2Purines
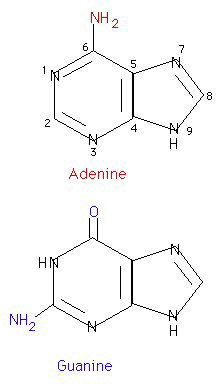
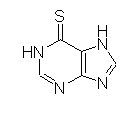
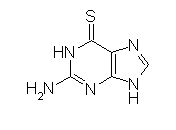
6-Thiopurines (Mercaptopurine [6-MP]; Thioguanine [6-TG])
Mechanism of Action:Activation by hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT) to form 6-thioinosinic acid which inhibits enzymes involved in purine metabolism. (thioguanylic acid and 6-methylmercaptopurine ribotide (MMPR) also active)
Clinical Use:
childhood acute leukemia
the analog, azathioprine (Imuran)-- immunosuppressive agent.
purine nucleotide pathway enzyme-inhibitor
decreased intracellular concentration of guanine nucleotides
inhibition of glycoprotein synthesis
Mechanism of Action: inhibits DNA/RNA synthesis
Clinical Use:
Synergistic with cytarabine in treating adult acute leukemia.
Drug resistance
Decreased HGPRT activity
In acute leukemia -- increased alkaline phosphatase, which dephosphorylates thiopurines nucleotides
Adverse Effects:
Both mercaptopurine and thioguanine, given orally, are excreted in the urine.
6-MP is converted to an inactive metabolite, 6-thioruric acid, by xanthine oxidase .6-TG: requires deamination before metabolism by xanthine oxidase.
In cancer (hematologic) chemotherapy, allopurinol is used to inhibit xanthine oxidase, to prevent hyperuricemia associated with tumor cell lysis {xanthine oxidase inhibition blocks purine degradation -- purines (more soluble) are excreted instead of uric acid (less soluble)}
use of allopurinol thus blocks acute gout and nephrotoxicity.
However, the combination of allopurinol and 6-mercaptopurine, because of xanthine oxidase inhibition, can lead to mercaptopurine toxicity; This interaction does not occur with 6-TG.
parenteral administration; renal excretion
dephosphorylated to active form:
Mechanism of Action: DNA synthesis inhibition
Clinical Use:
lymphoproliferative disease
Adverse Effect: dose-limiting -- myelosuppression.
phosphorylated by deoxycytidine kinase
incorporated into DNA
Mechanism of Action: increased strand breaks (inhibition of repair mechanisms)
Clinical Use:
Hairy cell leukemia
Adverse Effects:
Transient severe myelosuppression; possibly associated with infection.
irreversible inhibitor adenosine deaminase
results in toxic accumulation of deoxyadenosine nucleotides (especially in lymphocytes)
Adverse Effects:
immunosuppression (T cell mediated immunity)
myelosuppression
kidney function impairment
CNS toxicity
liver toxicity
 |
 |
Return to main menu