|
|
Anesthesia Pharmacology Chapter 9: Pharmacology of Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Electrophysiology and Cardiac Arrhythmias
Normal rate: 60-100 beats per minute
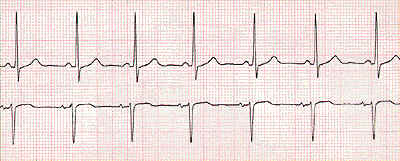
Impulse Propagation: sinoatrial node to the atrioventricular (AV node) to the His-Purkinje followed by distribution throughout the ventricle
Normal AV nodal delay (0.15 seconds) -- sufficient to allow atrial ejection of blood into the ventricles
Definition: arrhythmia -- cardiac depolarization different from above sequence --
abnormal origination (not SA nodal)
abnormal rate/regularity
abnormal conduction characteristics
Transmembrane potential -- determined primarily by three ionic gradients:
Na+, K+, Ca 2+
water-soluble, -- not free to diffuse through the membrane in response to concentration or electrical gradients: depended upon membrane channels (proteins)
Movement through channels depend on controlling "molecular gates"
Gate-status controlled by:
Ionic conditions
Metabolic conditions
Transmembrane voltage
Maintenance of ionic gradients:
Na+/K+ ATPase pump
termed "electrogenic" when net current flows as a result of transport (e.g., three Na+ exchange for two K+ ions)
Initial permeability state -- resting membrane potential
sodium -- relatively impermeable
potassium -- relatively permeable
Cardiac cell permeability and conductance:
conductance: determined by characteristics of ion channel protein
current flow = voltage X conductance
voltage = (actual membrane potential - membrane potential at which no current would flow, even with channels open)
Concentration gradient: 140 mmol/L Na+ outside: 10 mmol/L Na+ inside;
Electrical gradient: 0 mV outside; -90 mV inside
Driving force -- both electrical and concentration -- tending to move Na+ into the cell.
In the resting state: sodium ion channels are closed therefore no Na+ flow through the membrane
In the active state: channels open causing a large influx of sodium which accounts for phase 0 depolarization
|
|
|
Concentration gradient (140 mmol/L K+ inside; 4 mmol/L K+outside)
Concentration gradient -- tends to drive potassium out
Electrical gradient tends to hold K+ in.
Some K+ channels ("inward rectifier") are open in the resting state -- however, little K+ current flows because of the balance between the K+ concentration and membrane electrical gradients
Cardiac resting membrane potential: mainly determined
By the extracellular potassium concentration and
Inward rectifier channel state
Spontaneous Depolarization (pacemaker cells)-- phase 4 depolarization
Spontaneous Depolarization occurs because:
Gradual increase in depolarizing currents (increasing membrane permeability to sodium or calcium)
Decrease in repolarizing potassium currents (decreasing membrane potassium permeability)
Both
Ectopic pacemaker: (not normal SA nodal pacemakers) --
Facilitated by hypokalemic states
Increasing potassium: tends to slow or stop ectopic pacemaker activity
Depolarization to threshold voltage--Na+
m gate activation (activation gate); assuming inactivation (h) gates are not closed then
sodium permeability dramatically increased; intense sodium current
depolarization
h gate closure; Na+ current inactivation
Ca2+ --
|
|
|
|
|
|
Five Phases: cardiac action potential associated with HIS-purkinje fibers or ventricular muscle
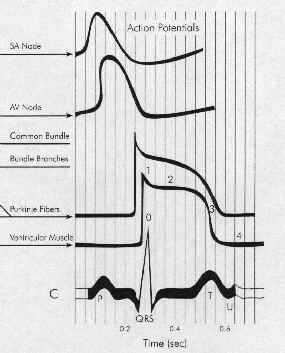
Phase 0 corresponds to Na+ channel activation.
The maximum upstroke slope of phase 0 is proportional to the sodium current.
Phase 0 slope is related to the conduction velocity in that the more rapid the rate of depolarization the greater the rate of impulse propagation.
Phase 1 corresponds to an early repolarizing K+ current.
rapidly inactivated.
Phase 2 is the combination of an inward, depolarizing Ca2+ current balanced by an outward, repolarizing K+ current (delayed rectifier).
Phase 3 is also the combination of Ca2+ and K+ currents.
Phase 3 is repolarizing because the outward (repolarizing) K+ current increases while the inward (depolarizing) Ca2+ current is decreasing.
Phase 4 in normal His-Purkinje and ventricular muscle cells is characterized by a balance between outward Na+ current and inward K+ current.
As a result, the resting membrane potential would normally be flat.
In disease states or for other cell types (SA nodal cells) the membrane potential drifts towards threshold.
This phenomenon of spontaneous depolarization is termed automaticity and has an important role in arrhythmogenesis.
Influence of Membrane Resting Potential on Action Potential Properties
The extent and synchrony of sodium channel activation is dependent on the resting membrane potential.
Inactivation gates of sodium channels close in the membrane potential range of -75 to -55 mV (less channels available for sodium ion inward current)
For example: less intense sodium current if the resting potential is - 60 mV compared to -80 mV
Consequences of reduced sodium activation due to reduced membrane potential (less negative)
reduced of velocity upstroke (Vmax) [phase 0] (maximum rate of membrane potential change)
reduced excitability
reduced conduction velocity-- a significant cause of arrhythmias
prolongation of recovery:-- an increase in effective refractory period
Plateau Phase:
Plateau phase -- Na channels mostly inactivated
Repolarization (h gates reopen)
"Refractory period": time between phase 0 and phase 3 -- during this time the stimulus does not result in a propagated response
Altered refractoriness may cause or suppress arrhythmias
Factors that reduce the membrane resting potential & reduce conduction velocity
Hyperkalemia
Sodium pump block
Ischemic cell damage
Conduction in severely depolarized cells
With decreased membrane potentials (e.g., -55 mV), sodium channels are inactivated
Under some circumstances, increased calcium permeability or decreased potassium permeability allow for slowly conducted action potentials with slow upstroke velocity
Ca2+-inward current-mediated action potentials are normal for the specialized conducting SA nodal and AV nodal tissues, which have resting membrane potentials in the -50 to-70 mV range.
Hondeghem, L.M. and Roden, D.M., "Agents Used in Cardiac Arrhythmias", in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, Katzung, B.G., editor, Appleton & Lange, 1998, pp 216-241.
