|
|
Anesthesia Pharmacology Chapter 18: Neuromuscular Blocking Drugs
Spasmolytic agents
Increased in tonic stretch reflexes
Increased flexor muscle spasm
Muscle weakness
Clinical conditions associated with spasticity: Cerebral palsy, Multiple sclerosis, Stroke
Clinical spasticity -- mechanisms:
Reflex arc involvement
Higher center involvement ("upper motor neuron disease") affects descending pathways leading to alpha motoneurons hyperexcitability
Mechanisms of drug action (diminishing spasticity)
Alteration in stretch reflex arc
Attenuation of excitation-contraction coupling
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enhances CNS GABA inhibitory activity; active at most (all) GABAA synapses.
Anti-spasmolytic effect in part due to action in the spinal cord (effective in patients with cord transection)
Tends to be sedating
Mechanism: GABA agonist at GABAB receptors
Receptor activation causes increased K+ conductance (hyperpolarization) in the brain and spinal cord
Spinal cord effects probably occur following increased presynaptic inhibition which reduces transmitter released by reducing calcium influx.
Similar anti-spasticity compared to diazepam (Valium) but with less sedation
Pharmacokinetics:
Orally active;well absorbed
half-life: 3-4 hours
Adverse Effects:
drowsiness; increased seizure activity in patients with epilepsy
Intrathecal Baclofen (Lioresal) use:
Management of severe spasticity/pain when nonresponsive to medication by other routes of administration.
Few peripheral symptoms; higher concentrations may be used
Partial tolerance may develop
Major disadvantage: maintaining the integrity of the delivery catheter.
Advantage: significant improvement of quality of life in some patients
Overview
Tizanidine (Zanaflex) is related to clonidine (Catapres)
Enhances both pre-and postsynaptic inhibition in the spinal cord
Also inhibits nociceptive transmission (dorsal horn)
Clinical Use
Probably a significant benefit for patients with spasticity (several types)
Comparable efficacy compared to: diazepam (Valium), baclofen (Lioresal), and dantrolene (Dantrium)
Dosage must be carefully titrated for each patient
. Adverse Effects:
drowsiness, dry mouth, asthenia, hypotension
Overview
Unique mechanism -- acts outside the CNS
Interferes with muscle fiber excitation-contraction coupling
Mechanism of action
Blockade of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium channel (ryanodine channel)
Reduced calcium concentration diminishes actin-myosin interaction
Motor units contracting more rapidly are more sensitive to dantrolene (Dantrium)
Cardiac muscle and smooth muscle are only slightly affected (different calcium release mechanism)
Pharmacokinetics
bioavailability: about 33% of oral dose absorbed
Adverse Effects:
Muscle weakness
Sedation
Hepatitis (occasional)
Malignant hyperthermia, is associated with hereditary abnormality in sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium sequestration affecting probably, in some cases affecting the ryanodine receptor (calcium channel in the SR) is triggered by:
General anesthesia
Neuromuscular blocking drugs
Clinical Presentations:
Significant muscle contractions
Sudden and prolonged calcium release
Increased lactic acid production
Increased body temperature
Dantrolene (Dantrium) reduces calcium release
Other interventions are required to reduce body temperature and manage acidosis

"The open and closed states of the Ca2+-release channel are shown side by side in three different views: top, side and bottom. Important details are marked: the clamp-shaped domain (C), the handle (H) which connects the clamp shaped domain to the central part of the cytoplasmic side (CY) of the tetramer. The putative transmembrane (TM) part of the assembly resembles the stem of the mushroom-shaped protein. In the open-state reconstruction the transmembrane region of the channel appears open towards the SR, whereas in the closed state a central opening is not seen in this region. As is clearly visible in these images, the clamp-shaped domains (C) are open in the open-state reconstruction whereas the fingers of the clamps touch in the closed state reconstruction." From Orlova, E. et al. Nature Structural Biology v3(6) 547-52. 1996.
Sedatives acting at the brain stem or spinal cord level include:
Carisoprodol (Soma, Rela)
Chlorphenesin (Maolate)
Chlorzoxazone (Paraflex,generic)
Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril)-- not useful for muscle spasms secondary to spinal cord injury or cerebral palsy; strong antimuscarinic and sedative effects
Metaxalone (Skelaxin)
Methocarbamol (Robaxin)
Orphenadrine (Norflex)
Katzung, B.G.., Skeletal Muscle Relaxants, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, pp 434-449;White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996
NMJ blockers: Structural similarity to acetylcholine
Succinylcholine (Anectine) (depolarizing blocker, SCh) -- two linked acetylcholine molecules
Nondepolarizing agents also contain a "double-acetylcholine" form; however this form is hidden by ring systems-- e.g. pancuronium (Pavulon)
Contains 1-2 quaternary nitrogens which result in limited lipid-solubility (limited CNS penetration)
Major classes of nondepolarizing blocking drugs:
|
|
Isoquinoline derivatives
Tubocurarine
Atracurium (Tracrium)
Doxacurium (Nuromax)
Mivacurium (Mivacron)
Steroid derivatives -- e.g.
Pancuronium (Pavulon)
Vecuronium (Norcuron)
Pipecuronium (Arduan)
Rocuronium (Zemuron)
|
NMJ blockers: Isoquinoline derivatives, Atracurium (Tracrium) |
NMJ blockers: Isoquinoline derivatives, Mivacurium (Mivacron) |
|
NMJ blockers: Steroid derivatives, Pancuronium (Pavulon) |
NMJ blockers: Depolarizing blocker Succinylcholine (Anectine) |
Pharmacokinetics: Neuromuscular Blocking Drugs
Nondepolarizing agents --Elimination characteristics
Fast initial distribution; slower elimination
Limited volume of distribution (expected for highly ionized agents -- tending not to cross readily biological membranes)
Route of elimination-- important determinant of duration of action
Renal elimination:
Long half lives; long durations of action (> 35 min)
Hepatic elimination:
Shorter half lives: (< 30 min)
|
Drug |
Elimination mechanism |
Duration of action (minutes) |
|
Pancuronium (Pavulon) |
renal (80%) |
> 35 |
|
Pipecuronium (Arduan) |
renal (60%) and hepatic |
> 35 |
|
Rocuronium (Zemuron) |
hepatic (75-90%) and renal |
20-35 |
|
Cecuronium (Norcuron) |
hepatic (75-90%) and renal |
20-35 |
|
Drug |
Elimination mechanism |
Duration of action (minutes) |
|
gallamine (Flaxedil) |
renal (100%) |
> 35 |
|
succinylcholine (Anectine) |
plasma pseudocholinesterase |
< 8 |
*-- adapted from Table 27-1: Miller, R.D., Skeletal Muscle Relaxants, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, p. 438
Introductory comments about specific Nondepolarizing agents
Overview: Intermediate-duration agents (e.g. vecuronium (Norcuron) and rocuronium (Zemuron)) --mainly dependent on hepatic metabolism and biliary excretion for elimination:
Intermediate-duration drugs are most commonly used clinically (compared to longer acting renal-excreted drugs)
Vecuronium (Norcuron) vs. pancuronium (Pavulon):
Similar steroid nucleus -- one contains a tertiary rather than quaternary nitrogen
Vecuronium (Norcuron) -- shorter duration of action; minimal cardiovascular effects; 85% hepatic metabolism/elimination
|
NMJ blockers: Steroid derivatives, Vecuronium (Norcuron) |
NMJ blockers: Steroid derivatives, Pancuronium (Pavulon) |
Rocuronium (Zemuron)
Most rapid onset among nondepolarizing blockers
A drug of choice for rapid-sequence anesthesia induction and intubation (when succinylcholine is contraindicated or clinical circumstances suggest that it not be used)
Atracurium (Tracrium) (isoquinoline derivative) -- similar characteristics as vecuronium (Norcuron)
Hoffman elimination inactivation (spontaneous breakdown)
Atracurium (Tracrium) breakdown product --laudanosine may accumulate due to very slow hepatic metabolism and upon crossing into the brain may cause seizures
Seizures occur at laudanosine concentrations above that obtained during surgical procedures; however long-term use of atracurium (Tracrium) within the intensive care setting may result in concentration sufficient to induce seizures
Cisatracurium (Nimbex) (atracurium (Tracrium) stereoisomer)
Similar to atracurium (Tracrium), but less laudanosine formed and less histamine released
Mivacurium (Mivacron): shortest duration of action among nondepolarizing agents
Rapid clearance of isomer mixture by plasma cholinesterase (pseudocholinesterase, i.e. butrylcholinesterase) activity
Prolonged duration of mivacurium (Mivacron) action in patients with renal failure (renal failure is associated with reduced plasma cholinesterase activity)
Depolarizing Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
Overview -- succinylcholine (Anectine)
Very brief duration of action (5-10 minutes)
Brief duration of action due to: rapid hydrolysis by plasma cholinesterase (butrylcholinesterase/pseudocholinesterase)
Extended duration of action would occur with reduced plasma cholinesterase activity.
