Chapter 4: Autonomic (ANS) Pharmacology: Introduction
Autonomic Nervous System: Anatomical Considerations
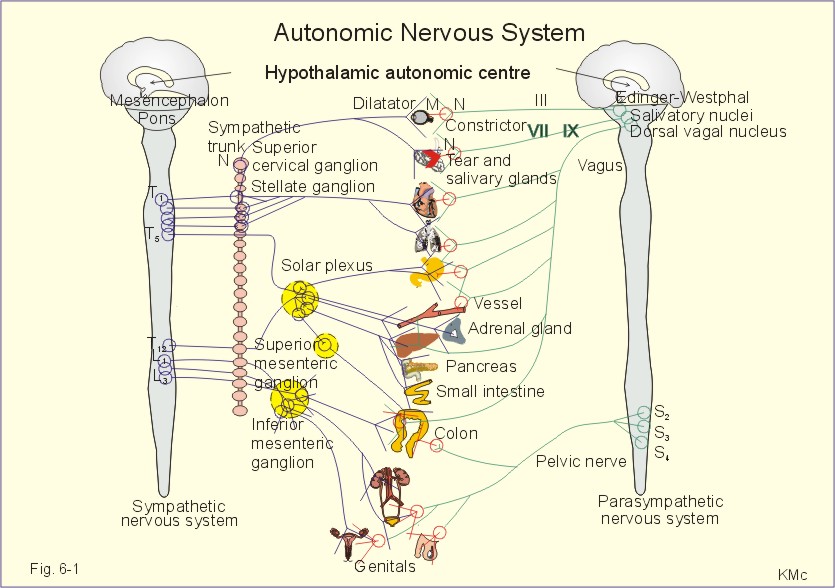
Figure by Poul-Erik Paulev, M.D., D.Sci, used with permission
Autonomic and Somatic Innervation
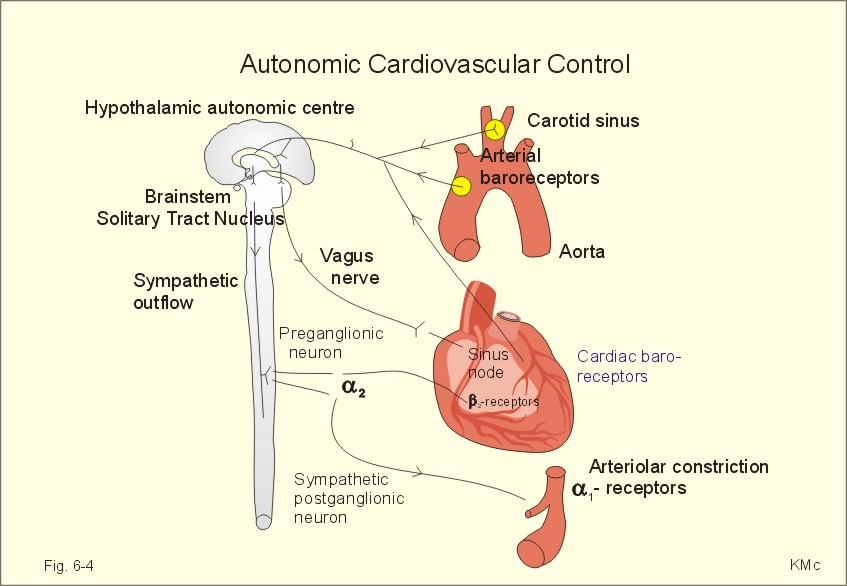 Figure by Poul-Erik Paulev, M.D., D.Sci, used with permission |
Substance P is an important sensory neurotransmitter, probably especially important in nociception, and is found in:
sensory afferent fibers
dorsal root ganglia
dorsal spinal cord horn
Other agents found in sensory neurons
Somatostatin
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) (found with Substance P in cardiovascular sensory nerve fibers)
Dorsal Spinal Cord (substantia gelatinosa) Interneurons
Enkephalins: Antinociceptive due to inhibition of substance P release and reduced transmission to higher centers
CNS and the Autonomic Nervous System
sweating
blood pressure changes
temperature-induced changes in vasomotor tone
emptying of the bowels, bladder, seminal vesicles
Hypothalamic and Nucleus tractus solitarii
Integration of ANS Functions
body temperature regulation
emotions
water balance
sexual response
fat/carbohydrate metabolism
sleep
blood pressure
respiration
Posterior and Lateral Hypothalamic Nuclei are associated with integration of autonomic sympathetic input
Midline nuclei in the region of the Tuber cinereum and anterior nuclei Nuclei are associated with integration of autonomic parasympathetic input
Sympathetic: (Thoracolumbar outflow)
Parasympathetic; (Craniosacral Outflow)
Autonomic Nervous System Neurotransmitters: Summary
Neurotransmitter: Acetylcholine
All preganglionic autonomic fibers
Parasympatheticfibers
A few post-ganglionic sympathetic fibers
Neurotransmitter: Norepinephrine
Postganglionic Sympathetic Fibers
Neurotransmitter: Primary Afferents
Substance P and/or glutamate
Comparisons between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nerves
Sympathetic system has a broader distribution, innervating effectors throughout the body
Sympathetic fibers show greater ramification.
