Anesthesia Pharmacology Chapter 27: Adult Cardiac Procedures in Anesthesia
Anesthesia Pharmacology Chapter 27: Adult Cardiac Procedures in Anesthesia
Critical factors influencing Coronary Blood Flow
Review: critical factors
Heart rate (diastolic filling time)
Coronary perfusion pressure
Coronary vascular tone
Intraluminal obstruction (e.g. plaques)
Most vulnerable region to reduce coronary flow (ischemia): subendocardial region--
Rationale: The subendocardium has enhanced metabolic requirements due to:
Relatively increased systolic shortening
Systolic blood flow restriction
Left ventricular subendocardium perfusion -occurs essentially during diastole only
Right ventricular subendocardial flow: occurs during systole
Rationale differences in left vs. right intracavitary systolic pressures
Volume of subendocardial perfusion blood flow-- dependencies
Diastolic pressure
Diastolic duration
Coronary Perfusion Pressure
Definition (approximation): aortic diastolic pressure (AoDP) - left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP)
Factors that reduce flow:
Increased coronary vascular tone
Intraluminal obstruction
An increased pressure gradient is favored by a reduced end-diastolic left ventricular pressure (ventricular filling pressure)
Reduced (low) ventricular filling pressures would be expected to have a positive consequence in terms of the myocardium because:
Improved coronary vascular perfusion
Reduced myocardial oxygen demand (MVO2) secondary to decrease ventricular volume and wall tension)
Recall that wall tension and contractility are the primary determinants of myocardial oxygen demand.
Ventricular wall tension is directly proportional to:
Intracavitary pressure and ventricular radius
Ventricular wall tension is inversely proportional to:
Wall thickness
Definition: the difference between supply (autoregulated) - blood supply available with maximal vasodilatation
Coronary Autoregulation-- maintenance of constant blood flow over range of perfusion pressures (50-120 mm Hg) to accommodate a given myocardial oxygen requirement
"Autoregulation" refers to pressure-dependent changes of the level of coronary resistance vessels, principally coronary arterioles (diameter < 150 um) into a lesser extent small coronary arteries
Changes in myocardial oxygen requirements induce changes in the autoregulation state -- principally in response to alter myocardial oxygen tension, PO2, mediated by agents such as adenosine.
Adenosine -mediated changes in vasodilatory state is related inversely to arterial diameter -- greatest changes (dilation) in the smaller vessels
Coronary autoregulation is associated (coupled) with coronary venous PO2 (especially with oxygen tension < 25 mm Hg)
Autoregulation:
Greater autoregulation in the subendocardium; increased autoregulation in left vs. right coronary arteries (reduced pressure/flow -- O2 requirement dependencies on the right side may explain this difference)
Regulators:
Metabolic, multiple pathways
Basal vascular tone and normal autoregulation dependent on KATP channels which are activated secondary to adenosine receptor activation.
Other possible mediators include: potassium, oxygen itself, prostaglandins, nitric oxide (NO, a.k.a. endothelium-derived relaxing factor), prostacyclin, histamine and ATP.
Prostaglandin E1: coronary vasodilator (adenosine -mediated)
Prostaglandin E2: coronary artery vasoconstrictor
Acetylcholine -- increases flow
Histamine promotes coronary arterial vasospasm.
Myocardial blood supply requirements (flow) are adjusted by regulation of diastolic vascular resistance in small intramyocardial arterioles
 |
|
With epicardial arterial obstruction, i.e. more stenosis, flow is maintained by progressive, increasing dilation of the small intramyocardial arterioles -- with attendant reduction in coronary reserve.
Note that as this pathological condition progresses, reduced coronary reserve makes it more likely that an imbalance between myocardial oxygen requirements and supply will occur.
This condition may lead to ischemia.
Generally, intraoperative hypotension is more likely to cause myocardial ischemic states than hypertension
Myocardial Oxygen Supply and Blood Oxygen Content
Blood oxygen content = hemoglobin concentration X O2 saturation X 1.34
Since blood volume and oxygenation is typically well maintained during anesthesia, management of oxygen supply with changing oxygen demand depends on management of coronary blood flow.
An example of "Supply" ischemia would be transient, possibly sudden, changes in cross-sectional luminal vessel area within attendant reduction in blood flow to the myocardium. These dimensional changes may be sufficient to induce ischemia.
Angina as well as myocardial infarction may occur even in patients with apparently normal arteriograms as a result of vasospastic constriction of coronary vessels.
The likelihood of supply ischemia is increased with preexisting coronary vascular disease, reflected by the presence of atheromas/plaques within the vessel.