Initial metabolite of succinylcholine (Anectine): succinylmonocholine (very weak neuromuscular blocking effect)
Termination of pharmacological effect--diffusion away from postsynaptic receptors (note the absence of pseudocholinesterase at post-junctional sites
Genetic variation: effects on duration of action of succinylcholine (Anectine) blockade
Abnormal plasma cholinesterase may prolong succinylcholine (Anectine) effects
"Dibucaine (Nupercainal, generic)-number" test identifies patients with abnormal plasma cholinesterase (dibucaine (Nupercainal, generic) inhibits the "normal" enzyme by 80% and the abnormal enzyme by only 20%)
dibucaine (Nupercainal, generic)-variants are the most common plasma cholinesterase genetic variants.
Pharmacodynamics
Neuromuscular blocking drug pharmacodynamic characteristics determined by measuring:
Speed of onset
Duration of neuromuscular blockade
Clinical method of determining neuromuscular-blockade properties --
Determine skeletal muscle response evoked by supramaximal electrical stimulation using a peripheral nerve stimulator
Typically: single twitch response to 1Hz (adductor pollicis muscle -- ulnar nerve stimulation)
Potency determination comparing neuromuscular-blocking drugs:
Dose required to suppress 95% of the single twitch response (ED95)
Potency determined in the presence of nitrous oxide-barbiturate-opioid anesthesia
Volatile anesthetics will significantly decreased ED95.
Neuromuscular blocking drugs: sequence of muscles affected
Small, rapidly moving muscles (fingers, eyes) before diaphragm
Recovery in reverse order
IV neuromuscular blocker injection (nondepolarizing) to an awake patient:
Initial difficulty in focusing and weakness in mandibular muscles
then ptosis, diplopia and dysphagia
Consciousness and sensorium: unaffected, even with complete neuromuscular block
Blockade onset:
More rapid, less intense effect at laryngeal muscles (vocal cords) then at adductor pollicis (peripheral muscle example)
More rapid laryngeal muscle onset is probably due to a more rapid drug plasma: drug muscle equilibration
Reduced initial intensity of effect at laryngeal muscle (fast fibers) follows from the requirement for more complete receptor blockade for effect then for muscles mainly composed of slow fibers, e.g. adductor pollicis.
Neuromuscular diaphragm blockade:
Requires 2 times the dose required for adductor pollicis muscle blockade
Adductor pollicis monitoring: poor indicator of cricothyroid muscle (laryngeal) relaxation
Facial nerve stimulation with orbicularis oculi muscle response monitoring is a better reflection of neuromuscular diaphragm blockade onset
Orbicularis oculi muscle monitoring is preferable to monitoring adductor pollicis as indicator of laryngeal muscle blockade
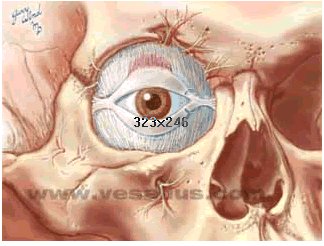
"The orbicularis oculi is the thin sphincter
muscle of the eyelids. It is
innervated by temporal and zygomatic branches of the facial nerve.",
Image courtesy of Vesalius, used with permission
Adductor Pollicis
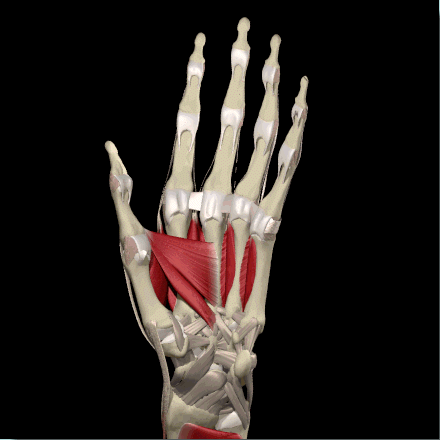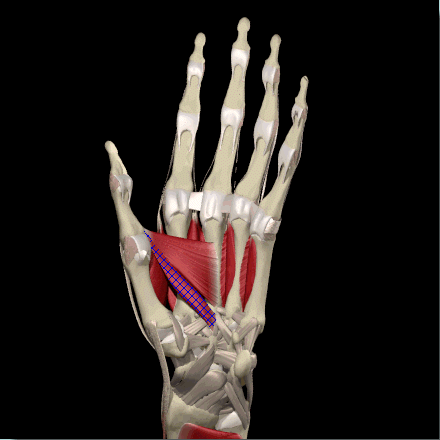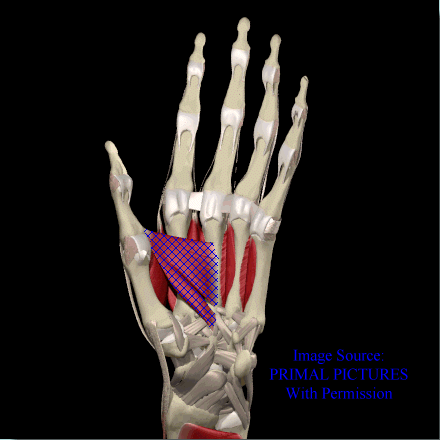
Image courtesy of EatonHand (http://www.eatonhand.com/mus/mus005.htm)
Cricothyroid Muscle
Cricothyroid Muscle: Vesalius Site, used with permission
Primary uses of neuromuscular-blocking drugs:
Skeletal muscle relaxation facilitating tracheal intubation
Skeletal muscle relaxation to improve intraoperative surgical conditions
Dose guidelines:
Facilitation of tracheal intubation -- 2 x ED95 dose of nondepolarizing muscle relaxant
Laryngospasm: effectively treated with succinylcholine (Anectine)
Optimal intraoperative conditions -- 95% single twitch response suppression
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs: -- no CNS depression; no analgesia therefore they do not substitute for anesthetic agents
Other clinical uses:
In managing patients requiring mechanical ventilation (intensive care environment)
Adult respiratory distress syndrome
Tetanus
Suppression of spontaneous respiration
Miller, R.D., Skeletal Muscle Relaxants, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, pp 434-449. Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219. White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.