Factors that may precipitate or exacerbate arrhythmias
Ischemia
Hypoxia
Acidosis
Alkalosis
Abnormal electrolytes
Excessive catecholamine levels
Autonomic nervous system effects (e.g., excess vagal tone)
Excessive catecholamine levels
Autonomic nervous system effects (e.g., excess vagal tone)
Drug effects: e.g., antiarrhythmic drugs may cause arrhythmias)
Cardiac fiber stretching (as may occur with ventricular dilatation in congestive heart failure)
Presence of scarred/diseased tissue which have altered electrical conduction properties
Hondeghem, L.M. and Roden, D.M., "Agents Used in Cardiac Arrhythmias", in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, Katzung, B.G., editor, Appleton & Lange, 1998, pp 216-241
Arrhythmias develop because of abnormal impulse generation, propagation or both.
Abnormalities of Cardiac Impulse Initiation
Factors that influence heart rate (altered frequency of pacemaker cell firing rate)
Heart rate determined (interval between pacemaker firing) by the sum of: Action potential duration + Diastolic duration interval
More important -- Diastolic duration interval: determined by 3 factors:
Maximum diastolic potential (most negative membrane potential reached during diastole
Slope of phase 4 depolarization: (increased slope: threshold is reached quicker causing a faster heart rate; decreased slope: longer to reach threshold resulting in a slower heart rate
Threshold Potential (membrane potential at which in action potential is initiated)
Decreased Heart Rate:--
Vagal Effects: (cholinergic influences on the heart rate)
more negative maximum diastolic potential (the membrane potential starts farther away from the threshold potential)
reduced slope of phase 4 depolarization (takes longer to reach threshold potential)
Increased Heart Rate:-
Adrenergic Effects: (sympathetic/sympathomimetic influences on heart rate)
Beta adrenergic receptor blockers (reduced phase 4 depolarization slope)
Factors that can increase automaticity:
hypokalemia
cardiac fiber stretch
beta-adrenergic receptor activation
injury currents
acidosis
Latent Pacemakers -- cells not normally serving pacemaker function, but exhibits slow phase 4 depolarization: conditions favoring latent pacemaker activity noted above
All cardiac cells (including normally inactive atrial/ventricular cells) may show pacemaker activity, particularly in hypokalemic states
Failure of impulse initiation can lead to excessively slow heart rate,bradycardia .
If an impulse fails to propagate through the conduction system from the atrium to the ventricle, heart block may occur.
An excessively rapid heart rate, tachycardia, is also encountered clinically
Hondeghem, L.M. and Roden, D.M., "Agents Used in Cardiac Arrhythmias", in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, Katzung, B.G., editor, Appleton & Lange, 1998, pp 216-241.
Introduction: Arrhythmias and Drug Therapy
Atrial fibrillation may result in a high ventricular following rate.
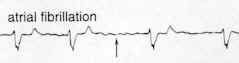
Accordingly, drugs which may reduce ventricular rate by reducing AV nodal conduction include:
calcium channel blockers (verapamil (Isoptin, Calan), diltiazem (Cardiazem))
beta-adrenergic receptor blockers (propranolol (Inderal)), and
digitalis glycosides.
Treatment of atrial fibrillation: Verapamil (Isoptin, Calan) & Diltiazem (Cardiazem)
Blocks cardiac calcium channels in slow response tissues, such as the sinus and AV nodes.
Useful in treating AV reentrant tachyarrhythmias and in management of high ventricular rates secondary to atrial flutter or fibrillation.
Major adverse effect (i.v. administration) is hypotension. Heart block or sinus bradycardia can also occur.
Treatment of atrial fibrillation: Propranolol (Inderal)
Antiarrhythmic effects are due mainly to beta-adrenergic receptor blockade.
Normally, sympathetic drive results in increased in Ca2+ ,K+ ,and Cl- currents.
Increased sympathetic tone also increases phase 4 depolarization (heart rate goes up), and increases DAD (delayed afterdepolarizations) and EAD (early afterdepolarization) mediated arrhythmias.
These effects are blocked by beta-adrenergic receptor blockers.
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockers increase AV conduction time (takes longer) and increase AV nodal refractoriness, thereby helping to terminate nodal reentrant arrhythmias.
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade can also help reduce ventricular following rates in atrial flutter and fibrillation, again by acting at the AV node.
Adverse effects of beta blocker therapy can lead to fatigue, bronchospasm, depression, impotence, and attenuation of hypoglycemic symptoms in diabetic patients and worsening of congestive heart failure.
Drugs assist in restoring and maintaining normal sinus rhythm include quinidine and procainamide
Quinidine {Quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan)}
Although classified as a sodium channel blocker, quinidine also blocks K+ channels.
Most antiarrhythmic agents have such multiple actions.
Sodium channel blockade results in
an increased threshold
decreased automaticity.
Potassium channel blockade results in action potential (AP) prolongation (width increases).
Quinidine gluconate-Clinical Use:
Maintains normal sinus rhythm in patients who have experienced atrial flutter or fibrillation.
Prevents ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation.
Quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan) administration results in vagal inhibition (anti-muscarinic) and alpha-adrenergic receptor blockade.
Adverse effects include cinchonism (headaches and tinnitus), diarrhea.
Quinidine is also associated with torsades de pointes, a ventricular arrhythmias associated with marked QT prolongation.
This potentially serious arrhythmia occurs in 2% - 8% if patients, even if they have a therapeutic or subtherapeutic quinidine blood level.
Procainamide (Procan SR, Pronestyl-SR)
Quinidine and Procainamide similar: electrophysiological properties.
By contrast to quinidine, procainamide does not exhibit either vagolytic or alpha-adrenergic blocking activity.
Useful in acute management of supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias.
Long term use is associated with side effects, including a drug-induced lupus syndrome which occurs at a frequency of 25% to 50%.
In slow acetylators the procainamide-induced lupus syndrome occurs more frequently and earlier in therapy than in rapid acetylators.
The red dot highlights the AV
node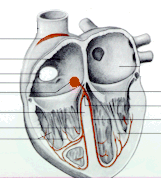
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachyarrthymias (PSVT) may be managed, depending upon clinical presentation, by increasing the vagal tone at the AV node
Valsalva maneuver
Alpha-adrenergic receptor agonist administration
digoxin administration
by administration of drugs that reduce AV transmission:
Adenosine (Adenocard), verapamil (Isoptin, Calan), diltiazem (Cardiazem), esmolol (Brevibloc) or DC cardioversion.
Adenosine (Adenocard)
Effects mediated through G protein-coupled adenosine receptor.
Activates acetylcholine-sensitive K+ current in the atrium and sinus and A-V node.
Decreases action potential duration, reduces automaticity
Increases A-V nodal refractoriness
Rapidly terminates re-entrant supraventricular arrhythmias (I.V)
Verapamil (Isoptin, Calan) & Diltiazem (Cardiazem)
Blocks cardiac calcium channels in slow response tissues, such as the sinus and AV nodes.
