Anesthesia Pharmacology: Physics and Anesthesiology
![]() The equation presented earlier, FA/FI = 1 - (
The equation presented earlier, FA/FI = 1 - (![]() B/FI)(Q/
B/FI)(Q/![]() A)
x ((PA-Pvenous)/Pbarometric)),
is suggestive of a more general relationship describing three important
factors that determine anesthetic uptake.
A)
x ((PA-Pvenous)/Pbarometric)),
is suggestive of a more general relationship describing three important
factors that determine anesthetic uptake.
10The
relationship may be described as uptake = ![]() B
x Q x (PA-Pvenous)/Pbarometric).
B
x Q x (PA-Pvenous)/Pbarometric).
This is another way of thinking about the above relationship, since uptake of the volatile agent from the lungs is the necessary first step in support of distribution to other compartments, perhaps most notably the brain.
As pointed out by Eger, uptake here is represented as a product of three factors, and in accordance with the relationship should any factor tend towards 0, uptake also would then be very limited an approach 0.
For example, if the gas solubility would be very small uptake would be limited.
Similarly with minimal cardiac output which might be seen in cardiogenic shock significant tissue uptake of anesthetic would be quite limited as pulmonary flow diminishes.
Finally, if the difference between the alveolar and venous partial pressures approaches 0, net uptake would also approach 0 (i.e., FA/FI = 1)
![]() 10Solubility
and the blood: gas partition coefficient
10Solubility
and the blood: gas partition coefficient
Different
anesthetics have different blood: gas partition coefficients, ![]() ,
which reflect underlying molecular affinities for the two different
phases.
,
which reflect underlying molecular affinities for the two different
phases.
Relatively higher blood: gas partition coefficients are associated with lower FA/FI ratios because there will be greater transfer of molecules from the alveolar volume into the blood, making FA smaller compared to a given inspired fraction FI .
To take a specific example, consider isoflurane (Forane) which exhibits a blood: gas partition coefficient of about 1.4 at equilibrium.
The use of the term "equilibrium" indicates that is sufficient time has elapsed such that there is no particular net flux from the alveolar volume to the blood or vice versa.
That is, roughly speaking an equilibrium is equally likely than a molecule will move from the blood phase into the alveolar phase as it is the molecule move from the alveolar phase into the blood phase, solely on the basis of probabilities.
The value of 1.4 also suggests that for a given volume of blood, such as 1 cc compared to the same volume of gas, the capacity for volume would be 1.4 times higher for the blood compared to the gas. (at equilibrium, a blood: gas partition coefficient of 1.4 does not indicate that there is a difference in partial pressure between phases (by definition at equilibrium the partial pressures are equivalent)
By contrast to isoflurane (Forane), methoxyflurane is exceedingly soluble in blood, with a blood: gas partition coefficient of about 15.
Before significant anesthetic molecule transfer will occur from blood to other tissues, one must begin to reach the capacity of the blood compartment.
With highly blood soluble agents, many more molecules must be transferred from the gas phase to the blood phase to result in significant increases in tension.
Such a process takes longer for the more blood soluble anesthetics and since this step is required first, before CNS concentrations of anesthetic are high enough to cause anesthesia, induction would, all other things being equal, take longer.
Very soluble agents such as methoxyflurane results in a sufficient delay that they may be rarely used just for this reason.
Isoflurane (Forane), enflurane (Ethrane), and halothane (Fluothane) are classified as exhibiting "moderate" solubility (blood: gas partition coefficients of 1.4,1.8, 2.5, respectively) by contrast to agents such as nitrous oxide (0.47), desflurane (Suprane) (0.45), or sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) (0.65).
Despite exhibiting moderate solubilities, referencing isoflurane (Forane), enflurane (Ethrane), and halothane (Fluothane), induction may be accelerated by the use of anesthetic overpressure
Anesthetic overpressure refers to using a higher vaporizer setting, e.g. 4%-5% for halothane (Fluothane) in order to obtain a relatively higher alveolar concentration.
