Nursing Pharmacology Chapter 15: Local Anesthetics
|
|
Overview --Chemical Properties
Lipophilic component
Connecting chain (ester or amide)
Ionizable group
Racemates/Pure Isomers
Pipecoloxylidide-agents (mepivacaine (Carbocaine), ropivacaine (Naropin))
Chiral agents (asymmetric carbon); left-(S), right-(R)-handed configurations
Mepivacaine (Carbocaine) and bupivacaine (Marcaine) are used clinically as racemates (50:50 mixture) of enantiomers
S enantiomers of mepivacaine (Carbocaine) and bupivacaine (Marcaine): less toxic than racemates
Ropivacaine (Naropin): pure S enantiomer
![]() Pharmacological activity
is based on 2 factors: one that considers chemical aspects alone and
the second that considers interaction with receptors.
Pharmacological activity
is based on 2 factors: one that considers chemical aspects alone and
the second that considers interaction with receptors.
Balance between lipophilic and hydrophilic characteristics
Potency of stereoisomers (e.g.,ropivacaine (Naropin) and mepivacaine (Carbocaine))
Esters: shorter duration of action, compared to local anesthetics with amide linkages.
Properties: Local Anesthetics are weak bases
Existing as either uncharged base or cation (postiively charged)
Proportions depending on pKa and pH (as described by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation)
log ([cationic form] / [uncharged form]) = pKa - pH
Most local anesthetics have pKa's ranging from 8.0-9.0, therefore at physiological pH, most local anesthetic molecules will be positively charged (cationic form)
Cationic form: probably physiologically active form at the receptor
Uncharged form: important for penetration across biological membranes to reach site of action
Local anesthetic receptor localization internal side of the cell membrane {requiring penetration by uncharged form}
In infected tissue, extracellular pH is lower; more drug in ionized state; less likely to diffuse into the cell; reduced local anesthetic effect
Esters:
Cocaine
Procaine (Novocain)
Benzocaine (Cetacaine)
Tetracaine
Chloroprocaine (Nesacaine)
Amides:
Lidocaine (Xylocaine)
Mepivacaine (Polocaine/Carbocaine)
Etidocaine (Duranest)
Etidocaine (Duranest)
Prilocaine
Local anesthetics: weak bases; pKa somewhat above physiologic pH
Less than 50% of molecules are in the lipid-soluble, un-ionized form at pH 7.4
At pH 7.4: 5% of tetracaine (pontocaine) molecules are un-ionized
![]() Local infection
(acidosis) increases the ionized drug
fraction (less drug available to
penetrate across membranes and bind to
intracellular local anesthetic receptor".
Local infection
(acidosis) increases the ionized drug
fraction (less drug available to
penetrate across membranes and bind to
intracellular local anesthetic receptor".
Local anesthetics with pKs closest to physiologic pH are associated with more rapid onset of action (better ratio of ionized to un-ionized drug)
Vasodilator properties of the local anesthetic:
Affect both apparent potency and duration of action
Lidocaine (Xylocaine), for example causes greater vasodilation compared to mepivacaine (Carbocaine) and therefore is associated with:
Enhanced systemic absorption
Shorter duration of action
Lipid solubility:
Bupivacaine (Marcaine) and etidocaine (Duranest) (similar vasodilation)
Following epidural: mepivacaine (Carbocaine) plasma concentration higher than that for etidocaine (Duranest)
Etidocaine (Duranest): greater lipid solubility leads to increased tissue sequestration (reduced drug available)
Factors
Vascularity:
Highly vascular area (e.g. tracheal mucosa): promotes rapid absorption resulting in higher blood levels
Poorly vascular area (tendon) is associated with relatively poor absorption
Regional anesthesia (block of large nerves):
Maximum blood levels (highest to lowest)
Intercostal (highest) > caudal > epidural > brachial plexus > sciatic nerve {lowest}
Dosage
Presence of vasoconstrictors (e.g. epinephrine)
Reduced systemic absorption due to local vasoconstriction
Increased neuronal uptake (higher local concentration)
Blood levels: reduced as much as 1/3
The presensce of vasoconstrictors have a particularly significant effect for local anesthetics with intermediate/short duration of action (e.g.,procaine (Novocain), lidocaine (Xylocaine), mepivacaine (Carbocaine) [not prilocaine (Citanest)])
Vasoconstrictor addition has a lesser effect for more lipid soluble (longer-acting) agents: bupivacaine (Marcaine), etidocaine (Duranest). The lipid solubility of these agents tend to keep them in the local tissue site intrinsically.
Cocaine: local anesthetic with intrinsic sympathomimetic, vasoconstrictive properties
Spinal anesthesia:-- enhancement and prolongation of local anesthetic spinal anesthesia by:
Activating alpha2 adrenergic receptors (inhibit substance P release and reduce dorsal horn neural activity)
Addition of clonidine (alpha2 receptor agonist, Catapres) to local anesthetic solutions enhance the local anesthetic effect through reduction in neuronal activity and inhibition to substance P release)
Reduced systemic absorption
Increased local neuronal uptake
Chemical properties of the drug
Plasma concentration is determined by:
Rate of tissue distribution
Rate of drug clearance
Consider lidocaine (Xylocaine) distribution-- IV infusion: duration = 1-minute
Initial high uptake into lungs and redistribution to highly perfusion tissues (heart, kidney, brain)
Redistribution: limited solubility important. A highly soluble agent in a tissue will be more likely to remain in that initial site of concentration.