Rationale for Monitoring Neuromuscular Blockade:
NMJ blocking drugs are dangerous in that they interfere with respiration.
Depression of ventilation is a significant cause of anesthesia-related morbidity/mortality--an important factor is the extent of residual neuromuscular blockade.
Narrow drug safety margin (corresponds to a narrow range of receptor occupancy)
Significant patient-to-patient response variabilty to the same dosage
Interactions between NMJ blocking drugs with other agents
Depolarization Neuromuscular Blockade
Succinylcholine (Anectine)
Time course:
rapid onset (30-60 seconds) -- IV
short duration of action: 3-5 minutes
Applications
Skeletal muscle relaxation, facilitating intubation
Mechanism of Action:
Succinylcholine (Anectine) binds to nicotinic cholinergic receptors
Promotes post synaptic membrane depolarization causing a relatively long-term depolarization (compared acetylcholine) due to reduced synaptic breakdown.
Blockade occurs because depolarized membrane is unresponsive to subsequent acetylcholine-receptor interaction
Depolarization component is the phase I blockade
Prolonged phase I blockade may be associated with potassium transport (from inside cell out): which may increase serum potassium by 0.5 mEq/L.
Properties of phase I blockade:
Reduced amplitude; sustained response to continuous electrical stimulation
Reduced contractile-response to single twitch stimulus
Enhanced neuromuscular-blockade following anticholinesterase drug administration
Train-of-four (TOF) ratio of > 0.7 (the height of the 4th twitch to that of the 1st twitch); a measure of presynaptic membrane effects. When the single twitch height has recovered to about 100%, the train-of-four ratio is about 70%.
No post-tetanic facilitation
Skeletal muscle fasciculations are associated with initial (onset) succinylcholine (Anectine) action.
Continued succinylcholine (Anectine) administration results in a transition from endplate depolarization to endplate repolarization.
However, this repolarization state is not susceptible to acetylcholine depolarization provided succinylcholine (Anectine) remains present
Blockade, even following repolarization, has led to the description of phase II block as "a desensitization blockade".
Transition from a phase I to a phase II blockade may be rapid (following a succinylcholine (Anectine) dose of 2-4 mg/kg IV)
Phase II onset: initial manifestation -- tachyphylaxis with need to increase succinylcholine (Anectine) infusion rate or to administer larger doses
Various degrees of phase I and phase II blockade may coexist
Mainly phase I: -- anticholinesterases enhance neuromuscular-blockade
Mainly phase II: --anticholinesterases antagonize phase II blockade
Small doses of edrophonium (Tensilon) (0.1-0.2 mg/kg, IV) may be useful in discriminating phase I vs. phase II block
Time course/Duration of Action -- Succinylcholine (Anectine)
Duration of action determined by plasma cholinesterase-mediated succinylcholine (Anectine) hydrolysis
Plasma cholinesterase: hepatic enzyme
Initial succinylcholine (Anectine) metabolite: succinylmonocholine (very weak neuromuscular-blocking)
Plasma cholinesterase activity determines the amount of succinylcholine (Anectine) reaching the endplate (most succinylcholine (Anectine) is hydrolyzed by plasma enzyme)
Factors influencing plasma cholinesterase (pseudocholinesterase) activity
Reduced hepatic enzyme synthesis
The presence of atypical (genetic) plasma cholinesterase which exhibits reduced succinylcholine (Anectine) hydrolytic capacity
Liver disease (severe)
Drug effects, e.g. neostigmine (Prostigmin) -- a carbamylating cholinesterase inhibitor
Drugs which may prolong succinylcholine (Anectine) action due to effects on pseudocholinesterase:
Insecticides
Nitrogen mustard, cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) -- plasma cholinesterase inhibition
Metoclopramide (Reglan) (10 mg IV)
High estrogen levels (parturients)
Resistance to succinylcholine (Anectine)
Genetic: increased plasma cholinesterase activity
Obesity -- more plasma cholinesterase activity
Pharmacodynamic effects, e.g. myasthenia gravis
In myasthenia gravis: reduced number of nicotinic, neuromuscular junctional receptors -- the target for the drug succinylcholine (Anectine)
Atypical Pseudocholinesterase (plasma cholinesterase)
Consequence: prolonged neuromuscular-blockade (1-3 hours) following normal succinylcholine (Anectine) dosage
Dibucaine (Nupercainal, generic)-related cholinesterase variant: most important
Dibucaine is an amide local anesthetic that inhibits wild type plasma cholinesterase by 80%; however, it inhibits atypical enzyme by only 20%.
If dibucaine (Nupercainal, generic) number equals 80: normal cholinesterase
If dibucaine (Nupercainal, generic) number equals 20: homozygous for atypical cholinesterase -- frequency = 1/3200
Clinical consequences of atypical cholinesterase on neuromuscular-blockade duration
1 mg/kg IV succinylcholine (Anectine): > three hours duration
25% recovery of single twitch response following 0.03 mg/kg IV (small dose) mivacurium (Mivacron): 80minutes
For heterozygous atypical plasma cholinesterase patients (frequency: 1/480) -- dibucaine (Nupercainal, generic) number equals 40-60
Moderately prolonged duration-- as long as 30 minutes following succinylcholine (Anectine)
Dibucaine (Nupercainal, generic) analysis only measures enzyme capability for succinylcholine (Anectine) hydrolysis--
reduced active enzyme (due to affects the liver disease [reduced synthesis] or enzyme inhibition due to anticholinesterases) will affect succinylcholine (Anectine) duration, but not be detected by dibucaine (Nupercainal, generic) analysis
Miller, R.D., Skeletal Muscle Relaxants, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, pp 434-449. Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219 White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.
Succinylcholine (Anectine) side effects
|
hyperkalemia |
arrhythmias |
myalgia |
increased intraocular pressure |
|
increased ICP (intracranial pressure) |
skeletal muscle contractions |
myoglobinuria |
increased intragastric pressure |
note: Many succinylcholine (Anectine) side effects may be reduced by prior administration of non-paralyzing doses of nondepolarizing neuromuscular-blocking agents
This pre-treatment does not reduce the extent of potassium release caused by succinylcholine (Anectine)
Small children are extremely sensitive to succinylcholine given that the parasympathetic system develops in advance of the sympathetic system. Should intubation not be successful following a single succinylcholine dose, the tendency to give a second dose should be resisted since the second dose may precipitate cardiac arrest.
