|
|
|
|
-
Foundations of Drug Metabolism
Drug Metabolism: Audio Overview (2025) -
 The liver is
the primary site for drug metabolism in the human body, although
drug metabolizing enzymes are also present in high concentration in
both small and large intestines.
The liver is
the primary site for drug metabolism in the human body, although
drug metabolizing enzymes are also present in high concentration in
both small and large intestines. -
This conclusion is supported by several factors:4
-
The liver is large and receives blood supply directly from the gastrointestinal tract by where the portal vein.
-
The liver itself receives about 30% of the cardiac output, receiving arterial blood from the hepatic artery as well as venous blood from the portal system.
-
The portal vein provides most (about 75%) of liver blood flow and contributes about 50% of the oxygen supply (the remainder supplied by the hepatic artery).
-
-
-
The liver also exhibits a high concentration of enzymes responsible for drug biotransformation, with most of the biotransformation occurring within hepatocytes.
-
-
-
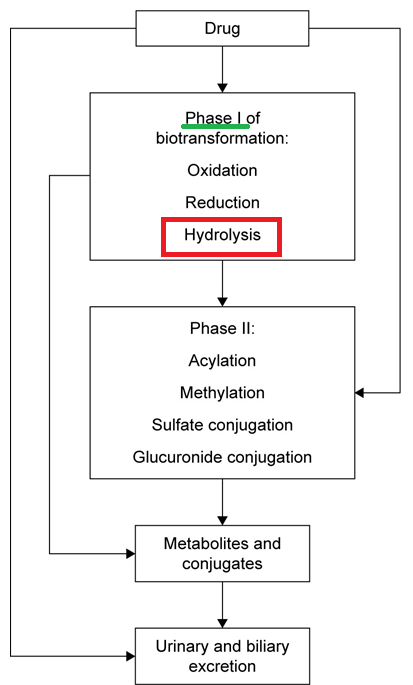
Drug metabolizing enzymes have been typically categorized as to phase I reactions or phase II reactions.1,5
-
Some categorizations include phase III, described as sites for additional metabolism and excretion and as belonging to superfamilies including ATP-binding cassette (ABC) and solute carrier transporters (SLC).
-
Mixed function oxidases system (cytochrome P450 system): Phase I Reactions
-
Microsomes have been used to study mixed function oxidases
-
Drug metabolizing enzymes are located in lipophilic, hepatic endoplasmic reticulum membranes.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum contains those enzymes responsible for drug metabolism.
-
-
The reaction
-
One molecule oxygen is consumed per substrate molecule.
-
One oxygen atom appears in the product while the other oxygen is in the form of water.
-
Oxidation-Reduction Process:
-
Two important microsomal enzymes:
-
Cytochrome P450: the terminal oxidase which exists in multiple enzyme isoforms.
Conversion of RH to ROH Representing Drug Oxidation29,30 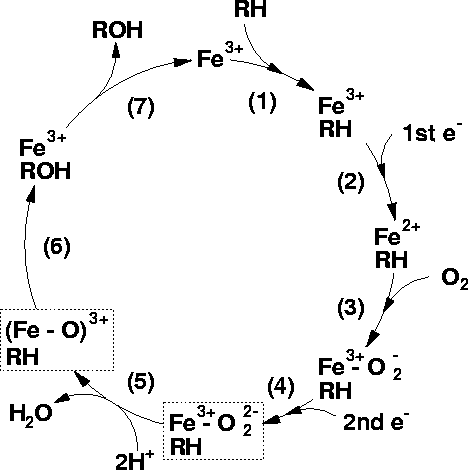
- Attribution
-
"The binding of a substrate to a P450 causes a lowering of the redox potential by approximately 100mV, which makes the transfer of an electron favourable from its redox partner, NADH or NADPH.
-
The first reduction -The next stage in the cycle is the reduction of the Fe3+ ion by an electron transfered from NAD(P)H via an electron transfer chain.
-
Oxygen binding An O2 molecule binds rapidly to the ion Fe2+ forming Fe2+-O2
-
Second reduction A second reduction is required by the stoichiometry of the reaction.
-
This has been determined to be the rate-determining step of the reaction
-
-
O2 cleavage: The O2 reacts with two protons from the surrounding solvent, breaking the O-O bond, forming water and leaving an Fe-O3+ complex.