Again, the rate at which the blood compartment is saturated by halothane (Fluothane) molecules will be dependent on the likelihood that relatively large numbers of halothane (Fluothane) molecules will exhibit significant flux from the alveolar volume to the blood compartment.
Increasing the number of halothane molecules per unit alveolar volume accomplishes this objective.
Accordingly, even though anesthetics may exhibit within reason differences in blood gas partition coefficients, i.e. blood solubilities, induction rates can be regulated to create rough equivalence by adjusting the concentration of anesthetic molecules entering the gas circuit.
Anesthetic overpressure can be thought of as an "IV bolus". In pharmacokinetic terms it would fall into the category of a "loading dose"
![]() Concentration
Effect 6Let us look at this issue a little more
thoroughly.
Concentration
Effect 6Let us look at this issue a little more
thoroughly.
We will focus first on the concentrating effect, noting that the inspired anesthetic concentration (FI) will influence the alveolar concentration as described above directly as well as increasing the rate of FA/FI rise.
These effects can be considered in two parts.
In this hypothetical, we will be administering 10% anesthetic which means that in terms of ratios the gas contains 10 parts anesthetic and 90 parts other gas molecules.
Furthermore, let's assumed that 50% of the anesthetic alveolar molecules will be absorbed by the blood, leaving five parts (0.5 x 10) remaining in the alveoli , along with 90 parts allocated to the other alveolar gas molecules.
So before gas transport we had 10% anesthetic and following transport of 5 parts into blood we now have an alveolar anesthetic concentration of 5.3% calculated by taking 5 and dividing by the total number of parts, i.e.5 + 90 or 5/95.
6Continuing along these lines, in this variation, administration will consist of 50% anesthetic, that is 50 parts anesthetic and 50 parts other gas molecules.
Again 50% of the anesthetic molecules will be absorbed by the blood, leaving 25 parts in the alveoli. Now the alveolar concentration, following this step would be 25/(50+ 25) = 33%.
When we compare the two cases we note that in the second case we gave 5 times more anesthetic (50% versus 10%); however, when we inspect the differences in alveolar concentration, the difference is not 5 times greater but rather 6.2 times greater (33%/5.3 = 6.2, although the initial ratios were 50% anesthetics in the second case and 10% in the first case (50%/10%=5).
This concentration effect would be most clear for anesthetics that are administered at high concentrations, with the best example being nitrous oxide usually administered at 50%-70%.
6In the curve below compare the rate of rises of nitrous oxide relative to desflurane (Suprane), recognizing that desflurane (Suprane) has a lower blood gas solubility.
On the basis of blood: gas solubility, one might predict that desflurane (Suprane) should exhibit a more rapid rate of rise in FA/FI .
However, when one takes into account is substantially higher concentration of nitrous oxide delivered, the importance of the concentration effect is clear and is responsible for the rapid increase in FA/FI seen with nitrous oxide.
(Ratio data from Yasuda et al: Kinetics of desflurane, isoflurane and halothane in humans, Anesthesiology 74:489, 1991; and Yasuda, N, Lockhart, SH, Eger, EI II et al: Comparison of kinetics of sevoflurane and isoflurane in humans Anesth Analg 72: 316, 1991)
![]() Augmented
gas inflow: An additional consideration has to do
with the replenishment by new gas for gas transferring from the
alveolar volume to the blood.
Augmented
gas inflow: An additional consideration has to do
with the replenishment by new gas for gas transferring from the
alveolar volume to the blood.
Sometimes this additional concentration effect is called "augmented gas inflow".
Using the same example as before, 10% represents anesthetic delivery and is associated with 50% anesthetic uptake into the blood. FI in this example is 10%.
The 5 parts anesthetic transferred to the blood would be replaced by gas from the circuit which is 10% anesthetic.
Let's see what's left in the alveolar volume after five parts of transferred to the blood; we have 5 parts anesthetic gas molecules and 90 parts other gas molecules.
Now we replace the five parts transferred to the blood with five parts from the circuit, which is equivalent to 5 x 10% (since only 10% of the circuit gas will be anesthetic molecules) or 0.5 parts anesthetic (5 x 0.1 = 0.5).
