-
Important anesthetic agents administered as racemic mixtures include:
-
Thiopental (pentothal)
-
Methohexital (Brevital)
-
Ketamine (Ketalar)
-
Halothane (Fluothane)
-
Enflurane (ethrane)
-
Isoflurane (Forane)
-
Sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane)
-
-
Barbiturates: Structural Analysis: 75% similar structures Pentobarbital sodium (Nembutal) 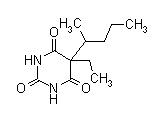

Thiopental sodium (Pentothal) 

Butabarbital sodium (Butisol) 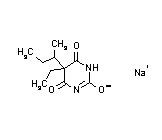

Thiamylal 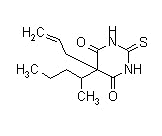
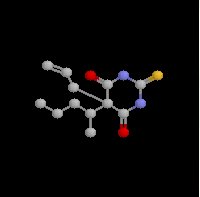
Amobarbital sodium 
-
 Metabolism:
Metabolism:-
Many enzymes exhibit stereoselectivity, a preference for one or the other enantiomeric form.
-
In the case of drug-metabolizing enzymes, stereoselectivity may result in a difference in the duration of action of one enantiomer compared to the other.
-
-
 Structure Activity
Relationships:
Structure Activity
Relationships:-
Understanding the relationship between drug structures and biological activities forms the basis of rational drug design.
-
Computer-enhanced molecular modeling and information concerning three-dimensional receptor structure may combine to improve the effectiveness of rational drug design approaches.
-
Katzung, B. G. "Basic Principles: Introduction" in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, p.1-4
Stoelting, R.K., "Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Injected and Inhaled Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, 1-17
3Dolin, S. J. "Drugs and pharmacology" in Total Intravenous Anesthesia, pp. 13-35 (Nicholas L. Padfield, ed), Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford, 2000.