Intraoperative factors that may induce "supply" ischemia may include:
An increase in circulating catecholamines
A possible enhancement of interaction between platelets and atherosclerotic regions
Intraoperative ischemia, as judged by ECG changes for example, may occur without changes in:
Heart rate
Blood pressure
Ventricular filling pressure
Most intraoperative ischemic episodes are not associated with hemodynamic changes
Intraoperative coronary vasospasm may be treated/prevented by:
Nitroglycerin
Calcium channel blockers
Hemodynamic Goals in Anesthesia
Primary goal: prevent myocardial ischemia
Secondary goal:
Rapid identification of intraoperative ischemic episodes
Rapid corrective measures
Electrocardiography
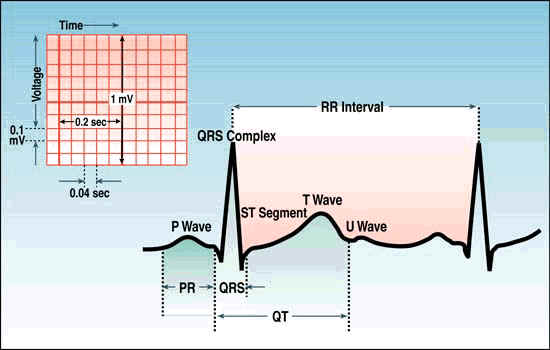 |
|
 |
|
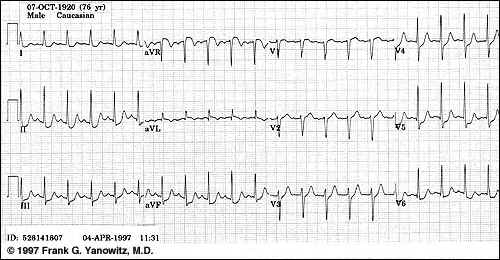
Subendocardial ischemia (above) -- exercise induced or during anginal episode
Courtesy of Frank G.Yanowitz, M.D. and The Alan E. Lindsey ECG Learning Center,used with permission.
Methods for detecting intraoperative ischemia
In the awake patient:Pain-especially if the pain in his been previously identified with angina
Problematic: similar pain may be associated with biliary spasm which may occur following opioid administration (biliary pain is naloxone (Narcan)-sensitive; angina is not sensitive)
Chest pain ( in just apresenting symptoms are similar to previously)
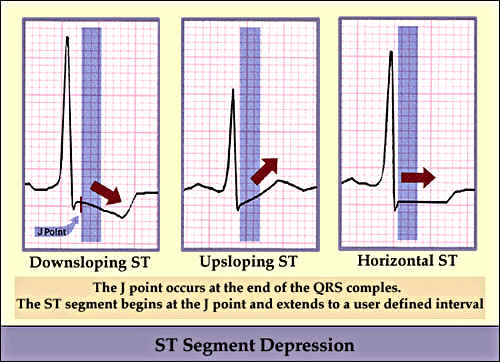
Current standard, primary method = monitoring ST segment in multiple ECG leads, typically leads II and V5.
 |
|
4Nature of ECG changes:
ST segment depression (usually > 1 mm): suggestive of "injury pattern", may indicates an actual infarct
Factors which may make ST segment analysis problematic (because of baseline changes in ST segment, secondary to repolarization)
Left bundle branch block
Ventricular hypertrophy
"Filtering" on the ECG monitor system (filtering reduces baseline change and limits interference due to use of electrocautery), which the limits detection ST segment changes
ST segmental changes observed on a "filtered" ECG system might not be apparent on a standard 12-lead ECG.
Suggestion: obtain a preoperative and preinduction baseline ECG strip (using the intraoperative monitoring system) in the diagnostic mode, if available, instead of the filtered monitoring mode.
The preinduction filtered monitoring mode ECG should be compared for other intraoperative recorded strips. This step may be particularly important for all patients who would appear to be at risk for ischemia (see reference 4)
Lead V5: most likely to detect lateral left ventricle ischemia
75% of ischemic episodes will be shown on lead V5 (manifestation is by ECG ST segment changes on 12-lead recording)
if both leads V5 and II are monitored, 80% of ST-segmental changes will be identified4--- (London, MJ, Hollenberg, M, Wong, MG, et al. Intraoperative myocardial ischemia localization by continuous 12 lead electrocardiography. Anesthesiology 1998: 69:237, primary reference)
Lead II: most likely to detect inferior wall ischemia.
 |
|
Rationale for monitoring lead choice:
Lead demonstrating previous changes, e.g. during preoperative stress test
Knowledge of location coronary artery lesion
Posterior wall ischemia best appreciated using:
Atrial lead
Esophageal lead
Three-lead intraoperative ECG monitor: modified V5 lead:
Left arm lead in the V5 position while monitoring lead I
Three-lead system modification which retains lead II and makes a modified V5, by placing the left arm electro-over the V5 position.
Modified V5 is monitored by using the lead selector on lead I" RA = right arm; LA = left arm; LL = left leg
Reference 4 (Figure 6-19:McGough, EK, in: Manual of Complications During Anesthesia, (Gravenstein, N, ed), J. B. Lippincott Co., Philadelphia, p 221 1991
Heart rate and Blood Pressure Monitoring: rate-pressure product (heart rate x peak systolic pressure) or pressure-rate ratio-- probably NOT sensitive or specific indicators of intraoperative ischemia (lack of correlation with ECG changes; lack of correlation with direct monitoring of ventricular wall motion changes by using transesophageal echocardiography)
Pulmonary Artery Catheter: usefulness in detecting/identifying myocardial ischemia: "Little value" in monitoring myocardial ischemia3.