Therefore at this moment the alveolar concentration would be 5 parts anesthetic (never transferred from the alveolar volume) + 0.5 parts anesthetic (new gas from the circuit) or 5.5%.
![]() This compares with
5.3% when we don't include "augmented flow".
This compares with
5.3% when we don't include "augmented flow".
![]() If we consider the
case in which the anesthetic inspired concentration is 50%,
again with 50% uptake, and by analogy 25 parts of anesthetic
are transferred to the blood replaced by 25 parts of 50%
anesthetic, the resulting alveolar concentration would be
(25 + 12.5)/100)*100% = 37.5%, compared to 33% not taking into
account augmented flow:
If we consider the
case in which the anesthetic inspired concentration is 50%,
again with 50% uptake, and by analogy 25 parts of anesthetic
are transferred to the blood replaced by 25 parts of 50%
anesthetic, the resulting alveolar concentration would be
(25 + 12.5)/100)*100% = 37.5%, compared to 33% not taking into
account augmented flow:
Five times the FI (50% versus 10% in FI ), results in 37.5/5.5 = 6.8 times greater alveolar gas fraction (FA ) compared to our earlier calculation of 6.2 times greater not taking into account augmented gas flow.
6The second gas effect is essentially a concentration effect as well, and although the administration of the potent volatile inhalational agent in combination with nitrous oxide.
This is a simultaneous administration of two different anesthetic gases.
Nitrous oxide exhibits relatively low solubility however, it is administered in very high concentration compared to the potent inhalational agents.
Because of the large number of nitrous oxide molecules actually administered, significant alveolar to blood transfer occurs despite relatively low solubility.
When this happens there is a disproportionate reduction in the number of nitrous oxide molecules compared to potent, volatile anesthetic molecules and as a result the actual concentration of the volatile agent (i.e. molecules for volume) increases.
The "second-gas" in the "second-gas effect" is typically the potent volatile agent.
Consider the case in which the administered alveolar concentration of the potent volatile agent is 2% and is given a combination with nitrous oxide at 70% and oxygen at 28%. (Fi -= 2 / (2 + 28 + 70) = 2%. (Figure A below)
Because of the high vapor pressure associated with nitrous oxide, significant reduction in the number of nitrous oxide molecules will occur and we set this reduction at 50% and assume no significant change in potent volatile anesthetic concentration, i.e. it remains at 2%.
So, if we started out at 70 parts nitrous oxide, we now have 35 parts nitrous oxide, still 2 parts volatile agent, and still 28 parts oxygen.
![]() The concentration of the potent agent has increased in
accord with the following proportionality: FA =2/(2+ 35+ 28) =
3.1%. (Figure
B below)
The concentration of the potent agent has increased in
accord with the following proportionality: FA =2/(2+ 35+ 28) =
3.1%. (Figure
B below)
![]() All that
has really happened with a second gas effect is that the probability
of alveolar to blood transfer of nitrous oxide molecules is
higher than the probability of alveolar to blood transfer of
volatile agent molecules simply because there are more nitrous oxide
molecules available for transfer across the alveolar membrane.
All that
has really happened with a second gas effect is that the probability
of alveolar to blood transfer of nitrous oxide molecules is
higher than the probability of alveolar to blood transfer of
volatile agent molecules simply because there are more nitrous oxide
molecules available for transfer across the alveolar membrane.
Again, it is a simple matter of probabilities that the relative proportion of potent inhalational agent will increase compared to nitrous oxide resulting in a concentration increase.
The calculation that gives us the 3.1% is a result of one respiratory cycle 2/(2+ 35+ 28) = 3.1%.
At the end of the first cycle than we have 35 parts nitrous oxide, 28 parts oxygen and 2 parts inhalational agent.
The same proportionality applies with the second breath.
We start with 65 parts already accounted for and given that we are administering 70% nitrous oxide then 0.7 x 35 ("parts available)= 24.5 parts of nitrous oxide is added with the second breath; similarly, 0.28 x 35 parts = 9.8 parts of oxygen and 0.02 x 35 = 0.7 parts inhalation agent are obtained.