Following distribution to brain, kidney, heart-- redistribution to other tissues (less perfused)-- e.g. muscle, fat
Other factors influencing local anesthetic distribution/plasma concentrations
Patient age, liver function, cardiovascular status, protein binding
"Amide" local anesthetic agents more widely distributed compared to "ester" local anesthetics
Pulmonary extraction from the venous circulation limits the amount of local anesthetic (lidocaine (Xylocaine), bupivacaine (Marcaine), and prilocaine (Citanest)) that will reach the systemic circulation
Bupivacaine (Marcaine): dose-dependent, first pass extraction (saturable, uptake)
Propranolol (Inderal) inhibits bupivacaine (Marcaine) extraction
Propranolol (Inderal) reduces lidocaine (Xylocaine) and bupivacaine (Marcaine) plasma clearance
Dependency:
Plasma protein binding influences:
Rate and extent of local anesthetic diffusion across the placenta
Ester-local anesthetics are not associated with significant placental transfer (due to rapid hydrolysis)
![]() Fetal acidosis which may
occur during prolonged labor, promotes, by ion trapping
mechanism, accumulation of local
anesthetic in the fetus
Fetal acidosis which may
occur during prolonged labor, promotes, by ion trapping
mechanism, accumulation of local
anesthetic in the fetus
Amides -- hepatic (minimal renal excretion of unchanged drug)
Esters--rapid clearance; short elimination halftime due to rapid hydrolysis
Miller, R.D., Local Anesthesia, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, pp 425-433.
Stoelting, R.K., "Local Anesthetics", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 158-181.
Vasocontrictors added to local anesthetic solutions
Purpose of adding epinephrine to a local anesthetic solution: Increased duration: addition of epinephrine (1:2000,000 or 5 ug/ml) to cause vasoconstriction
Reduced systemic absorption
Higher anesthetic concentration near nerve fibers
Prolongation of conduction blockade (about 50% longer)
Reduced systemic absorption (by about 33%)
Factors influencing the effectiveness of epinephrine on local anesthesia.
Which anesthetic is used
Reduced effect of epinephrine on duration of conduction blockade and systemic absorption comparing mepivacaine (Carbocaine) and etidocaine (Duranest) [these are more lipophilic] with lidocaine (Xylocaine), which is less lipophilic
More lipophilic local anesthetics will tend on their own to associate strongly with tissues
Level of sensory blockade needed for spinal or epidural anesthesia
Duration of lower extremity sensory anesthesia extended by epinephrine or phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine); this effect is not observed for abdominal region anesthesia
Conditions: epinephrine (0.2 mg) or phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine) (2 mg) added to mepivacaine (Carbocaine) or lidocaine (Xylocaine) -- placed in subarachnoid spaces
Spinal anesthesia and tetracaine (pontocaine):
Duration of action of tetracaine is extended by adding vasoconstrictors drugs to the injected solution.
Prolongation of local anesthetic action associated with vasoconstrictors added to local anesthetic solutions is associated with:
Decreased systemic absorption
Increased local anesthetic concentration in the vicinity of sensory nerves
Increased uptake of the local anesthetic
Advantages of reduced local anesthetic systemic absorption:
![]() Local anesthetic absorption
rate more likely to match metabolic rate resulting in less local
anesthetic systemic toxicity
Local anesthetic absorption
rate more likely to match metabolic rate resulting in less local
anesthetic systemic toxicity
![]() Toxicities associated with systemic
epinephrine absorption:
Toxicities associated with systemic
epinephrine absorption:
Local anesthetic + epinephrine combination is associated with increased cardiac irritability, which may cause an increased risk of cardiac arrhythmias.
The combination also may increase the possibility of hypertensive response in susceptible patients.
Other agents which may be added to local anesthetics that affect duration of action
Dextran (low-molecular-weight) when added to local anesthetic solutions result in increased peripheral nerve block anesthesia duration (probably due to a reduction in local anesthetic systemic absorption)
Local anesthetic combinations: Purpose
Prolonged duration (bupivacaine (Marcaine))and decreased time to onset (chloroprocaine (Nesacaine))
![]() Concerns
Concerns
Chloroprocaine (Nesacaine) in the epidural space may lead to possibly reduced subsequent epidural space bupivacaine (Marcaine) analgesia efficacy during labor.
Mechanism for this effect may be that chloroprocaine (Nesacaine) reduces pH which decreases the amount of nonionized (active) bupivacaine (Marcaine).
Tachyphylaxis to the mixture may be secondary to local acidosis caused by low pH of the chloroprocaine (Nesacaine) solution.