This anatomical characteristic is the basis for the diffuse nature of sympathic response in the human and other species.
Parasympathetic system is relatively limited
The parasympathetic system has its terminal ganglia near the end-organ.
Sometimes there is but a one-to-one ratio relationship between pre-and post-ganglionic fibers. The ratio between preganglionic vagal fibers and ganglion cells may be much higher, e.g. 1:8000 for Auerbach's plexus.
Lefkowitz, R.J, Hoffman, B.B and Taylor, P. Neurotrasmission: The Autonomic and Somatic Motor Nervous Systems, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics,(Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.107
Cell bodies of preganglionic fibers: found in intermediolateral columns of the spinal cord (first thoracic to second or third lumbar segments
Preganglionic fiber axons synapse with sympathetic ganglionic neurons which lie outside the cerebrospinal axis.
Sympathetic ganglia are found at three sites:
Paravertebral
Prevertebral
Terminal
Paraverebral ganglia: 22 interconnected pairs on either sides of the vertebral column. (para: Gr: at the side of along side)
Myelinated preganglionic fibers (white rami: thoracolumbar outflow only) leave through the anterior spinal roots.
Postganglionic fibers (gray rami) runs back to spinal nerves for distribution to:
blood vessesls of the skin
blood vessels of skeletal muscle
sweat glands
pilomotor muscles
Prevertebral Ganglia: abdominal and pelvic location, comprised of:
celiac ganglia
superior mesenteric ganglia
aorticorenal and inferior mesenteric ganglia
Terminal Ganglia: few, residing near the innervated organ, including
ganglia associated with the urinary bladder and rectum
cervical ganglia (neck): three ganglia (chain) mediating vasomotor, secretory, pupillodilatory and pilomotor responses of the head and neck)
All postganglionic fibers arise from cell bodies located within these ganglia; the preganglionic fibers come from upper thoracic segments: No sympathetic preganglionic fibers come from above the first thoracic level
Lefkowitz, R.J, Hoffman, B.B and Taylor, P. Neurotrasmission: The Autonomic and Somatic Motor Nervous Systems, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics, (Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.105-107.
ANS Neurotransmitters: Effector Organs
Adrenergic |
Effects |
Cholinergic |
| Iris: Radial Muscle | N.E., alpha-1 receptor | contraction (mydriasis) | ----- |
| Iris: Sphincter muscle | ----- |
----- |
contraction (miosis) |
| Ciliary Muscle | N.E., beta2 receptor | relaxation (far vision) | contraction (near vision) |
Adrenergic |
Effects |
Cholinergic |
| Sino-atrial (SA) Node | beta1; beta2 | increase rate | decrease rate (vagal) |
| Atrial muscle | beta1, beta2 | increased: contractility, conduction velocity | decreased: contractility, action potential duration |
| Atrio-ventricular (AV) node | beta1, beta2 | increased: automaticity*, conduction velocity | decreased conduction velocity; AV block |
| His-Purkinje System | beta1, beta2 | increased: automaticity, conduction velocity | ------ |
| Ventricles | beta1, beta2 | increased: contractility, conduction velocity, automaticity, ectopic pacemaker | small decrease in contractility |
*An increase in the slope of phase 4 depolarization results in ENHANCED AUTOMATICITY.