Useful in treating AV reentrant tachyarrhythmias and in management of high ventricular rates secondary to atrial flutter or fibrillation.
Major adverse effect (i.v. administration) is hypotension. Heart block or sinus bradycardia can also occur.
Esmolol (Brevibloc)
Esmolol is a very short acting, cardioselective beta-adrenergic receptor antagonist.
i.v. administration is used for rapid beta-receptor blockade in treatment of atrial fibrillation with high ventricular following rates.
Antiarrhythmic effects are due mainly to beta-adrenergic receptor blockade. Normally, sympathetic drive results in increased in Ca2+ ,K+and Cl- currents.
Increased sympathetic tone also increases phase 4 depolarization (heart rate goes up), and increases DAD (delayed afterdepolarizations) and EAD (early afterdepolarization) mediated arrhythmias. These effects are blocked by beta-adrenergic receptor blockers.
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockers
increase AV conduction time
increase AV nodal refractoriness, thereby helping to terminate nodal reentrant arrhythmias.
Three mechanisms have been associated with many tachyarrhythmias
Enhanced Automaticity
Enhance automaticity is associatied with an increase in the slope of phase 4 depolarization results in
As a result of the increase in phase 4 slope the cell reaches threshold more often per minute resulting in higher heart rate.
Factors that increase automaticity include
mechanical stretch
beta-adrenergic stimulation
hypokalemia
Ischemia can induce abnormal automaticity, i.e. automaticity that occurs in cells not typically exhibiting pacemaker activity.
Triggered Automaticity
Triggered automaticity occurs when a second depolarization occurs prematurely.
One type of triggered automaticity is a delayed afterdepolarization (DAD).
If this late depolarization reaches threshold (a) second beat(s) may occur.
Factors that predispose to delayed afterdepolarizations include:
excessive adrenergic activity
digitalis toxicity
high intracellular Ca2+
A second type of triggered automaticity is Early Afterdepolarization (EAD) which is associated with significant prolongation of the action potential duration.
In this case, during a prolonged phase 3 repolarization, the repolarization is interrupted by a second depolarization.
Factors that predispose to Early Afterdepolarizations include
bradycardia
low extracellular K+
certain drugs, including some antiarrhythmics
Torsades de pointes, a polymorphic ventricular arrhythmia- associated with
Prolongation of cardiac repolarization (prolonged Q-T interval)
Possibly induced by early afterdepolarizations.
The antiarrhythmic drug quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan) can cause this arrhythmia. Many other drugs can also cause this effect.
Reentry is the most common cardiac conduction abnormality leading to arrhythmias.
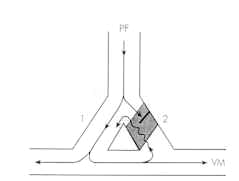
PF: Branched Purkinje Fiber terminating on ventricular muscle (VM).
Shaded Area: Depolarized region with unidirectional (one-way) block (Decremental conduction, impulse slowly dies out)
slowed conduction may be due to depression of Na + or Ca2+ currents (e.g. AV node)
Retrograde impulses (wavy line) propagate slow enough such that cells in branch 1 are no longer refractory and can be activated by the re-entry potential.
Drugs that terminate reentry may further depress conduction, converting the "unidirectional" block to a "bidirectional" block
A reentrant circuit involves a pathway that bifurcates into two branches.
One pathway is blocked to anterograde conduction, but can be excited in a retrograde manner by the impulse that traversed the unblocked path.
Retrograde conduction occurs until excitation of now non-refractory tissue re-initiates the process.
How do Antiarrhythmic Drugs Work?
Although for a given arrhythmia in a patient the mechanism may not be known, there are certain general explanations for the action of anti-arrhythmic agents. Anti-arrhythmic drugs may work by:
(a) Suppressing initiation site (automaticity/after-depolarizations) and/or
(b) Preventing early or delayed afterdepolarizations and/or
(c) By disrupting a re-entrant pathway.
(a) Automaticity: Automaticity may be diminished by:
(1) increasing the maximum diastolic membrane potential
(2) decreasing the slope of phase 4 depolarization
(3) increasing action potential duration
(4) raising the threshold potential
All of these factors make it take longer or make it more difficult for the membrane potential to reach threshold.
(1) The diastolic membrane potential may be increased by adenosine and acetylcholine.
(2) The slope of phase 4 depolarization may be decreased by beta receptor blockers
(3) The duration of the action potential may be prolonged by drugs that block cardiac K+ channels
(4) The membrane threshold potential may be altered by drugs that block Na+ or Ca2+ channels.
(b) Delayed or Early Afterdepolarizations:
Delayed or early afterdepolarizations may be blocked by factors that
(1) prevent the conditions that lead to afterdepolarizations.
(2) directly interfere with the inward currents (Na+, Ca2+) that cause afterdepolarizations.
(c) Reentry
For anatomically-determined re-entry such as Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) drugs the arrhythmia can be resolved by blocking action potential (AP) propagation. (In WPW syndrome, an accessory conduction pathway, linking atria and ventricles and bypassing the atrioventricular node, is the structure responsible for the arrhythmia)
In WPW-based arrhythmias, blocking conduction through the AV node may be clinically effective.
Drugs that prolong nodal refractoriness and slow conduction include: Ca2+ channel blockers, beta-adrenergic blockers, or digitalis glycosides.
For functional (non-anatomical) reentrant circuits, prolongation of refractoriness is the electrophysiological change most likely to terminate the reentry arrhythmia.
Prolongation of tissue refractoriness can be accomplished by those antiarrhythmic drugs that block Na+ channels.
Sodium channel blockers reduces the percentage of recovered channels (following inactivation by depolarization) at any given membrane potential.
Examples of antiarrhythmic drugs classified as sodium channel blockers include lidocaine, quinidine, and tocainide.
"Although any type of arrhythmia can occur in a patient with
WPW, the two most common are CMTs
(circus
movement tachycardias) and atrial fibrillation (AFib). CMT is the more common arrhythmia of the two
Treatment of CMTs associated with WPW is similar to treating PSVT
In a stable patient, adenosine (6 mg rapid IV push; if unsuccessful, 12 mg rapid IV push) should be the first-line treatment in any regular tachycardia, regardless of whether the complex is wide or narrow
Treatment of AFib associated with WPW is necessarily different than for a patient with a normal heart. AFib is an irregular rhythm as opposed to the regular rhythm seen in CMTs.