Suggestion: increased chloroprocaine (Nesacaine) solution pH just before use may enhance chloroprocaine (Nesacaine)-mepivacaine (Carbocaine) combination efficacy
![]() Local anesthetic combination: Toxicity is additive
Local anesthetic combination: Toxicity is additive
Stoelting, R.K., "Local Anesthetics", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 158-181.
![]() Local Anesthetic Side-Effects /Toxicities
and Neurotoxicity
Local Anesthetic Side-Effects /Toxicities
and Neurotoxicity
Primary side effects
Allergic reactions
Systemic toxicity
Secondary to high plasma/tissue local anesthetic concentrations
Manifestation:
Seizures
Frequency: 1-4/1000 cases
Bupivacaine (Marcaine) -- local anesthetic most likely to cause seizures
Rare occurrence -- < 1% of local anesthetic adverse reactions due to allergic mechanism
Higher-risk: ester-type local anesthetics (those which are metabolized to p-aminobenzoic acid-related compounds)
Allergic reaction following local anesthetic administration may be caused by preservatives (methylparaben or related structures) included in the preparation {preservatives are structurally similar to p-aminobenzoic acid}
Antibody production may have been previously induced by the preservative (not reaction to the local anesthetic)
May be due to common metabolite profile {p-aminobenzoic acid}
No cross sensitivity between ester vs. amide local anesthetic classes
Patient with allergy to an ester local anesthetic drug may receive an amide local anesthetic
The anesthetic agent thought to not produce an allergic reaction should not have preservatives {it is possible that the preservative is the allergen}
Basis/evidence for local anesthetic allergies
Clinical history, intradermal testing
Suggestive:
Rash, urticaria, laryngeal edema, possible hypotension, bronchospasm
Caution: hypotension with syncope/tachycardia following epinephrine-containing local anesthetic injection; accidental intravascular injection
Intradermal testing: must use preservative-free drug
![]() Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity
Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity
Overview
![]() Systemic
toxicity cause: Excessively high plasma local
anesthetic concentration
Systemic
toxicity cause: Excessively high plasma local
anesthetic concentration
The plasma drug concentration is determined by:
Rate of entry into systemic circulation balanced by redistribution to tissue sites and clearance
![]() Most common cause
of toxic plasma local anesthetic
concentrations:
Most common cause
of toxic plasma local anesthetic
concentrations:
Accidental direct intravascular injection during peripheral nerve block or epidural anesthesia
Other cause of toxic plasma levels
Excessive absorption from injection site (no intravascular injection)
Extent of systemic absorption is dependent upon:
Initial dose of administered
Injection site vascularity
Whether or not epinephrine was used to provide local vasoconstriction
Properties of the drug itself
![]() CNS Toxicity of local anesthetics
CNS Toxicity of local anesthetics
Symptom onset
Tongue and circumoral numbness (low concentration)
CNS changes with local anesthetic entering the brain
Initial symptoms: tinnitus, vertigo, restlessness
Subsequent symptoms: slurred speech and skeletal muscle fasciculation (muscle twitching: often immediately precedes seizures)
Tonic-clonic seizures
Presentation: generalized seizure (tonic general muscular contractions) with alternating contractions and relaxations.
Duration: one- two minutes
Consciousness: Loss of Consciousness
Factors influencing CNS toxicity
Plasma concentration of the local anesthetic is affected by which one is chosen to be used.
![]() Rate of
injection is an important factor and may be more
important than the total amount of drug used.
Rate of
injection is an important factor and may be more
important than the total amount of drug used.
Here the rate of injection is correlated with the rate of rise of serum drug concentration.
Lidocaine (Xylocaine):
To assess lidocaine toxicity active metabolites must also be considered.
For example, the metabolite monoethylglycinexylidide may contribute to additive toxicity with lidocaine (Xylocaine) following epidural administration.
Inverse relationship between PaCO2 and local anesthetic seizure thresholds.
This finding may be related to variation in cerebral blood flow and drug delivery.
![]() Hyperkalemia,
a condition which promotes membrane
depolarization tends to increase local
anesthetic toxicity.
Hyperkalemia,
a condition which promotes membrane
depolarization tends to increase local
anesthetic toxicity.
By contrast, hypokalemia which induces membrane hyperpolarization appears correlated with reduced local anesthetic toxicity.
An increase in lidocaine (Xylocaine) neurotoxicity may be observed in those patients treated with mexiletine (Mexitil) during perioperative time frame.
Assure adequate ventilation with oxygen
Rapid onset of arteriole hypoxemia and metabolic acidosis
Add supplemental oxygen when local anesthetic toxicity first appears
Seizure suppression
IV midazolam (Versed) or diazepam (Valium)
Overview: Neurotoxicity may be a consequence of local anesthetic injection into subarachnoid or epidural spaces.
Effects
Groin numbness
Long-lasting, isolated myotomal (muscle segment) weakness
Cauda equina syndrome
Subarachnoid-space injections
Transient radicular irritation
Permanent neurological injury following regional anesthesia is considered rare.