As a result of the increase in phase 4 slope the cell reaches threshold more often, with a higher heart rate as a result.
Factors that increase phase 4 depolarization include
mechanical stretch
beta-adrenergic stimulation
hypokalemia
Adrenergic |
Effects |
Cholinergic |
| Coronary | alpha1,2; beta2 | constriction;dilatation | constriction |
| Skin/Mucosa | alpha 1, 2 | constriction | dilatation |
| Skeletal Muscle | alpha; beta2 | constriction,dilatation | dilatation |
| Cerebral | alpha1 | slight constriction | dilatation |
| Pulmonary | alpha1, beta2 | constriction; dilatation | dilatation |
| Abdominal viscera | alpha1, beta2 | constriction; dilatation | ------- |
| Salivary glands | alpha1,2 | constriction | dilatation |
| Renal | alpha 1, 2;beta1,2 | constriction;dilatation | --------- |
|
Adrenergic Effects |
Cholinergic |
| systemic veins | alpha1,2; beta2 | constriction; dilatation | ----- |
|
Adrenergic Effects |
Cholinergic |
| Tracheal and bronchial muscle | beta2 | Relaxation | contraction |
| Bronchial glands | alpha1, beta2 | decrease secretion; increased secretion | stimulation |
|
Adrenergic Effects |
Cholinergic |
| Renin Secretion | alpha1; beta1 | decrease; increase | ------- |
Adrenergic Effects |
Cholinergic |
| Pilomotor muscles | alpha1 | contraction | ----- |
| Sweat glands | alpha1 | localized secretion | generalized secretion |
Adrenergic Effects |
Cholinergic |
| Adrenal medulla | -- | ---- | Secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine (mainly nicotinic and some muscarinic) |
Adrenergic Effects |
Cholinergic |
| Skeletal Muscle | beta2 | increased: contractility; glycogenolysis; potassium uptake |
---------- |
Adrenergic Effects |
Cholinergic |
| Liver | alpha1;beta 2 | glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis | -------- |
|
Adrenergic Effects |
Cholinergic |
| Posterior Pituitary | beta 1 | Antidiuretic hormone secretion (ADH) | ------------ |
Based on Table 6-1: Lefkowitz, R.J, Hoffman, B.B and Taylor, P. Neurotransmission: The Autonomic and Somatic Motor Nervous Systems, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics, (Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.110-111
Characteristics of Autonomic Organ Innervation
Usually, parasympathetic and sympathetic systems are physiological antagonists; that is, if one system facilitates or augments a process the other system inhibits the process.
Since most visceral organs are innervated by both system, the activity of the organ is influenced by both, even though one system may be dominant.
The general pattern of antagonism between sympathetic and parasympathetic systems is not always applicable. The interaction between sympathetic and parasympathetic systems may be independent or interdependent.
Examples of Antagonistic Interactions between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Systems
Actions of sympathetic and parasympathetic influences on the heart.
Actions of sympathetic and parasympathetic influences on the iris.
Interdependent or Complementary Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Effects
Actions of sympathetic and parasympathetic systems on male sexual organs are complementary.
Independent Effects
Vascular resistance is mainly controlled by sympathetic tone.
Fight or Flight: General Functions of the Autonomic Nervous System
ANS regulates organs/processes not under conscious control including:
circulation
digestion
respiration
temperature
sweating
metabolism
some endocrine gland secretions
Sympathetic system is most active when the body needs to react to changes in the internal or external environment: The requirement for sympathetic activity is most critical for:
temperature regulation
regulation of glucose levels
rapid vascular response to hemorrhage
reacting to oxygen deficiency
During rage or fright the sympathetic system can discharge as a unit--affecting multiorgan systems.
Sympathetic fibers show greater ramification.
Sympathetic preganglionic fibers may traverse through many ganglia before terminiating at its post-ganglionic cell. Synaptic terminal arborization results in a single preganglionic fiber terminating on many post-ganglionic cells.
This anatomical characteristic is the basis for the diffuse nature of sympathic response in the human and other species.