The basic treatment principle in WPW AFib is to prolong the anterograde refractory period of the accessory pathway relative to the AV node. This slows the rate of impulse transmission through the accessory pathway and, thus, the ventricular rate.
If AFib were treated in the conventional manner by drugs that prolong the refractory period of the AV node (eg, calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers, digoxin), the rate of transmission through the accessory pathway likely would increase, with a corresponding increase in ventricular rate. This could have disastrous consequences, possibly causing the arrhythmia to deteriorate into V fib.
Procainamide (17 mg/kg IV infusion, not to exceed 50 mg/min; hold for hypotension or 50% QRS widening) blocks the accessory pathway, but it has the added effect of increasing transmission through the AV node. Thus, although procainamide may control the AFib rate through the accessory pathway, it may create a potentially dangerous conventional AFib that may require treatment with other medications. Prompt cardioversion of patients with WPW and AFib is recommended.
Medical management may be a viable option in some patients, but it may have unpredictable results. Note that cardioversion is always the treatment of choice in unstable patients."----*From emedicine (http://www.emedicine.com/EMERG/topic644.htm) Authored by Mel Herbert, MD, MBBS, Assistant Professor of Medicine and Nursing, Department of Emergency Medicine, Olive View-University of California at Los Angeles Medical Center
Class I: Sodium Channel Blockers
Sodium channel blocking antiarrhythmic drugs are classified as use-dependent in that they bind to open sodium channels.
Their effectiveness is therefore dependent upon the frequency of channel opening.
There are three classes or types of sodium channel blockers:
Type Ia: prototype: quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan). Type Ia drugs slow the rate of AP rise and prolong ventricular effective refractory period.
Quinidine
Overview
dextroisomer of quinine; quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan) also has antimalarial and antipyretic effects
Pharmacokinetics:
80%-90%: bound to plasma albumin
Rapid oral absorption; rapid attainment of peak blood levels (60-90 minutes)
Elimination half-life: 5-12 hours
IM injection, possible but not recommended due to injection site discomfort
IV administration: limited due to myocardial depression & peripheral vasodilation
Metabolism:
Hepatic: hydroxylation to inactive metabolites; followed by renal excretion
20% excreted unchanged in urine
Impaired hepatic/renal function: accumulation of quinidine and metabolites
Sensitive to enzyme induction by other agents--
decreased quinidine blood levels with phenytoin, phenobarbital, rifampin
Mechanism of antiarrhythmic action-- primarily activated sodium channel blockade which results in:
Depression of ectopic pacemaker activity
Depression of conduction velocity
may convert a one-way conduction blockade to a two-way (bidirectional) block -- terminating reentry arrhythmias
Depression of excitability (particularly in partially depolarized tissue)
Recovery from sodium channel blockade is slower in depolarized tissue (compared to normal tissue):
This is the basis for relative selectivity of quinidine action in depolarized tissue compared to normal tissue, (i.e. lengthened refractory period, depressed conduction velocity, reduced excitability observed in depolarized tissue to greater extent the normal tissue)
Although classified as a sodium channel blocker, quinidine also blocks K+ channels.
Most antiarrhythmic agents have such multiple actions.
Effect on the ECG: QT interval lengthening
Basis: quinidine-mediated reduction in repolarizing outward potassium current
Result:
Longer action potential duration
Increased effective refractory period
Reduces reentry frequency; reduced rate in tachyarrhythmias
Sodium channel blockade results in
an increased threshold
decreased automaticity.
Used to manage nearly every form of arrhythmia especially acute and chronic supraventricular dysrhythmias
Ventricular tachycardia
Frequent indications:
Prevent recurrence of supraventricular tachyarrhythmias
Suppression ventricular premature contractions
Approximately 20% of patients with atrial fibrillation will convert to normal sinus rhythm following quinidine treatment
Supraventricular tachyarrhythmia due to Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome -- effective suppression by quinidine
Digitalization prior to quinidine administration:
Quinidine sulfate (Quinidex,Quinora)/quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan) may cause a paradoxical increase in ventricular response due to quinidine's vagolytic effect at the AV node (antimuscarinic action increases AV nodal throughput, allowing more SA nodal impulses to reach the ventricle)
Vagotonic effects on digitalis prevents this paradoxical increase by increasing vagal tone at AV node
Quinidine sulfate (Quinidex,Quinora) administration results in vagal inhibition (anti-muscarinic) and alpha-adrenergic receptor blockade.
Quinidine Side Effects
Cardiovascular--at (high) plasma concentrations (> 2ug/ml)
Prolongation (ECG) of PR interval, QRS complex, QT interval
Heart block likely with 50% increase in QRS complex duration (reduced dosage)
Quinidine syncope: may be caused by delayed intraventricular conduction, resulting in ventricular dysrhythmia
Patients with preexisting QT interval prolongation or evidence of existing A-V block (ECG): probably should not be treated with quinidine
Hypotension -- primarily following IV administration
Mechanism: peripheral vasodilation secondary to alpha-adrenergic receptor blockade
Increased hypotension risk associated with quinidine +verapamil treatment
Effects on heart rate:
increase secondary to either quinidine's antimuscarinic effect and/or reflex increase in sympathetic activity
Quinidine is associated with Torsades de pointes, a ventricular arrhythmias associated with marked QT prolongation.
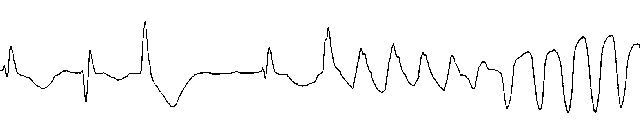
Torsades de pointes: Electrophysiological Features
ventricular origin
wide QRS complexes with multiple morphologies
changing R - R intervals
axis seems to twist about the isoelectric line
This potentially serious arrhythmia occurs in 2% - 8% if patients, even if they have a therapeutic or subtherapeutic quinidine blood level.
Other quinidine adverse effects include:
cinchonism
blurred vision, decreased hearing acuity, gastrointestinal upset,headaches and tinnitus.
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea (30% frequency)
Drug-drug interaction:quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan)-digoxin (Lanoxin, Lanoxicaps)
Quinidine increases digoxin plasma concentration; may cause digitalis toxicity in patients taking digoxin or digitoxin
Effects on neuromuscular transmission:
Quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan) interferes with normal neuromuscular transmission; enhancing the effect of neuromuscular-blocking drugs
Recurrence of skeletal muscle paralysis postoperatively may be associated with quinidine administration
Procainamide
Local anesthetic (procaine) analog
Long-term use avoided because of lupus-related side effect
Metabolism:
Elimination: renal excretion & hepatic metabolism; by contrast to procaine, procainamide is highly resistant to hydrolysis by plasma esterases.