![]() Transient Radicular Irritation
Transient Radicular Irritation
Anatomical Location: lumbosacral nerves
Manifestation: moderate/severe lower back, buttocks, posterior thigh pain
time to onset: by 24 hours following spinal anesthesia complete recovery
Type of pain (delayed onset): neural inflammatory
Pain treatment: if severe, opioids
Time to recovery: within one-week
Pharmacological issues:
Transient radicular irritation -- may not be dependent on anesthetic concentration {frequency comparable following several lidocaine (Xylocaine) concentrations}
Spinal anesthesia with tetracaine (pontocaine): reduced incidence of transient radicular irritation relative to lidocaine (Xylocaine)
Transient ischemia due to lengthened exposure to local anesthetic as a result of concurrent epinephrine or phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine) use {in the anesthetic solution} may contribute to transient neurological symptoms
Definition: injuries (diffuse) across lumbosacral plexus causing:
Sensory anesthesia
Bowel and bladder sphincter dysfunction
Paraplegia
Circumstances of clinical occurrence:
Microcatheters (28 gauge) delivering hyperbaric 5% lidocaine (Xylocaine) may cause nonhomogeneous local anesthetic distribution-- pooling of high anesthetic concentration on stretched nerves (lithotomy position).
Following intrathecal lidocaine (Xylocaine) [100 mg 5% lidocaine (Xylocaine), 25-gauge needle]
Intended epidural anesthesia
![]() Anterior Spinal Artery Syndrome
Anterior Spinal Artery Syndrome
Manifestation: lower-extremity paresis (variable sensory deficit following neural blockade resolution)
Possible mechanisms
Thrombosis
Anterior artery spasm
Hypotension/vasoconstrictor drugs
Possible Predisposing conditions:
Advanced age
Peripheral vascular disease
Differential diagnosis: similar symptoms tmay be caused by epidural abscess-mediated or hematoma-mediated spinal cord compression.
Primary Reference: Stoelting, R.K., "Local Anesthetics", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 158-181.
Miller, R.D., Local Anesthesia, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, pp 425-433.
White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.
Local Anesthetics: Clinical Uses
Most frequent use is regional anesthesia.
Less common uses:
Prevention and treatment of cardiac arrhythmias
Prevention/management: increased intracranial pressure (ICP)
Lidocaine (Xylocaine) is as effective as thiopental (Pentothal) in preventing ICP increases associated with tracheal intubation.
Mechanism: The likely mechanism is that lidocaine (Xylocaine) decreases cerebral blood flow (CBF) by increasing cerebral vascular resistance.
Reduced CBF leads to reduced cerebral blood volume leads to reduced ICP.
Advantage of lidocaine (Xylocaine) vs. barbiturates: reduced risk of drug-induced hypotension
Lidocaine (Xylocaine) also reduces blood pressure response to direct laryngoscopic tracheal intubation, an effect probably secondary to generalized cardiovascular depression
Analgesia
Treatment of grand mal seizure
![]()
|
Surface/topical anesthesia |
Local infiltration |
Peripheral nerve block |
|
Bier block (IV regional anesthesia) |
Epidural anesthesia |
Spinal anesthesia (subarachnoid) |
Epidural anesthesia
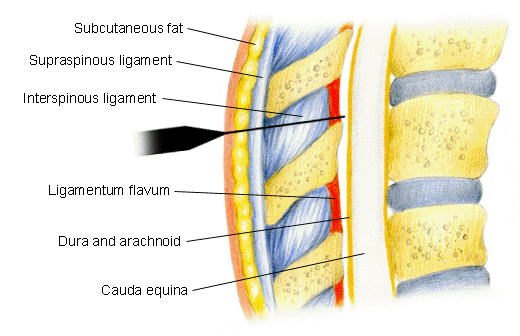
Spinal anesthesia (subarachnoid)
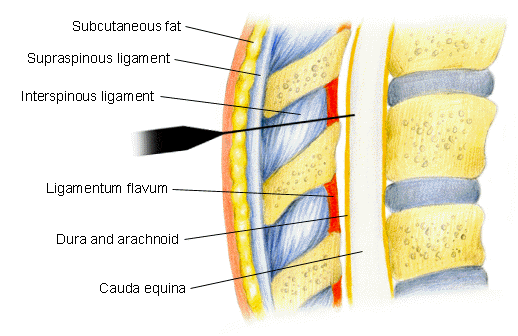
Location: application to mucous membranes
Nose
Mouth
Esophagus
Tracheobronchial tree
Genitourinary tract
Cocaine (4%-10%)
> 50% of rhinolaryngologic cases (USA)
Unique pharmacological property: produces localized vasoconstriction as well as anesthesia
Localized vasoconstriction:
Less bleeding
Improved surgical field visualization
Cocaine substitution:
Lidocaine (Xylocaine) -oxymetazoline (Afrin) combinations
Tetracaine (pontocaine)-oxymetazoline (Afrin) combinations
Tetracaine (pontocaine) (1%-2%)
Lidocaine (Xylocaine) (2%-4%)
Nebulized lidocaine (Xylocaine) is useful in surface anesthesia.