The running total after 2 breaths would be (2 + 0.7) / (0.7 + 9.8 + 24.5 + 2 + 28 + 35) or 2.7% inhalation agent. (Figure C below)
![]() The
clinical consequence of both concentration and second gas effects is to
decrease induction time.
The
clinical consequence of both concentration and second gas effects is to
decrease induction time.
|
|
|
|
|
|
The magnitude of the second gas effect can be appreciated in the graph below which compares administration of halothane (Fluothane), 0.5% either with 70% nitrous oxide or 10% nitrous oxide.
The rate of rise of FA/FI is enhanced at the higher nitrous oxide concentration.
Secondary source: 11Eger, II, E.I., "Concentration and Second Gas Effects" in Anesthetic Uptake and Action, The Williams & Wilkins Company, Baltimore, Maryland, Chapter 6, pp 113-121, 1974; primary source: Epstein, R.M, Rackow, H., Salanitre, E., and Wolf, G.L.: Influence of the concentration effect on the uptake of anesthetic mixtures: the second gas effect. Anesthesiology 25: 364-371, 1964. These experimental results were obtained in dogs.
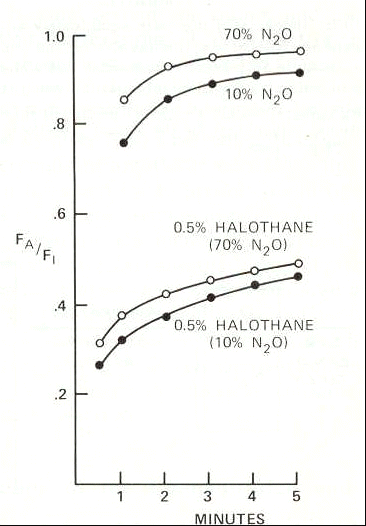 a
a
Generally, for volatile agents the rate of rise of FA/FI is typically fairly rapid, suggesting that small changes in ventilation rate would be unlikely to exhibit significant effect.
With anesthetics that are associated with rapid transfer from the alveoli to the blood, i.e. high blood: gas partition coefficients increased ventilation rate might increase rate of rise.
This result could only occur in ventilation rate were the rate determining step.
The minute ventilation rate, however, would not be expected to remain constant with increasing CNS anesthetic concentration, because of CNS depression.
The tendency then would be for reduction in ventilation rate and in FA/FI with time. One clinical benefit of this phenomenon, at least a potential benefit, is that an anesthetic overdose might be made somewhat less likely.
Most contemporary potent inhalational volatile anesthetics can significantly depressed respiration and consequently influence by this indirect method anesthetic uptake. (This effect presupposes spontaneous ventilation)
An example of CNS depression influencing percent alveolar anesthetic is noted below in the graph that depicts the effect of varying inspired halothane (Fluothane) concentration with respect to alveolar concentration. (reference: secondary source -10Eger II, E.I., "Uptake and Distribution" in Anesthesia 5th edition vol. 1 (Miller, R.D. editor; Cucchiara, R.F., Miller, Jr., E.D., Reves, J.G., Roizen, M.F. and Savarese, J.J., consulting editors) Churchill Livingstone, Philadelphia, 2000, pp 74-95; primary source: Munson, E.D, Eger, I.II, Boweres, D.L, Effects of anesthetic-depressed ventilation and cardiac output on anesthetic uptake. Anesthesiology 28: 251-259, 1973)
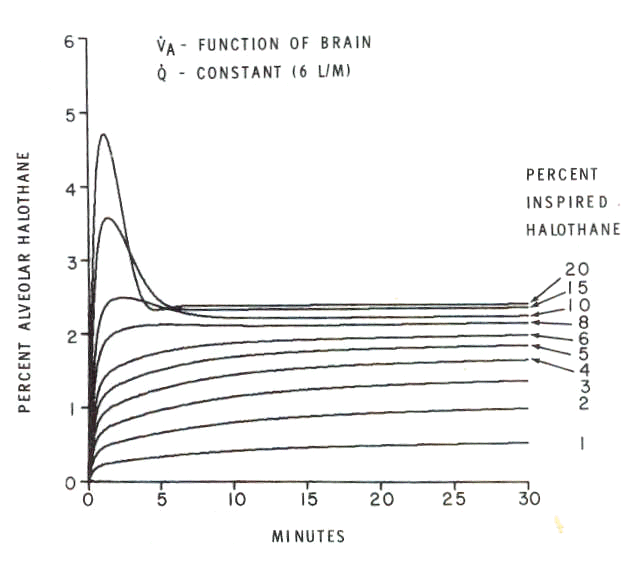
10The above graph illustrates that "an increase in inspired halothane concentration does not produce a proportional increase in the alvolar concentration because of progressively greater depression of ventilation which occurs as alveolar halothane is increased."