Classification:
sinus bradycardia
Junctional rhythm
Sinus arrest
Mechanism:
Direct activation by succinylcholine (Anectine) of muscarinic, cardiac cholinergic receptors
Cardiac Effects: most likely following a second succinylcholine (Anectine) dose, administered about five minutes following the initial dosage.
Atropine pre-treatment does not prevent bradycardia following a second succinylcholine (Anectine) dose
Other autonomic effects:
Succinylcholine (Anectine) activates ganglionic cholinergic receptors producing:
Increased heart rate
Increased systemic blood-pressure
Hyperkalemia -- following succinylcholine (Anectine)
Risk factors:
Muscular dystrophy (clinically unrecognized)
Severe skeletal muscle trauma
Skeletal muscle atrophy following denervation
Unhealed third degree burns
Other factors/considerations:
Succinylcholine (Anectine)-mediated potassium release secondary to severe abdominal infection
Potassium release following denervation (begins within four days, may last six months or more)
Pre-treatment with subparalyzing doses of nondepolarizing blockers is not effective in preventing or affecting the extent of potassium release following succinylcholine (Anectine)
Male children with undiagnosed myopathy -- predisposed to succinylcholine (Anectine)-induced:
Hyperkalemia
Rhabdomyolysis
Cardiac arrest
Muscular dystrophies:
Most common form of muscular dystrophy (frequency 1/3300 male births): Duchenne's muscular dystrophy
Diagnosis not possible until 2-6 years of age
Becker muscular dystrophy (X-linked; (frequency: 1/33,000 male births), less common then Duchenne's)
Probable small percentage of pediatric patients present with undiagnosed myopathy -- alternative to succinylcholine (Anectine) use -- a nondepolarizing neuromuscular-blocking agent
Myalgia-- postoperative succinylcholine (Anectine) skeletal muscle effect
Most common localization
Neck (pharyngitis)
Back
Abdominal muscles
Possibly due to succinylcholine (Anectine)-induced skeletal muscle fiber contractions (affect reduced by prior treatment with non-paralyzing doses of tubocurarine) -- vecuronium (Norcuron) when used in place of succinylcholine (Anectine) does not prevent myalgia following laproscopy.
Increased Intragastric Pressure
Succinylcholine (Anectine): frequently increases intragastric pressure
Thought to be related to intensity of succinylcholine (Anectine)-induced muscle fasciculation (intragastric pressure increases prevented by previous administration of nondepolarizing agent)
Associated risk:
Possible gastric fluid passage into esophagus, pharynx, and long
gastroesophageal sphincter more likely to open at pressures > 28 cm H2O
Rarely seen in children (probably due to limited muscle fasciculation associated with succinylcholine (Anectine))
Increased Intraocular Pressure
Succinylcholine (Anectine): transient increase beginning 2-4 minutes after administration and lasting about 5-10 minutes
Possible risk: in open eye injury (unsubstantiated by research); however, this concern may limit use of succinylcholine (Anectine) in this patient population
Masseter Jaw Anatomy
|
|
|
|
images obtain from: "The Structural and Functional Anatomy of Mastication" by Paul Surtees, B.Sc; The Victoria University of Manchester (1999). permission requested
Excessively-long skeletal muscle contraction -- masseter jaw rigidity
Halothane (Fluothane)-succinylcholine (Anectine) sequence associated with masseter jaw rigidity/incomplete jaw relaxation in children
Considered normal; frequency -- about 4%
Clinical Challenge:
Normal response vs. masseter jaw rigidity prodromal for malignant hyperthermia
Miller, R.D., Skeletal Muscle Relaxants, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, pp 434-449; .Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219; White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.
Non-depolarizing Blocking Drugs
Mechanism of Action: Nondepolarizing neuromuscular-blocking drugs
Combination with nicotinic, cholinergic receptors
Greater than 80%-90% receptor blockade required for neuromuscular transmission failure
Reflects wide safety margin as well as basis for neuromuscular blockade clinical monitoring
Cardiovascular Effects: nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockers
Secondary to:
Histamine/other vasoactive substance release
Effects mediated by cardiac muscarinic cholinergic receptors
Effects mediated by autonomic nicotinic cholinergic receptors
Factors responsible for cardiovascular effect variation between patients:
Basal autonomic state
Preoperative medications
Choice of agent for anesthesia maintenance
Other drugs' presence
Clinical Significance: cardiovascular effects of nondepolarizing agents are usually not significant
"Autonomic Margin of Safety": difference between dosage producing neuromuscular-blockade and dosage producing circulatory effects
Relatively low autonomic safety margin --
pancuronium (Pavulon): e.g. ED95 pancuronium (Pavulon) dosage which produces neuromuscular-blockade highly likely to produce cardiovascular effects (particularly chronotropic changes)
Relatively high autonomic safety margin --
vecuronium (Norcuron), rocuronium (Zemuron), cisatracurium (Nimbex): wide safety margins, i.e. neuromuscular-blocking doses are much less than doses required to influence cardiovascular status
Myopathy associated with Critical Illness
Definition: patients on nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockers to facilitate mechanical ventilation during prolonged illness may show skeletal muscle weakness following recovery
Critical illness may be associated with acute injury (multi-organ failure), or asthma
Moderate to severe quadriparesis (+/- areflexia) may be exhibited
Weakness time-course: unpredictable
Duration: weeks/months following discontinuation of nondepolarizing agent
Probably more common with aminosteroid agent (e.g. pancuronium (Pavulon) or vecuronium (Norcuron)); has also been observed with atracurium (Tracrium)
Possible increased risk: pre-treatment with glucocorticoids
Factors which alter patient responses to nondepolarizing agents
|
diuretics |
ganglionic blocking agents |
magnesium |
aminoglycoside antibiotics |
|
local anesthetics |
volatile anesthetics |
antiarrhythmic agents |
lithium |
|
hypotension |
altered serum potassium |
adrenocortical abnormality |
|
burned injury |
allergic reactions |
abnormal acid-base balance |
Gender may also influence duration of action; combinations of nondepolarizing neuromuscular-blocking agents may result in different effects than agents used separately
Volatile Anesthetics: interactions with neuromuscular, nondepolarizing agents
Dose-dependent increases in magnitude + duration of neuromuscular-blockade (nondepolarizing agents)-- decreasing neuromuscular blocker dose requirement
Most prominent with:
Isoflurane (Forane)
Desflurane (Suprane)
Sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane)
Intermediate effects with:
halothane (Fluothane)
Least effect with:
nitrous oxide-opioid combinations
Differential effects based on duration of action of neuromuscular blocking drug:
Less reduction in blocker dosage as a result of volatile anesthetic use with intermediate-duration agents:
Atracurium (Tracrium)
Vecuronium (Norcuron)
Rocuronium (Zemuron)
Cisatracurium (Nimbex)
Greater reduction in blocker dosage as a result of volatile anesthetic use are required with long acting agents:
Pancuronium (Pavulon)
Doxacurium (Nuromax)
Pipecuronium (Arduan)
Advantage of using intermediate-duration neuromuscular-blocking agents:
Reduced effects on dosage by volatile anesthetics allows "more predictable degree" of skeletal muscle block (in the Absence of and exact information about brain anesthetic partial pressures)
Anesthetic-induced CNS depression -- with secondary decrease in skeletal muscle tone
Decreased postjunctional synaptic membrane sensitivity to depolarization
Volatile anesthetics decreased twitch response (50% reduction) at higher MAC values, i.e. (1.25-1.75 MAC enflurane (Ethrane); 2.8-3.7 MAC halothane (Fluothane))
Antibiotic effects on neuromuscular-blockade (nondepolarizing agents)
Some antibiotics increase the effect of nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockers
Aminoglycoside antibiotics are most likely to produce this increased blocking effect
|
|
Local Anesthetics (low-dose): enhancement of blockade by nondepolarizing agents
Higher local anesthetic doses: complete neuromuscular blockade
Local anesthetics may:
Inhibit acetylcholine release
"Stabilize" postsynaptic membrane (making depolarization more difficult)
Direct muscle fiber depression
Cardiac antiarrhythmic agents/nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocker interactions
Lidocaine (Xylocaine) (IV): may increase preexisting blockade
Clinical context: lidocaine (Xylocaine) administration during general anesthesia (protocol includes neuromuscular-blockade) recovery.
Quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan)
Increased blockade (for both nondepolarizing and depolarizing drugs)
Probable mechanism: attenuation of acetylcholine release
Clinical Context: quinidine gluconate (Quinaglute, Quinalan) administration during recovery from general anesthesia (protocol includes neuromuscular blockers)
Diuretics -- furosemide (Lasix)
Increases neuromuscular-blocking by nondepolarizing agents
Probably due to reduced acetylcholine release
Related issues:
Hypokalemia associated with chronic diuretic use:
Decreases pancuronium (Pavulon) dose requirements
Increases neostigmine (Prostigmin) dosage required for neuromuscular blockade antagonism
Accentuates neuromuscular-blockade by nondepolarizing drugs; to a lesser degree also accentuates blockade by succinylcholine (Anectine)
Interaction may be more pronounced with magnesium and vecuronium (Norcuron) than with other agents
Clinical Context:
Observed as enhancement of neuromuscular blockade (nondepolarizing agent mediated) when magnesium is administered to patients treated with magnesium for pregnancy-caused hypertension (toxemia of pregnancy)
Patients chronically treated with phenytoin (Dilantin) are resistant to neuromuscular-blockade produced by nondepolarizing agents
Mechanism: pharmacodynamic (higher neuromuscular blocker-plasma concentration are required to produce a given level blockade in patients treated with phenytoin (Dilantin) than to produce same level of blockade in untreated patients)
Lithium: (used to treat bipolar disorder) -- possible enhanced neuromuscular-blockade by both depolarizing and nondepolarizing drugs
Cyclosporine (Sandimmune, Neoral) -- possible prolongation of neuromuscular-blockade by nondepolarizing drugs
Ganglionic blocking drugs (e.g., mecamylamine (Inversine)) may affect duration of neuromuscular-blockade by:
Reduced skeletal muscle blood flow
Plasma cholinesterase in addition
Reduced post-junctional, nicotinic cholinergic receptor sensitivity
Increased neuromuscular-blockade duration (pancuronium (Pavulon) and vecuronium (Norcuron))
Mechanism: decreased hepatic inactivating enzyme activity (temperature dependency); decreased biliary and renal drug clearance
Increased neuromuscular junctional sensitivity to pancuronium
Increased duration of atracurium (Tracrium) action (also reduces infusion rate necessary to maintain stable neuromuscular-blockade)
Atracurium (Tracrium) effect: probably caused by decreased rate of Hoffmann elimination and reduced ester hydrolysis
Prolonged resistance to nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockers
Starts about 10 days following injury
Peaks about 40 days later
Declines after about two months (may last considerably longer > one-year)
Mechanism: -- probably pharmacodynamic (higher plasma drug concentration required to cause a given extent of twitch suppression compared to similar extent in non--burn patients)
Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219; White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996; Miller, R.D., Skeletal Muscle Relaxants, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, pp 434-449.
Role of neuromuscular blockade in anesthesia.
Primary uses of neuromuscular-blocking drugs:
Skeletal muscle relaxation facilitating tracheal intubation
Skeletal muscle relaxation to improve intraoperative surgical conditions
Dose guidelines:
Facilitation of tracheal intubation -- 2 x ED95 dose of nondepolarizing muscle relaxant
Laryngospasm: effectively treated with succinylcholine (Anectine)
Optimal intraoperative conditions -- 95% single twitch response suppression
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs: -- no CNS depression; no analgesia therefore they do not substitute for anesthetic agents
Other clinical uses:
in managing patients requiring mechanical ventilation (intensive care environment)
Adult respiratory distress syndrome
Tetanus
Suppression of spontaneous respiration
Miller, R.D., Skeletal Muscle Relaxants, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, pp 434-449. Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219. White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.
Reversal of non-depolarizing blockers: Antagonist-assisted reversal of neuromuscular blockade produced by nondepolarizing neuromuscular-blocking agents
Antagonist-assisted neuromuscular-blockade reversal:
Edrophonium (Tensilon), neostigmine (Prostigmin), or pyridostigmine (Mestinon)-- effective by increasing acetylcholine availability of neuromuscular junction (secondary to acetylcholinesterase inhibition)
Physostigmine (Antilirium): not used because dosage requirement is excessive
Anticholinesterase agents are usually administered during spontaneous neuromuscular-blockade recovery
Recovery rate is the sum of (1) spontaneous recovery from the blocking drug and (2) the activity of the pharmacologic antagonist (anticholinesterase drugs)
Therefore: pharmacologic antagonism is more effective for short-or intermediate-acting neuromuscular-blocking drugs (undergoing plasma hydrolysis or Hofmann elimination) compared to long-acting nondepolarizing neuromuscular-blocking agents
Special Considerations: use of muscarinic antagonists with anticholinesterases in Reversal of Neuromuscular Blockade
Reversal of nondepolarizing neuromuscular-blockade: necessitates only nicotinic cholinergic effects of anticholinesterases agents
Minimizing muscarinic receptor-mediated effects of anticholinesterase drugs is beneficial an accomplished by a concurrent administration of atropine or glycopyrrolate (Robinul) (antimuscarinics)
The antimuscarinic agent should have a more rapid onset than the anticholinesterase drugs -- reducing drug-induced bradycardia
if edrophonium (Tensilon) (0.5 mg/kg) is used; atropine 7 ug/kg is appropriate
a higher dose atropine (10-15 ug/kg) has been recommended, particularly if opioid-based maintenance anesthetic has been used
if neostigmine is used (slower onset of action compared edrophonium (Tensilon)), then atropine or glycopyrrolate (Robinul) and may be administered as the antimuscarinic agent;
Concurrent administration of these drugs results in an initial tachycardia because of atropine's more rapid onset
Factors influencing the speed and extent of neuromuscular blockade reversal by anticholinesterase agents
Intensity neuromuscular-blockade when reversal is initiated (train-of-four visible twitches)
Which nondepolarizing neuromuscular-blocking drug is being reversed is a factor
Edrophonium (Tensilon): less effective than neostigmine in reversing deep neuromuscular blockade (twitch height < 10% of control) produced by continuous atracurium (Tracrium), vecuronium (Norcuron), or pancuronium (Pavulon) infusions.