40%-60% excreted unchanged (renal)
Renal dysfunction requires procainamide dosage reduction
Hepatic metabolism -- acetylation
cardioactive metabolite: N-acetylprocainamide (NAPA);
NAPA accumulation may lead to Torsades de pointes
Quinidine and Procainamide similar: electrophysiological properties.
Possibly somewhat less effective in suppressing automaticity; possibly more effective in sodium channel blockade in depolarized cells
Useful in acute management of supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias.
Drug of second choice for management of sustained ventricular arrhythmias (in the acute myocardial infarction setting)
Effective in suppression of premature ventricular contractions & paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia rapidly following IV administration
Most important difference compared quinidine: procainamide does not exhibit vagolytic (antimuscarinic) activity.
Procainamide is less likely to produce hypotension, unless following rapid IV infusion
Ganglionic-Blocking Activity
Side Effects/Toxicities
Long term use is associated with side effects, including a drug-induced, reversible lupus erythematosus-like syndrome which occurs at a frequency of 25% to 50%.
Consists of serositis, arthralgia & arthritis
Occasionally: pluritis, pericarditis, parenchymal pulmonary disease
Rare: renal lupus
Vasculitis not typically present (unlike systemic lupus erythematosus)
Positive antinuclear antibody test is common; symptoms disappear upon drug discontinuation
In slow acetylators the procainamide-induced lupus syndrome occurs more frequently and earlier in therapy than in rapid acetylators.
Nausea, Vomiting -- most common early, noncardiac complication
Hondeghem, L.M. and Roden, D.M., "Agents Used in Cardiac Arrhythmias", in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, Katzung, B.G., editor, Appleton & Lange, 1998, pp 216-241; Stoelting, R.K., "Cardiac Antidysrhythmic Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, 331-343
Disopyramide (Norpace)
Overview:
Very similar to quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan)
Greater antimuscarinic effects (in management of atrial flutter & fibrillation, pre-treatment with a drug that reduces AV conduction velocity is required)
Approved use (USA): ventricular arrhythmias
Metabolism:
Dealkylated metabolite (hepatic); less anticholinergic, less antiarrhythmic effect compared apparent compound
50% -- excreted unchanged, renal
Electrophysiological effects similar to quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan)
Similar to quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan) in effective ventricular and atrial tachyarrhythmia suppression
prescribed to maintain normal sinus rhythm in patients prone to atrial fibrillation and flutter and is also used to prevent ventricular fibrillation or tachycardia.
Side Effects/Toxicity
Adverse side-effect profile: different from qunidine's in that disopyramide (Norpace) is not an alpha-adrenergic receptor blocker but is anti-vagal.
Most common side effects: (anticholinergic)
dry mouth
urinary hesitancy
Other side effects: blurred vision, nausea
Cardiovascular:
QT interval prolongation (ECG)
paradoxical ventricular tachycardia (quinidine-like)
Negative inotropism (significant myocardial depressive effects)--undesirable with preexisting left ventricular dysfunction (may promote congestive heart failure, even in patients with no prior evidence of myocardial dysfunction)
Disopyramide is not a first-line antiarrhythmic agent because of its negative inotropic effects
If used, great caution must be exercised in patients with congestive heart failure
Can cause torsades de pointes, a ventricular arrhythmia
Hondeghem, L.M. and Roden, D.M., "Agents Used in Cardiac Arrhythmias", in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, Katzung, B.G., editor, Appleton & Lange, 1998, pp 216-241;Stoelting, R.K., "Cardiac Antidysrhythmic Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, 331-343
Type Ib:
Class Ib agents are often effective in treating ventricular arrhythmias. Example: lidocaine. Type Ib agents exhibit rapid association and dissociation from the channel.
Mexiletine (Mexitil) (Class IB, Sodium Channel Blocker)
Overview
Amine analog of lidocaine (Xylocaine), but with reduced first-pass metabolism.
Suitable for oral administration
Similar electrophysiologically to lidocaine
Clinical Use:
Chronic suppression of ventricular tachyarrhythmias
Combination with a beta adrenergic receptor blocker or another antiarrhythmic drug (e.g. quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan) or procainamide (Procan SR, Pronestyl-SR)): synergistic effects allow:
reduced mexiletine dosage
decreased side effect incidence
Possibly effective: decreasing neuropathic pain when alternative medications have proven ineffective-- applications (on-label use):
diabetic neuropathy
nerve injury
Side effects:
Epigastric burning: usually relieved by a taking drug with food
nausea (common)
Neurologic side effects:
diplopia, vertigo, slurred speech (occasionally), tremor
Lidocaine (Xylocaine) (Class Ib, Sodium Channel Blocker)
Overview/Pharmacokinetics:
Local anesthetic administered by i.v. for therapy of ventricular arrhythmias
Extensive first-pass effect requires IV administration
Half-life: two hours
Infusion rate: should be adjusted based on lidocaine plasma levels
Factors influencing loading and maintenance doses:
Congestive heart failure (decreasing volume of distribution and total body clearance)
Liver disease: plasma clearance -- reduced; volume of distribution -- increased; elimination half-life substantially increased (3 X or more)
Drugs that decrease liver blood flow (e.g. cimetadine, propranolol), decreased lidocaine clearance (increased possible toxicity)
Metabolism
Hepatic;some active metabolites
Cardiovascular Effects:
Site of Action: Sodium Channels
Blocks activated and inactivated sodium channels (quinidine blocks sodium channels only in the activated state)
During diastole, in normal tissue, as membrane potential returns to normal resting levels (-90 mV) lidocaine rapidly dissociates from the channel (low affinity for the channel resting state)
During diastole, in ischemic tissue, the membrane potential does not return to normal resting levels but remains partially depolarized and lidocaine remains bound (higher affinity, longer time constant for unblocking that at less negative resting potentials)
Therefore, lidocaine is more effective in suppressing activity in depolarized, arrhythmogenic cardiac tissue but has little effect on normal cardiac tissue -- the basis for this drug's selectivity.
Very effective antiarrhythmic agent for arrhythmia suppression associated with depolarization (e.g., digitalis toxicity or ischemia)
Comparatively ineffective in treating arrhythmias occurring in normally polarized issue (e.g., atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter)
No significant effect on QRS or QT interval or on AV conduction (normal doses)
Lidocaine (Xylocaine) decreases automaticity by reducing the phase 4 slope and by increasing threshold.