Sympathetic Responses
heart rate increases
blood pressure increases
blood is shunted to skeletal muscles
blood glucose increase
bronchioles dilate
pupils dilate
Parasympathetic responses
slows heart rate
protects retina from excessive light
lowers blood pressure
empties the bowel and bladder
increases gastrointestinal motility
promotes absorption of nutrients
Lefkowitz, R.J, Hoffman, B.B and Taylor, P. Neurotrasmission: The Autonomic and Somatic Motor Nervous Systems, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics, (Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.108.
![]()
Neurotransmitters and the Autonomic Nervous System
Neurotransmitter Criteria: To support the idea that a chemical is a neurotransmitter, several conditions must be satisfied---
The chemical should be found in the appropriate anatomical location (e.g. synaptic terminal)
Enzymes that are involved in "transmitter" synthesis should also be present.
Where possible (as in autonomic transmission), recovery of the "transmitter" in higher quantities following nerve stimulation than in the absence of stimulation.*
Externally applied (e.g. iontophoretically applied) chemical produces the same effect as stimulation. For example, the reversal potential is the same.
Effects of antagonists influence the response to externally applied chemical in the same manner as antagonists modify responses following nerve stimulation.
* may not be possible in many instances
Neurotransmission Steps

"The electron micrograph shows synaptic vesicles, purified from rat brain (negative staining, courtesy of Dr. Peter R. Maycox). Each is about 50 nm in diameter (1/20,000th of a millimeter). The inset shows a few vesicles labeled by immunogold for one of the major synaptic vesicle proteins (synaptophysin)."--Research group of Reinhard Jahn (http://www.mpibpc.gwdg.de/abteilungen/190/sv.html)
"Synaptic vesicles belong to the most abundant organelles in the body.
The human CNS contains about 1011 neurons. Each of these neuron forms on average about 1000 synapses, and each synapse contains about 500 vesicles, resulting in more than 1017 synaptic vesicles.
This is more than eight magnitudes more than the human genome has base pairs!
Synaptic vesicles can be purified in high yields to high degrees of purity, allowing for their biochemical characterization. Presently, synaptic vesicles are probably the best characterized organelles.
They contain a limited number of proteins that in many cases were discovered as the prototype of small protein families with a widespread distribution on trafficking organelles.
According to our current estimates, the majority of all vesicle-associated proteins are known. The vesicle proteins can be divided into two groups according to their function: the trafficking proteins and the proteins involved in neurotransmitter uptake and storage.
The first group includes proteins of diverse structure such as synaptobrevin/VAMP (involved in exocytotic membrane fusion), synaptotagmin (the exocytotic Ca2+-sensor), rab proteins (probably mediators of protein assembly required for membrane fusion) and several proteins of unknown function that contain four transmembrane domains (synaptophysins, synaptogyrins, SCAMPs).
The second group includes the neurotransmitter transporters, the vacuolar proton ATPase, and probably ion channels required for compensatory charge equilibration." ---Research group of Reinhard Jahn
Isolated neurotransmitter "quanta", perhaps corresponding to single vesicle neurotransmitter quantity, is randomly released in the basal state. This level of release, generating miniature end-plate potentials (mepp's), is necessary for resting skeletal muscle tone.
Action Potentials, promoting calcium influx, induce large, synchronous release of several hundred quanta . Calcium facilitates vesicular membrane-synaptic membrane fusion, resulting in vesicular content discharge into the synaptic cleft.
Many chemical can inhibit norepinephrine or acetylcholine release through receptor interactions at the appropriate terminal. Examples:
Norepinephrine + presynaptic alpha 2-adrenergic receptor (autoreceptor) inhibits norepinephrine release
Alpha2 receptor antagonists increase release of norepinephrine
Neurally-mediated acetylcholine release from cholinergic neurons is inhibited by alpha2-adrenergic receptor agonists
Stimulation of presynaptic beta2 adrenergic receptors increases slightly norepinephrine release
These agents Inhibit neurally-mediated norepinephrine released by interacting with presynaptic receptors
Adenosine
Acetylcholine
Dopamine
Prostaglandins
Enkephalins
Transmitter Synthesis and Degradation
Acetylcholine is synthesized from the immediate precursors acetyl coenzyme A and choline in a reaction catalyzed by choline acetyltransferase (choline acetylase).