Edrophonium (Tensilon), probably better than neostigmine (Prostigmine for reversing atracurium (Tracrium) blockade
Neostigmine (Prostigmin), probably better than edrophonium (Tensilon) for reversing vecuronium (Norcuron) blockade
Prevention/inhibition of anticholinesterase-mediated antagonism of neuromuscular-blockade -- Possible factors
Certain antibiotics
Hypothermia
Respiratory acidosis (PaCO2 >50 mm Hg
Hypokalemia/metabolic acidosis
Reversal of phase II block (following prolonged/repeated succinylcholine (Anectine)): may be reversed with edrophonium (Tensilon) or neostigmine (Prostigmin) in patients with normal plasma cholinesterase
In patients with atypical plasma cholinesterase, phase II block reversal may not be reliable, requiring mechanical ventilation until blockade subsides.
Stoelting, R.K., "Anticholinesterase Drugs and Cholinergic Agonists", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, 224-237.
Neuromuscular blockade: depolarizing agent followed by nondepolarizing agent (Succinylcholine (Anectine), then nondepolarizing agent)
Clinical Context
Initial administration of succinylcholine (Anectine)(1 mg/kg, IV)-- supporting tracheal intubation
Subsequent administration nondepolarizing agent
Greater neuromuscular-blockade in this case (even if evidence of succinylcholine (Anectine) effect has significantly diminished)
Counterintuitive effect: since the drug effects should be antagonistic
Duration of action of nondepolarizing agents (atracurium (Tracrium) or vecuronium (Norcuron))is not affected -- just the initial increased response
At lower succinylcholine (Anectine) doses (0.5 mg/kg)-- no initial enhancement of vecuronium (Norcuron) mediated neuromuscular-blockade.
Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219
Combinations of Neuromuscular-blocking agents
Neuromuscular-blockade enhancement due to drug combinations:
Example-- Different major site of action (postsynaptic vs. presynaptic)
Pancuronium (Pavulon) + metocurine (Metubine Iodide) or tubocurarine
shorter duration than with pancuronium (Pavulon) alone
Vecuronium (Norcuron) + tubocurarine
Combinations of nondepolarizing agents -- same degree of blockade with smaller dose of each drug
Benefit: fewer dose-related side effects
Example: BP/heart rate effects of pancuronium (Pavulon) + metocurine (Metubine Iodide) < with pancuronium (Pavulon) monotherapy
Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219
Gender and neuromuscular-blockade
Differential drug sensitivity due to gender:
Pancuronium (Pavulon)
Vecuronium (Norcuron)
Rocuronium (Zemuron)
Women:
require 22% less vecuronium (Norcuron) than men to obtain the same degree of neuromuscular junctional blockade
30% more sensitive to rocuronium (Zemuron) than men.
Clinical significance:
Normal rocuronium (Zemuron) dose should be reduced in women compared to men
Possible mechanism: men have a greater skeletal muscle mass percentage-- requiring a higher neuromuscular-blocking dosage
Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219
|
Overview: Doxacurium (Nuromax)
Nondepolarizing agents; ED95 -- 30 ug/kg
Time to onset: 4-6 minutes
Duration of action: about 60-90 minutes
Renal clearance (similar to pancuronium (Pavulon))
Extended duration in elderly patients
No histamine release; no cardiovascular effects
Drug interactions:
Volatile anesthetics
Reduce doxacurium (Nuromax) dose requirements by 20%-40% compared to blocking doses for nitrous oxide-fentanyl (Sublimaze) anesthesia
Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219
Overview: pancuronium (Pavulon)
Commonly used long-acting nondepolarizing agent
Low-cost advantage
Cardiovascular side effects (doxacurium (Nuromax) and pipecuronium (Arduan) -- similar to pancuronium (Pavulon) but without cardiovascular side effects)
Pancuronium (Pavulon) and related agents have replaced older, long-acting nondepolarizing drugs such as:
tubocurarine
metocurine (Metubine Iodide)
gallamine (Flaxedil)
No enhancement of histamine release
No autonomic ganglia blockade
General properties: pancuronium (Pavulon)
nondepolarizing agent: ED95 = 70 ug/kg
onset: 3-5 minutes
duration: 60-90 minutes
Pancuronium (Pavulon) block enhanced by respiratory acidosis which opposes neostigmine (Prostigmin) antagonism
Pharmacokinetics: pancuronium (Pavulon)
Renal excretion: 80% of dose excreted unchanged
Renal dysfunction: pancuronium (Pavulon) clearance may decrease by 33%-50%
Hepatic metabolism (10%-40%)-with at least one potent metabolite
Pancuronium (Pavulon) elimination halftime: affected by hepatic cirrhosis/total biliary obstruction
Aging: decreased pancuronium (Pavulon) plasma clearance
Mechanism: -- probably reduced renal function
Cardiovascular Effects: pancuronium (Pavulon)
Slight increase (10%-15%):
Heart rate
Mean arterial pressure
Cardiac output
Mechanism:
Atropine-like effect on cardiac, muscarinic cholinergic receptors
Sympathetic, autonomic nervous system activation
Adverse Effects:
Increased incidence of cardiac arrhythmias following pancuronium (Pavulon) (but not succinylcholine (Anectine)) in patients treated chronically with digitalis glycosides
Increased cardiac arrhythmias may occur due to enhanced sympathetic nervous system activity
Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219; White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.
Overview: pipecuronium (Arduan)
nondepolarizing neuromuscular for; ED95 -- 50-60 ug/kg
time to onset: 3-5 minutes
duration of action: 60-90 minutes
Enhanced potency increased/duration of action shortened in infants (relative to adults or children)
No histamine release; no cardiovascular changes associate with pipecuronium (Arduan) administration
Pharmacokinetics:
similar to pancuronium (Pavulon) in terms of renal clearance
Hepatic cirrhosis -- no effect on pipecuronium (Arduan) pharmacodynamics/ pharmacokinetics
Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219; White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.
Introduction: Intermediate-acting Nondepolarizing Blockers
Overview: Intermediate-acting Nondepolarizing Blockers
Atracurium (Tracrium), vecuronium (Norcuron), rocuronium (Zemuron), cisatracurium (Nimbex)
Efficient clearance mechanisms (reduced likelihood of significant accumulation following repeated administration)
Useful; but more expensive alternatives to succinylcholine (Anectine) and pancuronium (Pavulon)
Particularly useful for tracheal intubation/skeletal muscle relaxation for short procedures (e.g. outpatient)
Properties:
Intermediate-acting agents (compared to long-acting agents):
Similar time to onset (exception: roncuronium (Zemuron) -- rapid onset, similar to succinylcholine (Anectine))
Duration of action -- about one-third of long-acting agents
30%-50% more rapid recovery rate
Minimal/absent cardiovascular effects
Intermediate duration -- due to rapid/efficient plasma clearance
Special considerations:
Rocuronium (Zemuron)-- rapid onset (similar to succinylcholine (Anectine))
Rapid onset -- within one-minute; good choice for tracheal intubation facilitation
Method for accelerating onset for other "intermediate acting" agents
Use a small, subparalyzing dose (about 10% of ED95); followed about four minutes by the larger dose (2-3 X ED95)
Divided dose technique = priming principal (neuromuscular-blockade:two-step process)
Initial binding of spare receptors (no clinical effect)-- but reduces safety factor for neuromuscular transmission.