Note the initial overshoot seen at the higher halothane (Fluothane) inspired concentrations, reflecting the delay (a transport delay), between the alveoli compartment and the brain compartment. The principal result reported in the graph is that increasing inspired halothane (Fluothane) does not result in a proportional increase in alveolar concentration.
The interpretation for this phenomenon is that as the alveolar halothane (Fluothane) concentrations increased a progressive CNS depression occurs which manifests as reduced spontaneous ventilation.
Cardiovascular Effect: Perfusion
For reasons similar to that described above relative to ventilation effects, variation in cardiac output will have limited effect on FA/FI rate of rise during the initial transfer for sparingly soluble agents.
This result obtains because cardiac output will not be rate-limiting.
Recall that the increase in FA/FI will be affected by the probability of transfer of anesthetic gas molecules from the alveolar volume to the blood compartment and that initially there are no anesthetic molecules in the blood which could diffuse back into the alveolar volume.
For very soluble anesthetic gases, saturation of a given small volume of blood in immediate contact with the alveolar volume is more likely and therefore the possibility of significant transport of gas molecules from blood back to the alveolar volume is more likely.
In this special circumstance, with agents with the higher blood gas partition coefficients increasing cardiac output would be more likely to produce an effect.
The nature of the effect is that at higher cardiac output there is a reduction in the rate of rise of FA/FI as it is less likely that the anesthetic molecule which has already transferred to the blood compartment can diffuse back to the alveolar volume (since that particular molecule has, because of increased blood flow rates, been transported away from the alveolar membranes site). These relationships are noted in the graph below: (source: 12Eger, II, E.I., "Ventilation, Circulation and Uptake" in Anesthetic Uptake and Action, The Williams & Wilkins Company, Baltimore, Maryland, Chapter 7, p. 131, 1974.
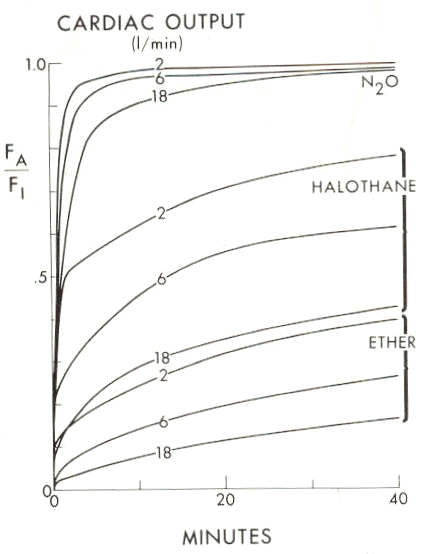
12 Cardiovascular Clinical Correlations:
Eventually, increased CNS or circulating anesthetic concentration leads to cardiovascular depression, which can be manifest as reduced cardiac output. Reduced cardiac output as noted above, would be associated with a more rapid rise in FA/FI .
12Again, alterations in cardiac output would be expected to cause effects for relatively soluble inhaled agents but would not as noted above produce much effect in sparingly soluble agents since the rate of rise in FA/FI is not affected much by local alveolar perfusion.
However, when more soluble or highly soluble agents are used and significant cardiac output reduction occurs such as in shock, an increase in the FA/FI ratio would be expected and in anticipation the concentration of inspired agent should be lowered.
Note in the above graph the difference in halothane (Fluothane) uptake as one goes from a cardiac output of 6 L/min to 2 L/min at any given time point.