Upper and lower respiratory tract prior to bronchoscopy or fiber-optic laryngoscopy
Treatment for intractable cough
Normal subjects: No effect on airflow resistance (they produce some bronchodilation)
Patients with asthma: nebulized lidocaine (Xylocaine) may increase airflow resistance (bronchoconstriction)-- concern if bronchoscopy is intended for this patient group
Systemic concentration following nebulized lidocaine (Xylocaine)
Following mucosal absorption: systemic concentration may be similar to IV injection
Reasons:
Large surface area
Significant vascularity of tracheobronchial region
Barrier: keratinized skin layer
Higher local anesthetic concentrations required:
5% lidocaine (Xylocaine)-prilocaine (Citanest) cream {2.5% lidocaine (Xylocaine) and 2.5% prilocaine (Citanest)}
No local irritation
Even absorption
No systemic toxicity
Combination of local anesthetic: Definition: eutectic mixture of local anesthetics (EMLA)
Melting point of combined drug is lower then either lidocaine (Xylocaine) or prilocaine (Citanest) alone.
General definition: eutectic--said of a mixture which has the lowest melting point which it is possible to obtain by the combination of the given components.
Application Characteristics
1-2 grams of EMLA cream/10 cm2 of skin plus occlusive dressing
Duration of application to achieve adequate local anesthesia-- examples:
Skin-graft harvesting: two hours
Cautery of genital warts: 10 minutes
Clinical uses of EMLA applications include pain relief for:
Venipuncture
Lumbar puncture
Myringotomy in adults and children
Arterial cannulation
Special uses
in combination with nitroglycerin ointment -- makes venous cannulation easier by causing vasodilation
EMLA use in blood sampling: no effect on blood analysis
EMLA use in preventing pain associated with intradermal skin tests:
Predisposes to false negatives [decreases flare response associated with weakly positive reactions]
Factors affecting EMLA analgesia time to onset, duration of action, and efficacy
Skin blood flow
Epidermal/girl thickness
Application duration
Presence of pathology
Blacks: possibly less responsive than whites
Methemoglobin levels secondary to prilocaine (Citanest) metabolism may be of concern in young children (< three months)
[if EMLA cream is used while other methemoglobin-inducing drugs are used [e.g. sulfonamides, acetaminophen, phenytoin (Dilantin), nitroglycerin, nitroprusside sodium (Nipride)]
EMLA cream not recommended for mucosal application due to faster lidocaine (Xylocaine)/prilocaine (Citanest) absorption
EMLA cream not recommended for application to skin wounds (wound infection risk, increased)
EMLA cream not recommended for patients taking mexiletine (Mexitil, amine lidocaine analog) (in antiarrhythmic drug) since additive/synergistic effects may occur
EMLA cream: contraindicated in patients are allergic to amide local anesthetics
Other topical local anesthetic formulations
Pramoxine (Tronothane, Prax) with the following applications:
Skin or mucous membrane application: pain or leave due to
Dermatoses
Hemorrhoids
Minor burns
Reduce pain associated with sigmoidoscopy
Upper airway anesthesia prior to direct laryngoscopy
Not recommended for:
nasal/tracheal mucosal application (irritation)
Dyclonine (Dyclone, Seroquel 5%-1%), piperocaine, hexylcaine-- applications
Mucous membrane anesthesia for direct laryngoscopy
Dyclonine (Dyclone): upper airway anesthesia for patients allergic to bupivacaine (Marcaine) and procaine (Novocain)
Rationale: ketone structure dyclonine (Dyclone) makes cross sensitivity with amide or ester local anesthetics less likely
Primary Reference: Stoelting, R.K., "Local Anesthetics", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 158-181; Miller, R.D., Local Anesthesia, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, pp 425-433.
Definition: Extravascular placement of the local anesthetic in the region to be anesthetized
Example: subcutaneous local anesthetic injection in support of intravascular cannula placement
Preferred local anesthetics for local infiltration
Most common: lidocaine (Xylocaine)
Other choices: 0.25% Ropivacaine (Naropin) or Bupivacaine (Marcaine) (effective for pain management at inguinal operative location)
Duration of action:
Duration extended by 2X using 1:200,000 epinephrine
![]() Caution:
Epinephrine-containing local
anesthetic solution should not be injected intracutaneously (intradermal) or into tissues
supplied by
"end-arteries" such as
ears, nose, fingers because
vasoconstriction may be
sufficiently severe to produce
tissue ischemia and gangrene.
Caution:
Epinephrine-containing local
anesthetic solution should not be injected intracutaneously (intradermal) or into tissues
supplied by
"end-arteries" such as
ears, nose, fingers because
vasoconstriction may be
sufficiently severe to produce
tissue ischemia and gangrene.
Procedure involves local anesthetic injection into tissues around individual nerves or nerve plexuses (e.g. brachial plexus).
Mechanism:
Local anesthetic diffusion path: nerve outer surface (mantle) to the nerve core [driving force: concentration gradient]
Anesthetized first: mantle fibers (innervating more proximal structures)
Anesthetized last: core fibers (innervating more distal anatomy)
Explanation of why anesthesia develops proximately first
Recovery in the opposite direction (sensation returns proximally first; lastly the distal anatomy)
Mixed peripheral nerves: (motor/sensory)
Sequence of onset and recovery (motor anesthesia first or sensory anesthesia first): dependent on anatomical locations within the nerve fiber
Rapidity of onset: Dependencies
Drug pK dependency: pK (at a given tissue pH) determines the fraction all of local anesthetic in the nonionized formed.