Deeper blockade
Priming dose technique may be less valid now with the availability of single, large IV roncuronium (Zemuron) dose -- providing rapid onset -- no risk of drug-induced weakness in awake patients
Antagonism of blockade cause by intermediate-acting nondepolarizing drugs:
anticholinesterase agents -- effective (within 20 minutes of administration of the paralyzing intermediate-acting nondepolarizing drug dose)
Pharmacologic antagonism (administration of anticholinesterase drugs) coupled with rapid clearance of the blocker results in enhanced, recovery rates
Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219; White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.
Overview:atracurium (Tracrium)
Nondepolarizing, neuromuscular blocker (multiple isomers)
ED95: 0.2 mg/kg
Time to onset: 3-5 minutes
Duration of action: about 20-35 minutes
Site of action:
Presynaptic and postsynaptic membrane nicotinic receptors
Degradation: spontaneous, in vivo (Hofmann elimination)
More stable in acid pH (storage --pH 3.25-3.65)
Should not mix atracurium (Tracrium) with alkaline drugs (e.g. barbiturates) or expose to solutions of more alkaline pH
alkaline pH: accelerated breakdown
Clearance-- two mechanisms
Hofmann elimination -- nonenzymatic; accounts for one-third of the degradation
Hydrolysis catalyzed by plasma esterases (nonspecific, i.e. not plasma cholinesterase); accounts for about two-thirds of degraded atracurium (Tracrium)
Clearance not dependent on hepatic or renal function
Clearance not affected in patients with atypical cholinesterase
Laudanosine -- major metabolite of both catabolic atracurium (Tracrium) pathways
CNS stimulant --even with long, continues atracurium (Tracrium) infusions in the surgical setting--laudanosine concentrations remain below those apparently required for cardiovascular/CNS action; in the ICU setting with longer durations seizure potential becomes much more likely
Cumulative effects
No significant cumulative effect due to rapid clearance from plasma (hydrolysis + Hofmann elimination)
Cardiovascular Effects:
With these background anesthetics: nitrous oxide, fentanyl (Sublimaze), halothane (Fluothane), isoflurane (Forane)
no BP/heart rate change associated with rapid IV atracurium (Tracrium) up to (2 X ED95)
With nitrous oxide-fentanyl (Sublimaze) anesthesia, IV atracurium (Tracrium) (3 X ED95): slight increase in heart rate (8%); decreased in mean arterial pressure (20%)
Cardiovascular effects: transitory (< 5 minutes)
Facial/truncal flushing may be due to histamine release (no circulatory effects if patients are pretreated with H1/H2 receptor blockers)
H1/H2 receptors may be activated by prostacyclin (not histamine)
Special Patient Populations
Pediatric patients
Similar atracurium (Tracrium) doses in adults and children (2-16 years old) when doses are calculated using mg/m2 rather than on a mg/kg basis.
Infants -- 1-6 months: require about 50% of the atracurium (Tracrium) dose given to older children
continuous infusion rate (to maintain steady-state blockade): 25% less during the first month of life
Elderly patients
Increasing age: no effect on atracurium (Tracrium) continuous infusion rate required for constant degree of neuromuscular-blockade
Mechanism -- age independence of Hofmann elimination and plasma ester hydrolysis inactivation processes (renal/hepatic state independent)
Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219; White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.
Overview: cisatracurium (Nimbex)
nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocker
ED95: 50 ug/kg
Time to onset: 3-5 minutes
Duration of action: 25-30 minutes
Similar pharmacological profile to atracurium (Tracrium) compared atracurium (Tracrium)
Cisatracurium (Nimbex)(Tracrium) onset slightly slower
Cisatracurium (Nimbex) much less likely to cause histamine release, compared atracurium (Tracrium)
Spontaneous neuromuscular blockade recovery not affected by prolonged infusion (80 hr) to patients requiring ventilation in the intensive care environment-- by contrast to vecuronium (Norcuron)
Recovery: accelerated by the use of anticholinesterase agents
Clearance: cisatracurium (Nimbex)
Hofmann elimination (77% cisatracurium (Nimbex) clearance)
16%: renal
Neuromuscular-blockade characteristics not affected by hepatic or renal dysfunction
Cisatracurium (Nimbex) pharmacokinetics: not appreciably affected by advanced age (slight delay in time to onset)
Cardiovascular Effects: cisatracurium (Nimbex)
No histamine-releasing effects (by contrast yo atracurium (Tracrium))
Large doses (8 X ED95, IV) do not typically induce cardiovascular changes
Less change in cerebral hemodynamics compared to equal potent atracurium (Tracrium) dosage
Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219; White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.
Overview: vecuronium (Norcuron)
Nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocker
ED95: 50 ug/kg
Time to onset: 3-5 minutes
Duration of action: 20-35 minutes
Structurally resembles pancuronium (Pavulon) -- vecuronium (Norcuron) reduced anti-vagal properties compared to pancuronium (Pavulon)
Unstable in solution; supplied as lyophilized powder
Clearance
Overview
hepatic metabolism and renal excretion
metabolites generally much less active than vecuronium (Norcuron)
More lipid-soluble compared pancuronium (Pavulon) -- promotes biliary excretion and significant hepatic uptake
Rapid hepatic uptake may be responsible for short duration of action
Reduced renal function
Vecuronium (Norcuron) action prolonged in patients with renal failure -- increased concentration of metabolites also contribute to prolonged skeletal muscle paralysis following long-term vecuronium (Norcuron) infusion
Reduced liver function
When used in patients with hepatic cirrhosis, vecuronium (Norcuron) at 0.2 mg/kg IV, longer duration of action (longer elimination halftime); not observed that the 0.1 mg/kg IV dose level
In patients with cholestasis, undergoing biliary surgical procedures: vecuronium (Norcuron) duration of action is increased (at the 0.2 mg/kg IV dosage)
Cardiovascular Effects
Minimal even at 3 X ED95, with rapid IV administration
No vagolytic action
apparently no/minimal histamine release
possible vagotonic vecuronium (Norcuron) effect if administered nearly concurrently with potent opioids (e.g. sufentanil (Sufenta))
vagotonic action may be serious -- promoting sinus nodal exit block and cardiac arrest
Use in pediatric patients
Vecuronium (Norcuron) potency (during nitrous oxide-halothane (Fluothane) anesthesia): similar in --
infants (7-45 weeks)
children (1-8 years)
adults (18-38 years)
Onset of action: more rapid in infants compared to adults; (infants have high cardiac output -- promoting rapid onset)
Duration of action: longest in infants; shortest in children-- (infants have less/immature enzyme systems -- increased volume of distribution)
Use in Elderly patients
With increased age: decreased continuous infusion rate required to maintain a given level of block
Mechanism:
Age-related hepatic blood flow decrease;
Age-related decreased renal blood flow;
Age-related reduced hepatic microsomal enzyme system activity (possibly)
With increased age: prolonged recovery time if vecuronium (Norcuron) was administered by continuous infusion (recovery from individual IV doses of vecuronium (Norcuron): not age sensitive)
Use in Obstetric patients
Clinically significant fetal effects not observed with nondepolarizing neuromuscular-blocking drugs.
