Overview: Halothane (Fluothane)
Halothane (Fluothane), a nonflammable liquid at room temperature is a halogenated alkane derivative.C2-H-Br-Cl-F3
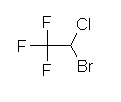
Halothane (Fluothane) vapor has been described as having a sweet, non-pungent odor which made it and agent of choice among the older inhalational agents for pediatric anesthesia.
Other inhalational agents are effective in anesthesia maintenance both for infants and children; however, most of these agents have sufficiently unpleasant, pungent odor that they should not be used for inhaled induction. [isoflurane (Forane) and desflurane (Suprane) are examples of agents which may be used in pediatric cases for anesthesia maintenance, but because of their odor they really cannot be used for mask induction.
Concerns about halothane (Fluothane)'s use in children have to do with the following hemodynamic characteristics:
Halothane (Fluothane) is a myocardial depressant, an effect which is particularly apparent in children, especially in hypovolemic patients.
The extent of cardiac depression can be reduced if halothane (Fluothane) requirements are reduced by concurrent administration of other agents such as opioids or muscle relaxants.
Halothane (Fluothane) can sensitize the myocardium to catecholamines, thus predisposing towards arrhythmias. This effect is more likely to occur during "light" anesthesia or in the presence of hypercarbia. When epinephrine is required, up to 10 ug/kg may be given in the normocarbic pediatric patients without incurring significant risk.
Alternatives to halothane (Fluothane) for mask induction in pediatric patients: Sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane), an inhalational agent with a non-pungent odor, is probably the agent of choice for pediatric patients.
Sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) combines both rapid induction and emergence, secondary to its low lipid solubility, with very low myocardial depression -- even at high vaporizer output.
Furthermore, there probably is a reduced likelihood of cardiac arrhythmias with sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) compared halothane (Fluothane) in this patient group.
Halothane (Fluothane), a nonflammable relatively potent inhalational agent exhibits a low blood:gas partition coefficient, predicting relatively rapid induction and recovery
This agent can be used to provide controlled hypotension bleeding control
Intermediate solubility (blood) + high-potency result in rapid onset/recovery from anesthesia (either alone or in combination with nitrous oxide or injected opioids)
Chemical Considerations: (see structure above)
Consequences of halogenated structure:
Nonflammability
Intermediate blood solubility
Anesthetic potency
Molecular stability
Carbon-fluorine: decreased flammability
Trifluorocarbon: molecular stability
Carbon-chlorine and carbon-bromine components (with retention of a hydrogen atom) contributing to anesthetic potency
Decomposition concerns:
susceptible to decomposition to: HCl, hydrobromic acid, bromide and phosgene.
amber-colored bottle storage + thymol (reduces spontaneous oxidative decomposition)
Thymol: remaining in vaporizers, following halothane (Fluothane) vaporization leading to malfunction of temperature-compensating devices or vaporizer turnstiles
Halothane (Fluothane) anesthesia: provides unconsciousness
Clinical Indication:
Halothane (Fluothane) is effective for general anesthetic maintenance and may be an induction agent of choice in difficult airway
Systems Physiology:
CNS:
Generalized CNS depression
Cerebrovascular dilation causes increased ICP
Cardiovascular:
Halothane (Fluothane) causes a slight decrease in heart rate, a decrease in mean arterial pressure (MAP)-- both associated with its well-documented cardiac depressant property.
Halothane (Fluothane) may also sensitize the myocardium to circulating catecholamines, explaining the pro-arrhythmogenic property.
Pulmonary:
Halothane (Fluothane) causes decreasing tidal volume with increasing MAC, increasing respiratory rate with increasing MAC
Halothane (Fluothane) also promote significant bronchodilation
Hepatic: fulminant hepatic failure (halothane hepatitis): Case history for slides below: "Forty four year old lady had uterine curettage for metrorrhagia. Eight weeks later she had hysterectomy. Three days after hysterectomy she became jaundiced. Seven days later she died in liver failure. Halothane was used as anesthetic in both surgical procedures. The autopsy showed massive liver necrosis. It appears that the liver damage was mediated by an immunoreactive mechanism. Multiple exposures increase the incidence of liver damage." DRUG-INDUCED LIVER INJURY by Dr. Emilio Orfei
|
|
|
Musculoskeletal: relaxation
Contraindications:
Trigger to malignant hyperpyrexia
Recent halothane (Fluothane) exposure
Drug-drug interactions:
Muscle relaxants potentiation
Reduced MAC with opioids, nitrous oxide and benzodiazepines
Concerns:
Inadequate analgesia
May not provide adequate muscle relaxation
May not provide adequate suppression of visceral reflexes
Reversible reduction of GFR
Halothane Disadvantages
Unpredictable occurrence of hepatitis
Status: infrequently used due to the availability of isoflurane (Forane), enflurane (Ethrane) and desflurane (Suprane).
Kennedy, S.K. and Longnecker, D.E., History and Principles of Anesthesiology In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics,(Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, p 313.
White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996, p. 249.