Rapid inactivation of acetylcholine is mediated by acetylcholinesterase.
Acetylcholinesterase is present at ganglia, visceral neuroeffector junctions, and neuromuscular junctional endplates.
Another type of cholinesterase, called pseudo-cholinesterase or butyrylcholinesterase has limited presence in neurons, but is present in glia. Most pseudocholinesterase activity is found in plasma and liver.
Pharmacological effects of anti-cholinesterase drugs are due to inhibition of acetylcholinesterase.
Botulism
Cholinergic Transmission: Site Differences
Neurotransmitter: Acetylcholine
Receptor Type: Nicotinic
Sectioning and degeneration of motor and post-ganglionic nerve fibers results in:
an enhanced post-synaptic responsiveness, denervation hypersensitivity.
Denervation hypersensivity in skeletal muscle is due to
increased expression of nicotinic cholinergic receptors
and their spread to regions aways from the endplate.
Neurotransmitter: Acetylcholine
Receptor type: Muscarinic
effector coupled to receptor by a G protein
In smooth muscle and in the cardiac conduction system, intrinsic electrical activity and mechanism activity is present, modifiable by autonomic tone.
Activities include propagated slow waves of depolarization: Examples: intestinal motility and spontaneous depolarizations of cardiac SA nodal pacemakers.
Acetylcholine decreases heart rate by decreases SA nodal pacemaker phase 4 depolarization.
The cardiac action potential associated with HIS-purkinje fibers or ventricular muscle consists of five phases
Phase 0 corresponds to Na+ channel activation.
The maximum upstroke slope of phase 0 is proportional to the sodium current.
Phase 0 slope is related to the conduction velocity in that the more rapid the rate of depolarization the greater the rate of impulse propagation.
Phase 1 corresponds to an early repolarizing K+ current. This current like the Phase 0 sodium current is rapidly inactivated.
Phase 2 is the combination of an inward, depolarizing Ca2+ current balanced by an outward, repolarizing K+ current (delayed rectifier).
Phase 3 is also the combination of Ca2+ and K+ currents.
Phase 3 is repolarizing because the outward (repolarizing) K+ current increases while the inward (depolarizing) Ca2+ current is decreasing.
Phase 4 in normal His-Purkinje and ventricular muscle cells is characterized by a balance between outward Na+ current and inward K+ current. As a result, the membrane potential would normally be flat.
In disease states or for other cell types (SA nodal cells) the membrane potential drifts towards threshold. This phenomenon of spontaneous depolarization is termed automaticity and has an important role in arrthymogenesis.
Rate of phase 4 depolarization is decreased by an increase in K+ conductance--which leads to membrane hyperpolarization (takes longer to reach threshold)
Nicotinic Receptors
Ligand-gated ion channels
Agonist effects blocked by tubocurarine
Receptor activation results in:
rapid increases of Na+ and Ca2+ conductance
deplorization
excitation
Subtypes based on differing subunit composition: Muscle and Neuronal Classification
Muscarinic Receptors
G-protein coupled receptor system
Slower responses
Agonist effects blocked by atropine
At least five receptor subtypes have been described by molecular cloning. Variants have distinct anatomical locations and differing molecular specificities
Lefkowitz, R.J, Hoffman, B.B and Taylor, P. Neurotransmission: The Autonomic and Somatic Motor Nervous Systems, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics,(Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.112-137
Adrenergic Neurotransmission: Introduction to the Neurotransmitters
Norepinephrine: transmitter released at most postganglionic sympathetic terminals
Catecholamine Synthesis, Storage, and Release
Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (DOPA decarboxylase)
In adrenergically innervated tissue: norepinephrine is localized in post-ganglionic nerve terminals
large dense core vesicles (corresponding to chromaffin granules)
small dense core vesicles (containing norepinephrine, ATP, and membrane-bound dopamine ß-hydroxylase
In the adrenal medulla, catecholamines are localized in chromaffin granules.