Value of pulmonary artery catheter data -- identification of systolic +/- diastolic dysfunction by sudden pulmonary arterial or capillary wedge pressure elevations
Cardiac surgical patients (even high-risk) may be safely interoperability managed without routine pulmonary artery catherization -- the pulmonary artery catherization is required during the operative procedure, contemporary placement does not change surgical outcome
Pulmonary artery catheter data provide important information concerning patient's volume status and cardiac output, is not considered a reliable/sensitive index for identification of ischemic episodes
 |
|
Summary:
Most common method for monitoring possible myocardial ischemia: ECG-ST analysis
Sensitivity of specific leads:
V6: 82% detection frequency
V5: 72% detection frequency
V4:: about 50% detection frequency
lead II: about 33% detection frequency
ST segment changes
ST segment depression --most likely associated with ischemia
ST segment elevation-less specificity, but suggestive if it is known that the patient has coronary vascular disease
"Trend" analysis is not available for patients with left bundle branch block or in the presence of ventricular pacing
Hemodynamic changes-with impairment of overall left ventricular function
Elevated pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP): manifestation-large V waves in the PAOP tracing secondary to (a) changed left ventricular compliance, (b) papillary muscle dysfunction causing mitral valve regurgitation
Cardiac output reduction-least sensitive index of ischemia
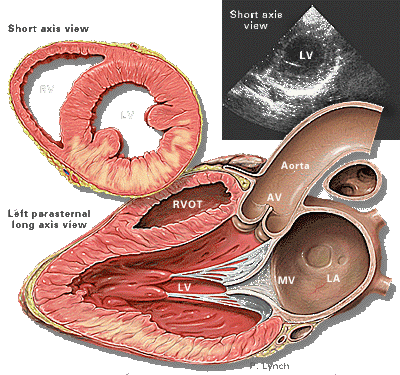
Transesophageal ultrasound (TEE ultrasound) -- indications
new ventricular wall motion anomaly in a patient with coronary artery disease: a good indication of ischemia
TEE more sensitive than ECG in detecting ischemia; however, the methods may be complementary in that one method will detect ischemia in some circumstances in which the other method will not -- also transesophageal ultrasound may not be routinely available
Ischemia occurring in the post-bypass time frame tend to be more common and more related to negative clinical outcomes such as perioperative myocardial infarction, serious, life-threatening ventricular tachyarrhythmias and death.
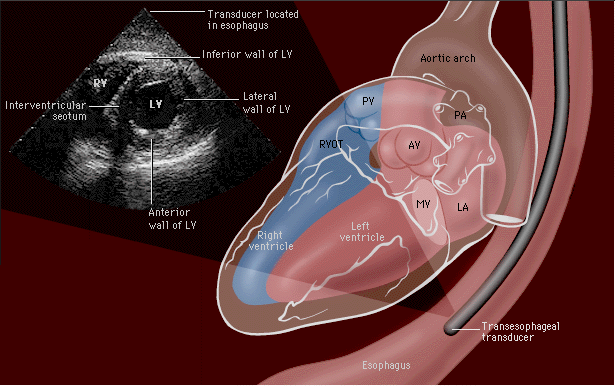
Intraoperative Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE): Utility and Assessment of Myocardial Ischemia
Source: Practice Guidelines for Perioperative Transesophageal Echocardiography, A Report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists and the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists Task Force on Transesophageal Echocardiography,Anesthesiology 1996: 84:986-1006
TEE Overview
Regional ventricular dysfunction during surgery probably increases patient risk of perioperative myocardial infarction and sudden death
Transesophageal echocardiography is one method that allows detection of regional ventricular wall motion dysfunction
There is a high incidence of intraoperative ventricular dysfunction which may be correlated with myocardial ischemia; there is an important concern about the frequency of false-positive results.
Analysis of animal experiments and angioplasty research studies indicates that wall motion anomalies precede ECG changes during myocardial ischemia.
Transesophageal echocardiography may provide a "more meaningful" reference standard for ischemia than ECG.
Limitations of TEE:
TEE changes are often more subjective compared to quantifiable ECG changes (e.g. ST segment depression)
Interpretation is influenced by translational cardiac motion, bundle branch block, and ventricular pacing
A clear worsening no segmental wall motion and thickening is required ("in the absence of similar global changes") to suggest strongly a diagnosis of ischemia
Segmental wall motion may be caused by other factors, non-ischemia, e.g.:
Previous myocardial infarction
Myocarditis
Myocardial stunning following cardiopulmonary bypass
Conclusions:
Use of TEE may allow early identification of myocardial ischemia, permitting early treatment which will improve survival
Intraoperative TEE detection of ischemia allows corrective action including common
Changes in anesthetic management
Alterations in surgical procedure
Postoperative triage -- preventing perioperative complications
5Increasing availability and the usefulness of TEE suggest that the cardiac anesthesiologist should acquire skills required for TEE applications.