Overview: Low-molecular weight
Oderless to sweet smelling
Nonflammable
Low-potency gas
Poor blood solubility (0.46)
Low blood solubility allows rapid attainment of alveolar and brain partial pressure
Most commonly administered in combination with opioids or volatile anesthetics.
With a MAC value of 105%, nitrous oxide, by itself is not suitable or safe as a sole anesthetic agent.
Effective analgesic.
Minimal skeletal muscle relaxation
Effective: Nitrous oxide in combination with thiopental for induction, a skeletal muscle relaxant, and hyperventilation to reduce CO2
Nitrous oxide can be used as an adjunct to other agents: For example, using 70% nitrous oxide + oxygen significantly reduces MAC for halothane, enflurane, and isoflurane.
Despite the relative insolubility of nitrous oxide, large quantitities of gas are rapidly absorbed due to its high inhaled concentration.
This concentration effect speeds induction as fresh gas is literally drawn into the lung from the breathing circuit.
Since nitrous oxide is often administered with a second gas, the second gas effect also enhances the rate of induction
If administration of nitrous oxide is abruptly discontinued, rapid transfer of NO from blood and tissues to the alveoli decreases arterial tension of oxygen. This process is diffusional hypoxia.
|
|
Nitrous Oxide Disadvantages
No skeletal muscle relaxation
Weak anesthetic
Air pockets in closed spaces expand
Post-anesthesia hypoxia (diffusion hypoxia)
Not suitable as a sole anesthetic agent
Kennedy, S.K. and Longnecker, D.E., History and Principles of Anesthesiology In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics,(Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, p 319 - 321.
Stoelting, R.K., "Inhaled Anesthetics", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 36-76
|
|
Desflurane (Suprane) Overview:
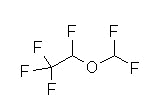
Fluorinated methyl ethyl ether and, similar to isoflurane (Forane). Substitution of a fluorine atom for chlorine (isoflurane)
Fluorination (compared to chlorination) results in:
increased vapor pressure-- 3X (= decreased intermolecular attraction)
High vapor pressure would result in boiling at operating room temperatures requires:
implementation of new vaporizer technology converts desflurane (Suprane) to a gas (heated and pressurized electric vaporizer) which is blended with fresh gas flow
increased molecular stability
decreased potency: 5 fold < isoflurane (Forane)
Minor desflurane (Suprane) metabolism
Pungent odor --desflurane (Suprane) less likely to be used for inhalation induction compared to halothane (Fluothane) or sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane).
Airway irritation, breath-holding, coughing, laryngospasm is greater than 6% desflurane (Suprane) administered to an awake patient.
Significant salivation
Carbon monoxide:
Secondary to desflurane (Suprane) degradation by strong base present in carbon dioxide absorbants.
Carbon monoxide concentration: desflurane (Suprane) > enflurane (Ethrane) > isoflurane (Forane) {carbon monoxide produced by halothane (Fluothane) or sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane): extremely small)
Solubility (blood: gas partition coefficient = 0.45) and potency (MAC 6%):
Rapid achievement of alveolar partial pressures required for anesthesia along with rapid awakening
Distinguishing features of desflurane (Suprane) and sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) compared to earlier volatile anesthetics:
Lower blood-gas solubility
More rapid recovery from anesthesia
Desflurane (Suprane) Systems Physiology:
CNS:
Generalized depression
Extremely rapid emergence
Increased ICP
Cardiovascular:
Vascular resistance
MAP
Heart rate (deep anesthesia); tachycardia with rapid concentration change
Pulmonary:
decrease tidal volume
increase respiratory rate
irritant
Gastrointestinal: nausea
Musculoskeletal:relaxation
Desflurane (Suprane): Clinical Indications:
General anesthesia maintenance
Agent of choice when:
Rapid emergence desirable
Precise anesthetic depth control required
Contraindications:
Trigger to malignant hyperpyrexia
Drug-drug interactions:
Muscle relaxant effect potentiation
MAC with opioids, nitrous oxide, and benzodiazepines
Stoelting, R.K., "Inhaled Anesthetics", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 36-76
White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996. p.248
|
|
Isoflurane[Forane]: Overview:
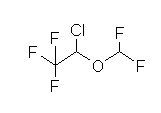
Halogenated methyl ethyl ether
Non-flammable liquid (room temperature);pungent odor; ether-like
Intermediate solubility (blood) + high-potency ® rapid onset and recovery using isoflurane (Forane) alone or in combination with nitrous oxide or opioids (injected)
Very high physical stability; no need to add preservatives e.g. thymol
Isoflurane anesthesia: results in unconsciousness
Initially, until deeper levels of anesthesia are reached, isoflurane stimulates airway reflexes with:
increases in secretions
coughing
laryngospasm. (greater with isofluorane than enflurane (Ethrane) or halothane (Fluothane))
Isoflurane[Forane]: Systems Physiology:
CNS:
Generalized CNS depression; Rapid emergence
Increased ICP
Cardiovascular:
Little effect on cardiac output and decreased vascular assistance and decreased MAP
Increased heart rate
Gastrointestinal: nausea
Musculoskeletal: relaxation
Contraindications: trigger to malignant hyperpyrexia
Drug-drug interactions:
muscle relaxants potentiation
MAC with opioids, nitrous oxide, and benzodiazepines
Isoflurane[Forane] Comparative Pharmacology
By contrast to enflurane (Ethrane) or halothane (Fluothane) cardiac output is well maintained with isoflurane (Forane)
May provide adequate muscle relaxation greater than seen with halothane (Fluothane);
Perhaps adequate for abdominal procedures. Otherwise, reduced amounts of tubocurarine may be required
As with enflurane, isoflurane (Forane) relaxation of uterine muscle is not desirable if uterine contraction is required to limit blood loss.