In the case of very soluble agent, a significant fraction of the inspired (alveolar) anesthetic is transported in to the blood; let's say nearly all is moves into the blood.
If we decrease blood flow by 50%, we have the effect of concentrating the anesthetic in that volume.
In this case, arterial anesthetic (in equilibrium with the alveolar anesthetic), partial pressure would be doubled.
The doubling in anesthetic concentration would mean ultimately that the brain will "see" a double than expected number of anesthetic molecules transferring in and so there is a greater likelihood of anesthetic-mediated depression of respiratory & cardiac CNS control.
The increase in the rate of rise in FA/FI is influenced not only by the cardiovascular depression, but also by the typically concomitant increase in ventilation.
In order to manage patients who exhibit shock, agents with relatively low blood: gas solubility might be preferable as the alveolar concentration of these agents would not be especially sensitive to cardiopulmonary changes.
Nitrous oxide, a sparingly soluble agent, is often used in anesthetic management in patients with shock.
10Concurrent changes in perfusion and ventilation:
10Let's suppose that cardiac output is doubled, anesthetic uptake (transfer from the alveolar volume to the blood) would typically also be doubled all other factors remaining constant.
This effect would reduce the rate of rise in FA/FI .
If instead, ventilation rate were doubled, the rate of rise in FA/FI would presumably the doubled.
So the effects should cancel because we are doubling removal rate from the lungs (cardiac effects) and doubling anesthetic delivery to the lungs (ventilation rate).
Thus, considering the case in which both the cardiac output is doubled and the ventilation rate is doubled, the question is what would happen to FA/FI?
An initial inspection might suggest offsetting effects in which doubling of transfer from the alveolar volume to the blood (cardiac output is doubled) would be balanced by doubling of input to the alveolar volume (ventilation rate is doubled).
Accordingly, it might be guessed that these effects would be offsetting so that no change in FA/FI rate of rise would be observed.
10However, the assumption that doubling cardiac output doubles uptake into the blood is dependent on no change in the probability of net flux. (alveolar volume gas molecules transferred to the blood per unit time)
The validity of this assumption rests on a constant concentration of blood anesthetic in the face of a doubling of alveolar volume anesthetic concentration.
However, this condition does not obtained since the venous blood concentration of anesthetic steadily increases and therefore the likelihood is that the net flux decreases over time as the probability of anesthetic molecule transfer from the blood back into the alveolar volume is made more likely with decreasing alveolar: venous partial pressure difference.
The result of this analysis is that a doubling of both cardiac output and alveolar ventilation rates cause an increase in FA/FI rate of rise, probably small in magnitude
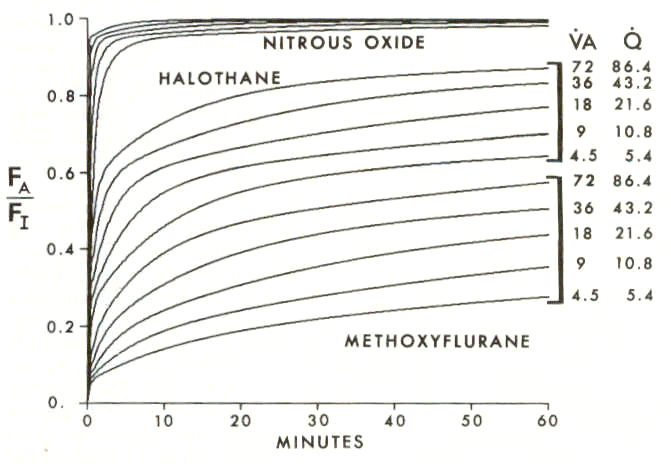
10This graph illustrates (by simulation analysis) the increase in FA/FI rate of rise associated with proportional alveolar ventilation and cardiac output increases.
The theoretical curves agree with experimental data (see original citation) The relatively small effect in FA/FI rate of rise, as elaborated below, might be expected for perfusion enhancement to all tissues. However the effect may be greater if preferential perfusion enhancement occurs to vessel-rich tissue and the process in general is dependent on the use of the relatively more soluble volatile agents. Primary source:as noted in reference 10, Eger, EI II, Bahman, SH, Munson, ES: Effect of age on the rate of increase of alveolar anesthetic concentration. Anesthesiology 35: 365-372. 1971.