Un-ionized form = lipid soluble, active form, capable of penetrating membranes combining with local anesthetic receptors located on the internal membrane surface.
Examples:
Lidocaine (Xylocaine) time to onset = 3minutes
Bupivacaine (Marcaine) time to onset = 15 minutes
Rationale: greater lidocaine (Xylocaine) fraction present in the un-ionized (uncharged) active form
Specific examples:
0.5% bupivacaine (Marcaine) or ropivacaine (Naropin): similar onset and duration of brachial plexus block
Ropivacaine (Naropin) (subclavian perivascular block): time to onset -- 4 minutes; sensory block duration -- > 13 hours
Ropivacaine (Naropin): onset and duration of action similar to bupivacaine (Marcaine)
Not recommended:
Tetracaine (pontocaine): slow onset and more likely to cause systemic toxicity; not recommended for peripheral nerve block or for local infiltration
Duration of action-dependencies
Drug lipid solubility
Extent of drug protein binding
Dose
Prolongation of drug effect:
Safer with added vasoconstrictor (e.g. epinephrine) than by increasing local anesthetic dose
Example: bupivacaine (Marcaine) + epinephrine: peripheral nerve block may last 14 hours (in some reports)
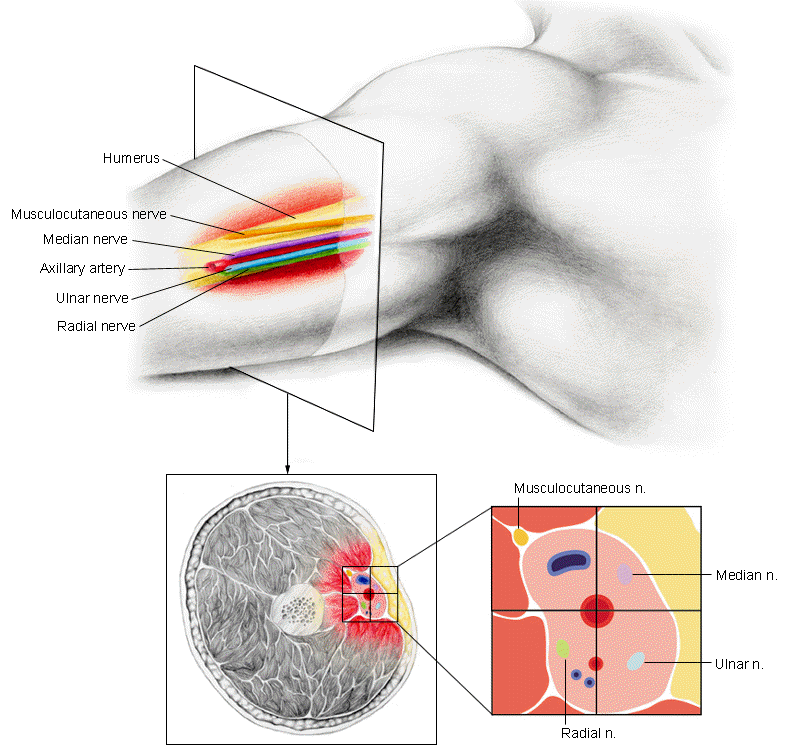
Axillary Block: Drawing by Lindsey Parker, (c) University of Kansas Medical Center
Intravenous Regional Anesthesia (Bier Block)
Procedure:
Local anesthetic injection into an extremity isolated by tourniquet
Result: rapid anesthesia onset; skeletal muscle relaxation
Duration of anesthetic action:
Dependent on how long the tourniquet is kept inflated
Following tourniquet deflation: rapid recovery as blood dilutes local anesthetic concentration
Probable Mechanism:
Drug action on nerve endings and nerve trunks
Choice of local anesthetics
Ester or amide type IV local anesthetics may be used
Most frequently used amide agents:
Lidocaine (Xylocaine)
Prilocaine (Citanest)
At deflation, no clinically significant methemoglobinemia (3% of hemoglobin as methemoglobin)-- 10% required for cyanosis.
Comparing comparable IV regional anesthesia with 50 ml (0.5%) lidocaine (Xylocaine) or prilocaine (Citanest): lower plasma prilocaine (Citanest) concentrations following tourniquet deflation, compared to lidocaine (Xylocaine)
Prilocaine (Citanest) may be safer in terms of reduced systemic toxicity risk
Agents not recommended:
Chloroprocaine (Nesacaine) because of possible incidence of thrombophlebitis.
Bupivacaine (Marcaine) since this agent is considered more likely than other local anesthetic to cause cardiotoxicity upon tourniquet deflation.
Ropivacaine (Naropin) as this drug may cause cardiotoxicity upon tourniquet deflation albeit less likely in effect compared to that associated with bupivacaine (Marcaine)).