Reversible reduction of GFR
Unlike enflurane (Ethrane), convulsive activity has not been seen with isoflurane (Forane).
Isoflurane Advantages
Rapid, smooth adjustment of depth of anesthesia with limited effects on pulse or respiration
Depth of anesthesia is easily controlled
No hepatic and renal toxicity
Cerebral blood flow and intracranial pressure are readily controlled.
Relaxation of skeletal muscles may be adequate for surgery
Arrhythmias are uncommon.
Isoflurane Disadvantage: As with halothane (Fluothane), enflurane (Ethrane), isoflurane (Forane) may cause malignant hyperthermia
Isoflurane Status: Isoflurane (Forane) may be the most widely used inhalational agent.
Kennedy, S.K. and Longnecker, D.E., History and Principles of Anesthesiology In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics,(Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, p 315 - 317.
White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996, p. 250.
|
|
Overview: Enflurane (Ethrane)
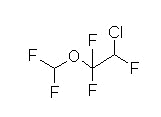
Halogenated, methyl ethyl ether
Clear, nonflammable volatile liquid (room temperature)
Pungent odor
Intermediate solubility + high potency leads to rapid onset/recovery (enflurane (Ethrane) alone or in combination with nitrous oxide or opioids)
Clinical Use: maintenance of general anesthesia
Systems Physiology:
CNS: increased ICP secondary to increased cerebral blood flow (CBF)
Cardiovascular:
myocardial depressant
decreased vascular resistance; decreased mean arterial pressure (MAP), tachycardia
Renal:
renal dysfunction
Gastrointestinal:
nausea
Musculoskeletal:
muscle relaxation
Contraindications
Renal failure
Long cases
Trigger to malignant hyperpyrexia
Epilepsy*
* may promote seizures (at concentrations > 3%); epileptiform paroxysmal spike occurrences
Drug Interactions:
Potentiation: muscle relaxants
MAC with opioids, nitrous oxide and benzodiazepines
Stoelting, R.K., "Inhaled Anesthetics", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 36-76
White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996, p. 248.
Sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane)
|
|
Overview: sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane)
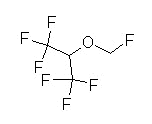
Fluorinated methyl isopropyl ether
Vapor pressure: similar to halothane (Fluothane) and isoflurane (Forane) (conventional, unheated vaporizer may be used)
Blood: gas partition coefficient of sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) = 0.69; similar to desflurane (Suprane) allowing:
rapid induction
rapid recovery upon anesthetic discontinuation
Non-pungent, bronchodilation similar to isoflurane (Forane)
Least airway irritation among current volatile anesthetics, thereby allowing direct anesthesia induction (like halothane (Fluothane))
Metabolism: sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane)
More likely to be metabolized (3%-5% metabolized) than desflurane (Suprane)
Principal metabolites:
inorganic fluoride (>than that seen following enflurane (Ethrane))
hexafluoroisopropanol (nontoxic)
No trifluoroacetylated liver proteins formed (no anti-trifluoroacetylated liver protein antibodies)
Such antibodies may be seen with halothane (Fluothane), enflurane (Ethrane), isoflurane (Forane), desflurane (Suprane); these agents, metabolized to reactive acyl halide intermediates may produce:
hepatoxicity
cross-sensitivity between agents
Sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) no carbon monoxide formation following exposure to carbon dioxide and absorbants
Level of major sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) metabolite, a vinyl-ether derivative (Compound A) is significantly below possible toxic levels, even with gas flows > 1 liter per minute
Clinical Use:sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane)
First-line, excellent induction agent
Rapid emergence
Allows excellent anesthetic depth control
Systems Physiology: sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane)
CNS:
CNS depression (generalized)
Rapid emergence
Increased ICP
Cardiovascular:
reduced vascular resistance
decreased MAP (mean arterial pressure)
Pulmonary:
Nonirritant
Respiratory depression
Musculoskeletal:
Muscle relaxation
Contraindications/Issues:
Trigger to malignant hyperpyrexia
Long cases (fluoride accumulation)
Closed-circuit anesthesia
Drug-drug interactions
Muscle relaxants effect potentiation
MAC decreases when sevoflurane is combined with opioids, benzodiazepines, nitrous oxide
Stoelting, R.K., "Inhaled Anesthetics", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 36-76 White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.