Clinical Uses:
Suppression of ventricular arrhythmias (limited effect on supraventricular tachyarrhythmias)
Suppression of reentry-type rhythm disorders:
premature ventricular contractions (PVCs)
ventricular tachycardia
May reduce incidence of ventricular fibrillation during the initial time frame following acute myocardial infarction; no evidence to support prophylactic use and myocardial infarction
Side Effect/Toxicities
Overdosage:
vasodilation
direct cardiac depression
decreased cardiac conduction -- bradycardia; prolonged PR interval; widening QRS on ECG
Major side effect -- neurological
Large doses, rapidly administered can result in seizure.
Factors that reduce seizure threshold for lidocaine:
hypoxemia, hyperkalemia, acidosis
Otherwise: CNS depression, apnea.
Tocainide (Class I, Sodium Channel Blocker)
Amine analog of lidocaine, similar to mexiletine, orally active --but with reduced first-pass metabolism.
Used for chronic suppression of ventricular tachyarrhythmias
Electrophysiologically similar to lidocaine
Similar to mexiletine: tocainide + if beta-adrenergic receptor blocker or another antiarrhythmic drug: synergism
e.g.--Combination with quinidine may increase efficacy and diminish adverse effects.
Side Effects:
Profile similar to mexiletine
suitable for oral administration, but RARELY USED due to possibly fatal bone marrow aplasia and pulmonary fibrosis.
tremor and nausea are major dose-related adverse side effects
Excreted by the kidney, accordingly dose should be reduced in patients with renal disease
Stoelting, R.K., "Cardiac Antidysrhythmic Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, 331-343
Phenytoin
Overview
Effective in suppression of ventricular arrhythmias associated with digitalis toxicity
Less effective than quinidine, procainamide, or lidocaine, in treatment of ventricular arrhythmias due to other etiologies
Pharmacokinetics:
Routes of administration: oral, or IV
Normal saline preferred -- phenytoin may precipitate in 5% dextrose in water
Slow IV injection into large peripheral or central vein preferable-- decreased chance of:
discomfort
thrombosis at injection site
Hepatic Metabolism --hydroxylation and conjugation (glucuronidation):
Elimination half-life: approximately 24 hours
Impaired hepatic function may cause excessive phenytoin blood levels
Mechanism of Action/Cardiac Effects:
Electrophysiological effects on automaticity and conduction velocity--somewhat like lidocaine
Shortens QT interval more than any other antiarrhythmic agent
No significant effect on ST-T waves or QRS complex
No significant myocardial depression
Improvement in AV Node Conduction;
Depression of SA Nodal Activity
Drug-Drug Interaction:
Significant SA nodal depression may occur when combining those volatile anesthetics that depress SA nodal activity and phenytoin
Drugs that lower phenytoin levels:
barbiturates (mechanism:metabolizing enzyme induction)
Drugs that increase phenytoin level (inhibit metabolism):
warfarin, phenylbutazone, isoniazid
Side effect/Toxicities:
Primary Toxicity: CNS disturbance (particularly cerebellar-- dose correlated > 18 ug/ml-- exceeding this concentration is unlikely to improve cardiac rhythm)
CNS symptoms:
ataxia, vertigo, slurred speech, sedation, nystagmus, confusion
Partial inhibition of insulin secretion: enhances blood glucose levels in hyperglycemic patients
Stoelting, R.K., "Cardiac Antidysrhythmic Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, 331-343
Type Ic: Type Ic drugs slowly dissociate from resting sodium channels
Flecainide (Tambocor)--( Na+ and K+ Channel Blocker)
Overview:
Fluorinated local anesthetic analog of procainamide (Procan SR, Pronestyl-SR)
More effective than quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan) or disopyramide (Norpace) in:
suppressing ventricular tachycardia
suppressing ventricular premature contractions
Pharmacokinetics:
oral absorption: excellent
long elimination half-time (approximately 20 hours)
25% flecainide: excreted unchanged (kidneys)
Hepatic metabolism: weakly active metabolites
Factors reducing flecainide elimination:
congestive heart failure
renal failure
Cardiac Effects/Clinical Use:
Suppression ventricular tachycardia & ventricular premature contractions
Effective in management of atrial tachyarrhythmias
Effective in tachyarrhythmias associated with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (suppression of conduction bypass tracts)
Chronic flecainide (Tambocor) treatment following myocardial infarction not recommended:
increased incidence of sudden death in treated patients
In CAST, flecainide increased mortality in patients recovering from myocardial infarction.
Flecainide: should be reserved for management of life-threatening arrhythmias
Slight/moderate negative inotropic property
Proarrhythmic effects in patients with preexisting left ventricular function deficiency
Electrophysiology:
Prolongation of PR interval (ECG)
Prolongation of QRS complex (> 25%)
Sinoatrial nodal depression (similar to beta-adrenergic blockers and calcium channel blockers)
Side-Effects/Toxicities
Most common:vertigo and difficulty in visual accommodation
Most serious of adverse effects is induction of potentially lethal arrhythmias such as reentrant ventricular tachyarrhythmias.
Stoelting, R.K., "Cardiac Antidysrhythmic Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, 331-343
Amiodarone (Cordarone) (Class I and III Channel Blocker)
Overview:
A benzofurane derivative, 37% iodine by weight, structurally similar to thyroxine
may cause hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism (frequency: 2%-4%)
Insidious development
Patients with previous thyroid dysfunction: more likely to develop amiodarone-mediated thyroid effects
Hyperthyroidism: most readily evidenced by increased plasma level of triiodothyronine
Secondary to iodine release from parent drugs;
Often refractory to conventional treatment
intolerant of beta-adrenergic receptor blockade (because of underlying cardiac disease)
Following failed medical management: surgical thyroidectomy is appropriate
bilateral superficial cervical plexus block has been used for anesthetic management of subtotal thyroidectomy in this patient group
Hypothyroidism: most readily evidenced by increased plasma level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
may interfere with certain radiologic procedures (Iodine accumulation)
Approved for use only in treatment of serious ventricular arrhythmias (USA)
also used for refractory supraventricular arrhythmias
Numerous adverse effects.
Metabolism & Excretion
Long elimination halftime: 29 days
Minimal renal excretion
Principal metabolite (desmethylamiodarone) -- longer elimination halftime compared to amiodarone
Extensive protein binding
Amiodarone concentrated in the myocardium (10-50 times plasma concentration)
Cardiovascular Properties and Uses:
Used in patients with ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation resistant to treatment with other drugs.
Effective inhibitor of abnormal automaticity.
Oral administration, preoperatively, reduces likelihood of atrial fibrillation following cardiac surgery.
Suppresses tachyarrhythmias associate with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
secondary to depression of conduction in the AV node and accessory bypass tracts.