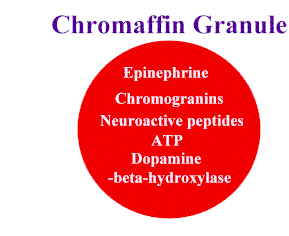
The most abundant catecholamine in the adrenal medulla is epinephrine.
The adrenal medulla has two cells types containing catecholamines:
one type contains mainly norepinephrine
the second type contains mainly epinephrine.
Epinephrine-containing cells express cytoplasmic phenylethanolamine-N-methyl transferase, allowing conversion of norepinephrine to epinephrine.
Norepinephrine:
synthesized in granules
diffuses out, is methylated in the cytoplasm to epinephrine
then reenters the chromaffin granules.
About half of dopamine is formed in sympathetic neuronal cytoplasm is actively translocated into dopamine ß-hydroxylase-containing vesicles, where the final step, conversion to norepinephrine occurs.
The remaining dopamine is converted to homovanillic acid.
Shannon, M.T., Wilson, B.A., Stang, C. L. In, Govoni and Hayes 8th Edition: Drugs and Nursing Implications Appleton & Lange, 1995, pp. 616-619
Besides reuptake and diffusion away from receptor sites, catecholamine action can end due to metabolic transformation.
Two primary degradative enzymes:
Monoamine Oxidase (MAO)
Catechol-O-Methyl Transferase (COMT)
Inhibitors of MAO, such as pargyline, phenelzine (Nardil), and tranylcypromine (Parnate) increase norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin (5-HT) brain concentrations.
These concentration increases may be responsible for antidepressant action of MAO inhibitors.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor: Phenelzine [Nardil]
Hydrazine MAO inhibitor with amphetamine-like activity
Termination of drug action requires new MAO enzyme synthesis
May cause Hypertensive crisis
Labeled Uses
treatment of endogenous depression
management of depressive phase of bipolar disorder
treatment of severe reactive depression not responsive to other drugs.
Shannon, M.T., Wilson, B.A., Stang, C. L. In, Govoni and Hayes 8th Edition: Drugs and Nursing Implications Appleton & Lange, 1995, pp. 904-905
Catecholamine Release (Adrenal medulla)
Release steps: Chromaffin Granule Adrenal medulla
preganglion
fiber releases Ach ![]() nicotinic receptor
activation
nicotinic receptor
activation![]() depolarization
depolarization![]() Ca2+
entry
Ca2+
entry ![]() exocytosis of granular content
exocytosis of granular content
Ca2+ influx is important in excitation (depolarization)--release coupling
Lefkowitz, R.J, Hoffman, B.B and Taylor, P. Neurotransmission: The Autonomic and Somatic Motor Nervous Systems, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics,(Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.112-137
Order of agonist potency
Isoproterenol > epinephrine > norepinephrine
ß2 receptor activation mediates relaxation of vascular smooth muscle
ß2 receptor activation mediates relaxation of G.I. smooth muscle. alpha2 adrenergic receptor activation acts presynaptically to reduce Ach release and promote G.I. smooth muscle relaxation. The alpha2 receptor effect is the more important.
Order of agonist potency
epinephrine > norepinephrine >> isoproterenol
Lefkowitz, R.J, Hoffman, B.B and Taylor, P. Neurotransmission: The Autonomic and Somatic Motor Nervous Systems, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics,(Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.112-137.Hoffman, B. B. Adrenoceptor-Activating & Other Sympathomimetic Drugs: Introduction to Antimicrobial Agents in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, p.118-122
![]()
Other Autonomic Neurotransmitters/Cotransmitters
ATP and catecholamines are found together in neuronal and adrenal medullary storage granules. ATP is released along with transmitters and, in certain cases, has an important role in synaptic transmission.
Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP)
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is found in association with ACh in autonomic parasympathetic fibers innervating blood vessels and exocrine glands and cholinergic sympathetic fibers innervating sweat glands.
VIP may be involved in salivation, tracheal and the GI tract responsiveness to parasympathetic input.
The neuropeptide Y family includes NPY, pancreatic polypeptide, and peptide YY.
NPY in the periphery is associated with sympathetic fibers and assists in maintaining vascular tone.
NPY is a potent, long-lasting vasoconstrictor, especially of small vessels
Purines such as ATP and adenosine may be responsible for apparent non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic autonomic neurotransmission.
