyway characterized most importantly as:
- Ionic bonding
- Hydrogen bonding
- Covalent bonding
- Vanderwall's interactions
Reactivation of proton pumps inhibited by proton pump inhibitors:
- Depend on slow diffusion of the drug away from the proton pump.
- Hydrolysis of the drug catalyzed by water thus breaking the drug-enzyme bond.
- Re-synthesis of new proton pumps, thus allowing a resumption of acid secretion.