Similar to beta-blockers (unlike most class I antiarrhythmics), amiodarone decreases mortality after myocardial infarction
Antiarrhythmic effectiveness begins within 72 hours following initiation of oral treatment; nearly immediate effect following IV administration
Following discontinuation of chronic oral therapy: pharmacological effects may last up to two months (long elimination half-time)
Mechanism of Action
Blocks sodium and potassium channels and prolongs action potential duration.
Prolongs effective refractory period in:
SA node
AV node
ventricle
atrium
His-Purkinje system
accessory bypass tracts (Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome)
Vascular Effects
Noncompetitive alpha and beta adrenergic receptor blocker
Systemic vasodilation
Antianginal properties, secondary to coronary vasodilation
Side Effects
Pulmonary:
Most serious adverse effect seen in long-term therapy is a rapidly progressive pulmonary fibrosis which may be fatal
Frequency: 5%-15% treated patients
Mortality rate: 5% to 10%
Cause: unknown (possibly related to amiodarone-mediated generation of free oxygen radicals in the lung)
Two types of amiodarone-pulmonary toxicity clinical presentations:
More common: Slow, insidious, progressive dyspnea, cough, weight loss, pulmonary infiltration (chest x-ray)
Acute onset: dyspnea, cough, arterial hypoxemia.
Anesthetic Implications: pulmonary
Suggested restriction of inspired oxygen concentration in patients receiving amiodarone and undergoing general anesthesia close level possible while retaining adequate systemic oxygenation
Postoperative pulmonary edema has been reported in patients treated with amiodarone chronically-- resembles acute onset form of amiodarone toxicity.
In patients with preexisting amiodarone-cause pulmonary damage are at increased risk for adult respiratory distress syndrome following surgery requiring cardiopulmonary bypass.
Cardiovascular Effects:
Prolongation of QT interval (ECG); increased incidence of ventricular tachyarrhythmias (including torsades de pointes)
Bradycardia (atropine-resistant)
Catecholamine responsiveness: diminished due to alpha and beta-receptor blocking activity
Hypotension; A-V block (following IV administration)
Anesthetic Implications: cardiovascular
With general anesthesia -- enhanced antiadrenergic action, presentation as:
A-V block, sinus arrest, decrease cardiac output, hypotension
Sinus arrest more likely in the presence of anesthetics that inhibit SA nodal automaticity (e.g. lidocaine, halothane)
Consideration should be given for temporary ventricular pacemaker and sympathomimetic administration (e.g. isoproterenol) for patients taking amiodarone and scheduled undergo surgery.
Ocular and other Side Effects:
Corneal microdeposits-- common;usually no visual impairment
Photosensitivity, rash: 10% frequency
Rare: cyanotic discoloration (slate-gray facial pigmentation)
Neurological:
peripheral neuropathy; sleep disturbance, headache, tremor, some skeletal muscle weakness
Drug-drug interaction
Potent inhibitor of hepatic metabolism or renal elimination of many drugs.
Warfarin, quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan), procainamide (Procan SR, Pronestyl-SR) and digoxin (Lanoxin, Lanoxicaps) are examples of drugs which may require dosage reduction during amiodarone (Cordarone).
Amiodarone (Cordarone) displaces digoxin (Lanoxin, Lanoxicaps) from protein binding sites
Digoxin (Lanoxin, Lanoxicaps) levels may increase as much as 70%
Digoxin (Lanoxin, Lanoxicaps) dose should be decreased as much as 50% when amiodarone is administered concurrently
Hondeghem, L.M. and Roden, D.M., "Agents Used in Cardiac Arrhythmias", in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, Katzung, B.G., editor, Appleton & Lange, 1998, pp 216-241; Stoelting, R.K., "Cardiac Antidysrhythmic Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, 331-343
Decrease the slope of phase IV depolarization slowing the heart
Depressing automaticity.
Conduction time through AV node is increased while contractility is diminished.
Class II Antiarrhythmic drugs
Propranolol (Inderal)
Metoprolol (Lopressor) (beta-1 "specific")
Pindolol (Visken) (partial agonist)
Esmolol (Brevibloc)(very short acting)
Propranolol
Antiarrhythmic effects are due mainly to beta-adrenergic receptor blockade. Normally, sympathetic drive results in increased in Ca2+ ,K+ ,and Cl- currents.
Increased sympathetic tone also increases phase 4 depolarization (heart rate goes up), and increases DAD (delayed afterdepolarizations) and EAD (early afterdepolarization) mediated arrhythmias. These effects are blocked by beta-adrenergic receptor blockers.
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockers increase AV conduction time and increase AV nodal refractoriness, thereby helping to terminate nodal reentrant arrhythmias.
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade can also help reduce ventricular following rates in atrial flutter and fibrillation, again by acting at the AV node.
Adverse effects of beta blocker therapy can lead to fatigue, bronchospasm, depression, impotence, and attenuation of hypoglycemic symptoms in diabetic patients and worsening of congestive heart failure.
Hondeghem, L.M. and Roden, D.M., "Agents Used in Cardiac Arrhythmias", in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, Katzung, B.G., editor, Appleton & Lange, 1998, pp 216-241
Esmolol (Brevibloc)
Esmolol (Brevibloc) is a very short acting, cardioselective beta-adrenergic receptor antagonist.
i.v. administration is used for rapid beta-receptor blockade in treatment of atrial fibrillation with high ventricular following rates.
Antiarrhythmic effects are due mainly to beta-adrenergic receptor blockade. Normally, sympathetic drive results in increased in Ca2+ ,K+and Cl- currents.
Increased sympathetic tone also increases phase 4 depolarization (heart rate goes up), and increases DAD (delayed afterdepolarizations) and EAD (early afterdepolarization) mediated arrhythmias. These effects are blocked by beta-adrenergic receptor blockers.
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockers
increase AV conduction time
increase AV nodal refractoriness, thereby helping to terminate nodal reentrant arrhythmias.
Hondeghem, L.M. and Roden, D.M., "Agents Used in Cardiac Arrhythmias", in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, Katzung, B.G., editor, Appleton & Lange, 1998, pp 216-241; Stoelting, R.K., "Cardiac Antidysrhythmic Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, 331-343
Class III: Potassium Channel Blockers
Blockade of potassium channels delay repolarization and prolong the action potential. As a result, the effective refractory period is increased.
Bretylium (Bretylol)
Overview:
Initially released as an antihypertensive agent.