Vecuronium (Norcuron) clearance: increased during late pregnancy; possibly due to enhance microsomal enzyme activity (by progesterone)
Vecuronium (Norcuron)-induced neuromuscular blockade: prolonged immediately postpartum
Obesity:
Vecuronium (Norcuron) duration of action (but not atracurium (Tracrium)) prolonged in obese (> 130% of ideal body weight) compared with nonobese adults
Malignant Hyperthermia
Not associated with vecuronium (Norcuron) or atracurium (Tracrium) administration in animal models
In a patient susceptible to malignant hyperthermia and therefore pretreated with dantrolene (Dantrium): duration of vecuronium (Norcuron) action prolonged
Mechanism: Dantrolene (Dantrium) may prolonged action of neuromuscular-blocking agents secondary to dantrolene (Dantrium)-mediated impairment of presynaptic calcium release
Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219; White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.
Overview: rocuronium (Zemuron)
Nondepolarizing agent; ED95 -- 0.3 mg/kg
Time to onset: 1-2 minutes
Duration of action: 20-35 minutes
reduced potency (relative to vecuronium (Norcuron)) probably responsible for relatively rapid onset [lower potency requires higher dose (more molecules administered) -- more molecules increased the likelihood of initial blockade]
Time to onset: Clinical implications --
Time to onset of maximal single twitch depression (following 3-4 X ED95): similar to time to onset for succinylcholine (Anectine) (when mg/kg, IV)
Rocuronium (Zemuron): only nondepolarizing agent which may substitute for succinylcholine (Anectine) when:
Succinylcholine (Anectine) is contradicted
Rapid onset is required to promote tracheal intubation
Differences between rocuronium (Zemuron) and succinylcholine (Anectine)
Laryngeal muscles more resistant to rocuronium (Zemuron) than adductor pollicis: large dose rocuronium (Zemuron) effects resemble succinylcholine (Anectine) at adductor pollicis but will be delayed relative to succinylcholine (Anectine) effects at laryngeal adductors.
Duration of action:
Similar to other intermediate-acting agents-- at normal doses
With large dose rocuronium (Zemuron) --3-4 X ED95-- to achieve onset rates similar to succinylcholine (Anectine)-- duration is prolonged (more similar to long-acting nondepolarizing drugs, e.g. pancuronium (Pavulon))
Large IM doses (rocuronium (Zemuron)) -- 1-8 mg/kg given to infants/children to support rapid tracheal intubation results in relatively long durations (sixty minutes) -- This long duration may limit clinical utility.
Effects on muscle groups
Laryngeal adductor muscles and diaphragm: more resistant to rocuronium (Zemuron) than adductor pollicis muscles
Therefore, complete single twitch response suppression of adductor pollicis is not sufficient to ensure paralysis of laryngeal muscles and diaphragm.
Maximal paralysis of laryngeal muscles may not be recognized if suppression of adductor pollicis single twitch response is being monitored as the clinical sign for optimal conditions supporting intubation.
Direct laryngoscopy for intubation performed at peak laryngeal muscle paralysis may result in abdominal muscle/diaphragmatic motion when the tracheal tube is positioned -- because the diaphragm and abdominal muscles are not yet fully paralyzed:
This condition is undesirable especially in those cases when pulmonary aspiration gastric contents is considered a risk.
Pharmacokinetics -- Clearance:
Rocuronium (Zemuron)
-- up to 50% excreted in the bile (animal studies)
-- > 30% renal excretion (in 24 hours)
Liver disease: possible increased drug effect duration due to increased volume of distribution
Elderly patients:
similar time to onset (compared to young adults)
prolonged duration (compared to young adults)
Cardiovascular Effects --
No histamine released (as with other non-polarizing agents)
Small anti-vagal effect -- may be useful in certain surgical procedures which cause vagal stimulation (e.g. opthalmological, laproscopic procedures)
Bradycardia (reflex) may occur with atracurium (Tracrium) or vecuronium (Norcuron) in patients undergoing these procedures
Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219; White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.
Short-acting nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocker: Mivacurium (Mivacron)
Overview: mivacurium (Mivacron)
Only clinically useful nondepolarizing agent classified as short acting
ED95: 80 ug/kg
Time to onset: 2-3 minutes
Duration of action: 12-20 minutes (about 2 X longer than succinylcholine (Anectine); about 30%-40% that of intermediate-acting neuromuscular-blocking agents)
mivacurium (Mivacron): no malignant hyperthermia likely (based on swine model)
Pancuronium (Pavulon), then mivacurium (Mivacron) leads to prolonged mivacurium (Mivacron) duration of action
Muscle effects: mivacurium (Mivacron)
Mivacurium (Mivacron) (2 X ED95):
Maximal depression (single twitch) of orbicularis oculi prior to maximal depression at adductor pollicis (different from succinylcholine (Anectine) which produces maximal depression at the sites concurrently)
Loss of orbicularis oculi function (but not adductor pollicis) correlates with maximal laryngeal adductor muscle and diaphragm paralysis
Clearance: mivacurium (Mivacron)
Short duration of action due to: plasma cholinesterase-mediated hydrolysis
Hydrolytic rate for mivacurium (Mivacron) about 90% that observed for succinylcholine (Anectine)
Mivacurium (Mivacron) hydrolysis decreased with increased duration of action in the presence of atypical plasma cholinesterase
In patients with atypical plasma cholinesterase: mivacurium (Mivacron) blockade is intense in prolonged
Effective antidote: administration of human plasma cholinesterase (anticholinesterase agents appear ineffective)
Renal status: renal excretion -- minor pathway for mivacurium (Mivacron) clearance
Hepatic status:
Patients with liver cirrhosis may experience prolonged mivacurium (Mivacron) blockade if the liver disease is associated with reduced plasma cholinesterase activity
Increase volume of distribution associate with liver disease because reduced neuromuscular-blockade
Pharmacological Antagonism:
May not be needed given rapid spontaneous recovery from mivacurium (Mivacron) blockade
Anticholinesterase agents (e.g. neostigmine (Prostigmin)) because they inhibit plasma cholinesterase may interfere with normal recovery mechanism
Moderate mivacurium (Mivacron)-mediated blockade may respond to neostigmine (Prostigmin)
Deep mivacurium (Mivacron)-mediated blockade maybe antagonized by edrophonium (Tensilon)
Cardiovascular Effects: mivacurium (Mivacron)
minor at doses up to 2 x ED95
rapid IV administration of 3 x ED95 may provoked a decrease in BP (10%-20%), secondary to histamine release
Stoelting, R.K., "Neuromuscular-Blocking Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, pp 182-219; White, P. F. "Anesthesia Drug Manual", W.B. Saunders Company, 1996.