Antatomical Site |
Predominant Autonomic Tone |
Arterioles |
Sympathetic-adrenergic |
Veins |
Sympathetic-adrenergic |
Heart |
Parasympathetic-cholinergic |
Ciliary Muscle |
Parasympathetic-cholinergic |
Gastrointestinal Tract |
Parasympathetic-cholinergic |
Salivary Glands |
Parasympathetic-cholinergic |
Sweat Glands |
Sympathetic-cholinergic |
| Taylor, P. Agents Acting at the Neuromuscular Junction and Autonomic Ganglia In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics,(Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.193-195. Adapted from Table 9-3 |
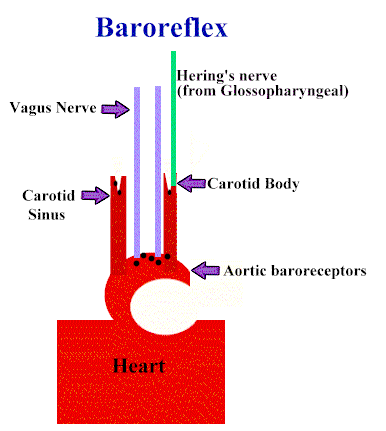
As pressure rises and especially for rapid increases in pressure:
|
 |
Pharmacological Modification of Autonomic Function
|
|
Cholinergic
Hemicholinium (HC-3) blocks the choline transport system into the nerve ending, thus limiting acetylcholine (ACh) synthesis.
Adrenergic
Alpha-methyltyrosine inhibits tyrosine hydroxylase thus preventing synthesis of norepinephrine.
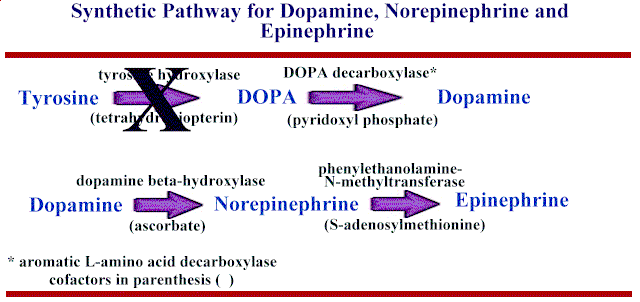
Methyldopa inhibits aromatic amino acid decarboxylase and is itself decarboxylated and hydroxylated to form the "false transmitter" alpha-methyl norepinephrine
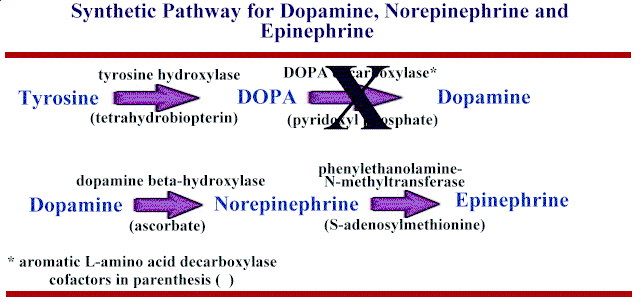
Cholinergic
Botulinum toxin can be used clinically to treat ocular muscle spasms, muscle dystonias, and spasms.
Botulinus toxin binding at a presynaptic site blocks ACh release.
Vesamicol blocks ACh transport into storage vesicles, thus limiting release.
Adrenergic
Bretylium and guanethidine prevent action-potential mediated norepinephrine release.
Transient release may occur with these agents because they displace norepinephrine from storage sites.
Tyramine, amphetamine, and ephedrine can produce a brief liberation of transmitter.
Reserpine, by inhibiting vesicular uptake, produces a slow, depletion of norepinephrine, ultimately causing adrenergic blockade. Cytoplasmic MAO metabolizes the neurotransmitter.
Reserpine similarly depletes dopamine and serotonin. Physiological effects of reserpine are due to depletion of many transmitters.
Cholinergic
Tetraethylammonium, trimethaphan and hexamethonium are nicotinic ganglionic antagonists.
Decamethonium, a depolarizing drug, selectively causes neuromuscular blockade.
All classes of muscarinic receptors are blocked by atropine.
Adrenergic