10Enhanced cardiac output and ventilation rate might be associated with thyrotoxicosis or hyperthermia. In this situation it is unlikely that a significant change in anesthesia would be noted as a result of modifying FA/FI.
The general analysis presupposes that an increasing cardiac output results in a generalized in proportional increased in tissue perfusion, not favoring any particular tissue group.
However if vessel-rich groups are preferentially perfused, greater effects on FA/FI rate of rise would be seen.
This effect results from the rapid equilibrium apparent between blood and vessel-rich tissue with the consequence that an even faster equilibration would occur with increased perfusion. In that circumstance, blood coming from vessel rich tissue groups would exhibit nearly the same anesthetic gas partial pressure and in alveolar volume.
Because the blood is more nearly saturated when it is re-exposed to the alveolar volume, limited additional gas transfer can occur even if the alveolar ventilation is increased. This increased perfusion of vessel rich groups and increased ventilation rates will cause a more substantial FA/FI rate of rise.
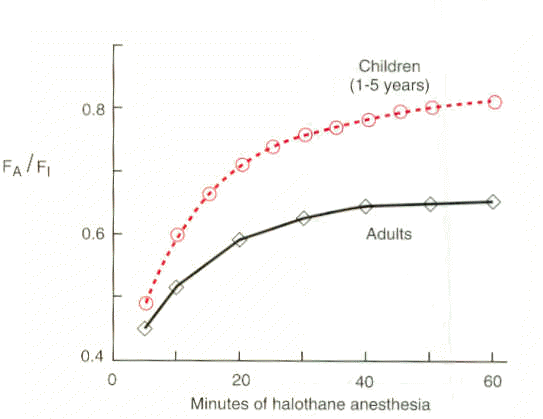
10In children, compared to adults, there is a relatively greater degree of ventilation and perfusion per kilogram and this observation may explain the significant increase in halothane (Fluothane) FA/FI rate of rise.
Another factor, is that in children, there appears to be a greater degree of vessel-rich tissue group perfusion compared to the adults.
So, in children and infants more rapid anesthesia development might be expected.
In additional factor is that there may be relatively higher CNS (brain) perfusion.
Below graph: reference 10 and Salanitre, E., Rackow, H: The pulmonary exchange of nitrous oxide and halothane in infants and children. Anesthesiology 30: 388-394, 1969.
5Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Stoelting, R.K., 3rd edition, Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, 1999, pp 36-37.
6Ebert, T. J. and Schmid III, P. G. "Inhalation Anesthesia" Ch. 15 in Clinical Anesthesia (Barash, P.G., Cullen, B. F., and Stoelting. R.K., eds) 4th Edition, Lippincott Williams& Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp. 377-387, 2001
7Family Practice Notebook (http://www.fpnotebook.com/LUN58.htm)
8Lung Function Fundamentals: (www.anaesthetist.com/icu/ organs/lung/lungfx.htm)
9General Biology Laboratory Exercises, Copyright ©2000, Purdue Research Foundation, Clark Gedney (http://biomedia.bio.purdue.edu/GenBioLM/GBRespiration/html/glossary.html)
10Eger II, E.I., "Uptake and Distribution" in Anesthesia 5th edition vol. 1 (Miller, R.D. editor; Cucchiara, R.F., Miller, Jr., E.D., Reves, J.G., Roizen, M.F. and Savarese, J.J., consulting editors) Churchill Livingstone, Philadelphia, 2000, pp 74-95.
11Eger, II, E.I., "Concentration and Second Gas Effects" in Anesthetic Uptake and Action, The Williams & Wilkins Company, Baltimore, Maryland, Chapter 6, pp 113-121, 1974
12Eger, II, E.I., "Ventilation, Circulation and Uptake" in Anesthetic Uptake and Action, The Williams & Wilkins Company, Baltimore, Maryland, Chapter 7, p. 131, 1974;