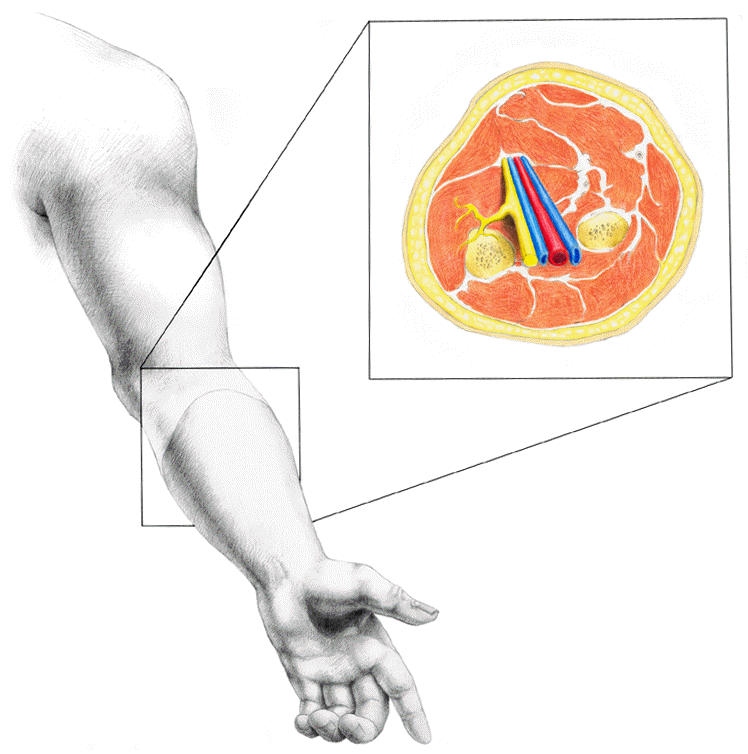
Bier Block: Drawing by Lindsey Parker
Primary Reference: Stoelting, R.K., "Local Anesthetics", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 158-181.; Miller, R.D., Local Anesthesia, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, pp 425-433.
Definition
Anesthesia caused by local anesthetic solutions injected into epidural or sacral caudal space
Mechanisms:
Direct action on nerve roots and spinal cord following local anesthetic diffusion across the dura
Diffusion of local anesthetic into paravertebral region through the intervertebral foramina causing paravertebral nerve blocks
Onset of action:15-30 minute delay
Choice of local anesthetics:
Lidocaine (Xylocaine): frequently used; diffuses well for tissues
Bupivacaine (Marcaine) and Ropivacaine (Naropin) (0.5%-0.75%):
Prolonged sensory anesthesia
Motor anesthesia: less intense and shorter duration with ropivacaine (Naropin); greater tendency for Alpha- delta and C fiber blockade
Reduced ropivacaine (Naropin) motor effects may be beneficial for obstetrical patients in labor and for patients experiencing acute/chronic pain
Ropivacaine (Naropin)-Reduced systemic toxicity compared to bupivacaine (Marcaine) allows ropivacaine (Naropin) concentrations of up to 1% to be used surgically.
Analgesia/anesthesia for labor/cesarean section similar with 0.5% bupivacaine (Marcaine) or ropivacaine (Naropin) [motor blocked duration shorter in parturients receiving ropivacaine (Naropin)]
0.25% ropivacaine (Naropin) and syrup.25% bupivacaine (Marcaine) (intermittent dosing into epidural space): equally effective in managing labor pain
Postoperative analgesic: 0.2% ropivacaine (Naropin) (6-10 ml/hr)
Local anesthetic plasma concentrations following epidural anesthesia in parturients:
Local anesthetics: traverse the placenta and may affect the fetus for 24-48 hours (not necessarily adversely)
Special considerations:
Mepivacaine (Carbocaine): less readily metabolized by the fetus or neonate compared to adult: longer halftimes of elimination
Increased lipid solubility and protein binding of bupivacaine (Marcaine) may reduce its access to the fetus.
Lidocaine (Xylocaine): (even low doses) leads to maternal systemic absorption and consequently fetal systemic presence
Bupivacaine (Marcaine): not detectable in neonatal plasma (one day following cesarean section using bupivacaine (Marcaine)-spinal anesthesia

Drawing by Lindsey Parker
Comparison of Epidural vs. Spinal anesthesia
|
|
|
|
|
|
Definition
Anesthesia following local anesthetic injection into lumbar subarachnoid space.
Site of action
Primary: preganglionic fibers leading the spinal cord in the anterior rami
Secondary: superficial spinal cord layers
Zones of differential anesthesia are likely due to:
Local anesthetic concentration gradient effects
Different nerve fiber types have different sensitivities to local anesthetics
Anesthesia levels
Level of sympathetic nervous system "denervation": extends about two spinal segments cephalad (above) the level sensory anesthesia
Level of motor anesthesia extends about two segments below sensory anesthesia
Reason: differential sensitivity to local anesthesia
Factors affecting local anesthetic dosages:
Patient height (determines subarachnoid spatial volume)
Segmental level of anesthesia required
Duration of anesthesia required
Total local anesthetic dose: more important than concentration or volume effects
Local anesthetics used for spinal anesthesia
Most commonly used agents: tetracaine (pontocaine), lidocaine (Xylocaine), bupivacaine (Marcaine)
Characteristics of some drugs:
Lidocaine (Xylocaine): may be associated with a higher risk of transient neurological adverse effects compared to bupivacaine (Marcaine)
If lidocaine (Xylocaine) used: limit dose to 60 mg
Bupivacaine (Marcaine): More effective than tetracaine (pontocaine) in preventing lower-extremity tourniquet pain (orthopedic surgery cases)
In parturients: intrathecal mepivacaine (Carbocaine, 2.5 mg) + 10 ug sufentanil (Sufenta): effective labor analgesia while allowing patients to continue to walk.