Orthostatic hypotension may occur following chronic use
Inhibits neuronal catecholamine release, following an initial direct early release of norepinephrine from adrenergic nerve terminals (transient hypertension)
Direct antiarrhythmic properties
Pharmacokinetics:
IV or IM Route of Administration
Following rapid IV administration: nausea & hypotension
After the first doses: bretylium-mediated norepinephrine release causes:
transient hypertension
increased ventricular irritability (particularly in patients also receiving digitalis)
Renal elimination: 8-12 hour halftime
Dosage reduction required in patients with renal dysfunction
Hepatic metabolism: not demonstrated
Cardiac Actions:
Antiarrhythmic effect due to prolongation of the cardiac action potential and inhibition of norepinephrine reuptake by sympthetic nerves
Increased ventricular (not atrial) action potential duration and effective refractory period
Somewhat selective for ischemic cells which have shortened action potential durations
Bretylium may reverse shortening of action potential duration due to ischemia
Possesses anti-fibrillatory activity; independent of sympatholytic action
Initial catecholamine release (prior to inhibition of release), results in some positive inotropic effect; however, this action may induce ventricular arrhythmias (catecholamines generally are pro-arrhythmogenic).
Inhibition of catecholamine release may result in bradycardia.
Clinical Use:
Management of serious ventricular arrhythmias refractory to lidocaine or procainamide
Possible initial drug for treatment of ventricular fibrillation--Rationale:
Increases ventricular fibrillation threshold;
Prolongs action potential duration;
Prolongs effective refractory period
Amiodarone (Cordarone)
Overview:
A benzofurane derivative, 37% iodine by weight, structurally similar to thyroxine
May cause hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism (frequency: 2%-4%)
Insidious development
Patients with previous thyroid dysfunction: more likely to develop amiodarone-mediated thyroid effects
Hyperthyroidism: most readily evidenced by increased plasma level of triiodothyronine
Secondary to iodine release from parent drugs;
Often refractory to conventional treatment
intolerant of beta-adrenergic receptor blockade (because of underlying cardiac disease)
Following failed medical management: surgical thyroidectomy is appropriate
bilateral superficial cervical plexus block has been used for anesthetic management of subtotal thyroidectomy in this patient group
Hypothyroidism: most readily evidenced by increased plasma level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
May interfere with certain radiologic procedures (Iodine accumulation)
Approved for use only in treatment of serious ventricular arrhythmias (USA)
Also used for refractory supraventricular arrhythmias
Numerous adverse effects.
Metabolism & Excretion
Long elimination halftime: 29 days
Minimal renal excretion
Principal metabolite (desmethylamiodarone) -- longer elimination halftime compared to amiodarone
Extensive protein binding
Amiodarone concentrated in the myocardium (10-50 times plasma concentration)
Cardiovascular Properties and Uses:
Used in patients with ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation resistant to treatment with other drugs.
Effective inhibitor of abnormal automaticity.
Oral administration, preoperatively, reduces likelihood of atrial fibrillation following cardiac surgery.
Suppresses tachyarrhythmias associate with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
secondary to depression of conduction in the AV node and accessory bypass tracts.
Similar to beta-blockers (unlike most class I antiarrhythmics), amiodarone decreases mortality after myocardial infarction
Antiarrhythmic effectiveness begins within 72 hours following initiation of oral treatment; nearly immediate effect following IV administration
Following discontinuation of chronic oral therapy: pharmacological effects may last up to two months (long elimination half-time)
Mechanism of Action
Blocks sodium and potassium channels and prolongs action potential duration.
Prolongs effective refractory period in
SA node
AV node
ventricles
atrium
His-Purkinje system
accessory bypass tracts (Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome)
Vascular Effects
Noncompetitive alpha and beta adrenergic receptor blocker
Systemic vasodilation
Antianginal properties, secondary to coronary vasodilation
Side Effects
Pulmonary:
Most serious adverse effect seen in long-term therapy is a rapidly progressive pulmonary fibrosis which may be fatal
Frequency: 5%-15% treated patients
Mortality rate: 5% to 10%
Cause: unknown (possibly related to amiodarone-mediated generation of free oxygen radicals in the lung)
Two types of amiodarone-pulmonary toxicity clinical presentations:
More common: Slow, insidious, progressive dyspnea, cough, weight loss, pulmonary infiltration (chest x-ray)
Acute onset: dyspnea, cough, arterial hypoxemia.
Anesthetic Implications: pulmonary
Suggested restriction of inspired oxygen concentration in patients receiving amiodarone (Cordarone) and undergoing general anesthesia to as low a level as while retaining adequate systemic oxygenation
Postoperative pulmonary edema has been reported in patients treated with amiodarone (Cordarone) chronically-- resembles acute onset form of amiodarone toxicity.
In patients with preexisting amiodarone-caused pulmonary damage are at increased risk for adult respiratory distress syndrome following surgery requiring cardiopulmonary bypass.
Cardiovascular:
Prolongation of QT interval (ECG); increased incidence of ventricular tachyarrhythmias (including torsades de pointes)
Bradycardia (atropine-resistant)
Catecholamine responsiveness: diminished due to alpha and beta-receptor blocking activity
Hypotension; A-V block (following IV administration)
Anesthetic Implications: cardiovascular
With general anesthesia -- enhanced antiadrenergic action, presentation as:
A-V block, sinus arrest, decrease cardiac output, hypotension
Sinus arrest more likely in the presence of anesthetics that inhibit SA nodal automaticity (e.g. lidocaine, halothane)
Consideration should be given for temporary ventricular pacemaker and sympathomimetic administration (e.g. isoproterenol) for patients taking amiodarone and scheduled undergo surgery.
Ocular and other Side Effects & Drug-drug interaction: As above
Hondeghem, L.M. and Roden, D.M., "Agents Used in Cardiac Arrhythmias", in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, Katzung, B.G., editor, Appleton & Lange, 1998, pp 216-241; Stoelting, R.K., "Cardiac Antidysrhythmic Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, 331-343
Class IV: Calcium Channel Blockers
These drugs block the inward calcium current and therefore slow conduction through the AV node and decrease the slow of phase 4 depolarization.
Calcium channel blockers are especially active at vascular smooth muscle and at the heart.
Verapamil (Isoptin, Calan) (main action on the heart)
Nifedipine (Procardia, Adalat) (main action on vascular smooth muscle (anti-hypertensive effect))
Diltiazem (Cardiazem) (action on both the heart and vascular smooth muscle)
Adenosine (Adenocard)
Effects mediated through G protein-coupled adenosine receptor.
Activates acetylcholine-sensitive K+ current in the atrium and sinus and A-V node.
Decreases action potential duration, reduces automaticity
Increases A-V nodal refractoriness
Rapidly terminates re-entrant supraventricular arrhythmias (I.V)