Ropivacaine (Naropin) (3 ml of 0.5% or 0.75%): Sensory anesthesia present; however, motor blockade present in only 50% of patients if 0.5% dosage used.
Chloroprocaine (Nesacaine) -- Not placed in subarachnoid space due to neurotoxicity risk
Factors determining spread of drug following lumbar injection:
Specific gravity of the local anesthetic solution
Glucose addition: increased specific gravity above that of CSF (hyperbaric)
Distilled water addition: decreased specific gravity below that of CSF (hypobaric)
Duration of action: amides vs. esters
CSF does not contain significant cholinesterase activity -- no enzymatic influence on ester local anesthetic duration:
Duration of action of amides and ester-local anesthetics placed in subarachnoid spaces --influenced by the vascular drug absorption rates
Intrathecal tetracaine (pontocaine): significant increase in spinal cord blood flow
(preventable/reversible by epinephrine addition, which increases tetracaine (pontocaine)-induced spinal anesthesia, up to 2X);{less vasodilation with lidocaine (Xylocaine)}
Bupivacaine (Marcaine): vasoconstriction

Drawing by Lindsey Parker
Physiological Effects-- Spinal anesthesia
![]() Consequences of sympathetic
blockade:
Consequences of sympathetic
blockade:
Arteriolar dilation
No significant effect on systemic BP due to compensatory upper extremity vasoconstriction.
No cerebrovascular vasoconstriction
Total sympathetic blockade due to spinal anesthesia: associated with a reduction in systemic vascular resistance of < 15%.
Rationale: arteriolar smooth muscle does not dilate maximally because of intrinsic tone
Many major cardiovascular response secondary to spinal anesthesia due to:
Effects on venous circulation
Venules: minimal intrinsic tone retention; maximal dilation during spinal anesthesia
![]() Consequences of
venous-side dilation
Consequences of
venous-side dilation
Reduced venous return to heart leads to decreased cardiac output and consequently decreased systemic blood-pressure
Severe systemic hypotension in hypovolemic patients
Treatment:
α-adrenergic receptor agonist administration
Slightly-head down patient repositioning
Cardiac slowing (bradycardia) secondary to blockade of preganglionic cardiac accelerator nerves (T1 to T4)
This bradycardia response may be worsened in the presence of reduced preload and as a result, reduce stimulation of atrial stretch receptors (which, when activated, cause cardioacceleration)
Management of bradycardia secondary to T1 to T4 blockade may include administration of low-dose epinephrine {Clark Albert, MD, personal communication}
High-spinal anesthesia: Effects on ventilation
Apnea may occur due to abnormal medullary ventilatory center function {secondary to ischemia due to reduced cerebral blood flow}
Apnea-- unlikely due to phrenic nerve paralysis
Primary Reference: Stoelting, R.K., "Local Anesthetics", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 158-181.;Miller, R.D., Local Anesthesia, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, pp 425-433.
Mechanism
Excessive sympathetic stimulation
Norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake blockade
Pharmacokinetics
Peak plasma concentrations:
30-40 minutes following intranasal administration
5 minutes following IV/smoke administration
Maximal physiological effects: intranasal cocaine (15-40 minutes)
Duration of effects: 60 minutes or longer following peak effect
Elimination halftime -- 60-90 minutes
Metabolism: plasma esterases
![]() Adverse Effects: acute
administration
Adverse Effects: acute
administration
Coronary vasospasm/myocardial ischemia/infarction
Cardiac arrhythmias (including ventricular fibrillation)
Hypertension
Myocardial ischemia may be long lasting, possibly secondary to delayed coronary artery vasospasm
Dose-dependent reduction in uterine blood flow may lead to fetal hypoxemia
Hyperpyrexia/seizures
Topical cocaine + epinephrine or cocaine administration in the presence of myocardium-sensitizing volatile anesthetics, e.g. halothane:
Enhanced cocaine-mediated cardiac stimulation
Cocaine may be contraindicated in patients with hypertension or coronary vascular disease and in patients receiving agents that enhance catecholamine effects (e.g., MAO inhibitors)
![]() Treatment of
cocaine toxicity
Treatment of
cocaine toxicity
Nitroglycerin
IV diazepam (Valium) for management of cocaine induced seizures
Caution: esmolol (Brevibloc) management of cocaine-induced tachycardia may predispose to coronary vasospasm
Primary Reference: Stoelting, R.K., "Local Anesthetics", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 158-181.; Miller, R.D., Local Anesthesia, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, pp 425-433.
|
|
|