-
Product formation The Fe-ligated O atom is transferred to the substrate forming an hydroxylated form of the substrate.
-
Product release The product is released from the active site of the enzyme which returns to its initial state."29
-
-
Seagall M Payne M Ellis S Tucker G Eddershaw P First principles investigation of singly reduce cytochrome P450. Xenobiotica 29(6): 561-571. July 1999. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/12872174_First_principles_investigation_of_singly_reduced_cytochrome_P450
- Attribution
-
-
-
Phase I Metabolism (left)
-
Attribution:
-
Saffarzadeh A Phase I Metabolism https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GGLddVpVg9M (9/2012).
-
Areo Saffarzadeh Youtube Channel
-
-
-
While the liver's role is preeminent, extrahepatic metabolism is also important.
-
Tissues such as the small intestine (noted above), kidneys, lungs, skin, and even the plasma contain drug-modifying-enzymes.
5 -
-
This presystemic elimination can significantly reduce the bioavailability of certain drugs, and its variability among individuals is a major source of differing drug responses.
6,7
-
-
-
-
Their primary purpose is to introduce or unmask a polar functional group—such as a hydroxyl (-OH), amino (-NH2), sulfhydryl (-SH), or carboxyl (-COOH) group—onto the parent drug molecule.
-
This modification is achieved through chemical reactions of oxidation, reduction, or hydrolysis.
-
The resulting metabolite is typically only slightly more water-soluble than the parent drug but now possesses a chemically reactive "handle" that makes it a suitable substrate for the next stage of metabolism
.8
-
-
Thus, Phase I reactions modify the drug’s chemical structure by oxidation, reduction, or hydrolysis processes.
-
 Phase I
metabolites are not necessarily inactive – some are
equally or
more active than the parent compound, and some
can be toxic.
Phase I
metabolites are not necessarily inactive – some are
equally or
more active than the parent compound, and some
can be toxic.
-
Sometimes on inactive drug is metabolized to become of the active form and the inactive drug is typically referred to as a "prodrug."1
-
An example of a prodrug activated by the cytochrome P450 system is cyclophosphamide, an antitumor agent, forming the "cell-killing" electrophilic form.
-
Another example is the anti-thrombotic drug clopidogrel, ultimately metabolized to an irreversible inhibitor form acting at platelet ADP P2Y12 receptors.1
-
-
-
-
Phase I metabolism is predominantly carried out by a family of oxidative enzymes known as cytochrome P450 (CYP) monooxygenases, located mainly in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of hepatocytes.5
-
The CYP450 system (also called the microsomal mixed-function oxidase system) is responsible for the oxidation of a wide variety of drugs. Key CYP isoenzymes include CYP3A4/5, CYP2D6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP1A2, among others.
Over 75% of phase I metabolism are due to the activity of the cytochrome P450 drug metabolizing system.
-
As a group these enzymes are classified as heme-coupled monooxygenases, binding oxygen (also binding carbon monoxide which leads to the wavelength absorption at 450 nm, providing the namesake for this enzyme system).
-
CYP3A4 is the most abundant isoform in the liver and alone accounts for ~50% of drug metabolism.5
-
CYP2D6, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 are also highly clinically relevant; together these enzymes metabolize a large portion of commonly used medications.
-
Non-CYP enzymes contributing to Phase I reactions include flavin-containing monooxygenases (FMOs), alcohol/aldehyde dehydrogenases, monoamine oxidases, and various esterases and amidases (which catalyze hydrolysis of ester or amide bonds).11,12
-
-
-
-
Although we will be discussing phase II reactions later, it is notable that the clinician may prescribe the same dose of an agent to two people and get different outcomes as result of differing states of drug metabolizing systems.
-
For example, underlying liver disease, age extremes (neonates and the elderly), and genetic polymorphisms in metabolizing enzymes can all impact the speed at which a drug is metabolized and cleared.13,14
-
Elderly patients often have reduced Phase I (CYP450-mediated) metabolism, while Phase II pathways are relatively preserved.15
-
Newborn infants have immature Phase II conjugation capacity – a classic illustration is “gray baby syndrome” from neonatal chloramphenicol toxicity, caused by infants’ inability to glucuronidate and clear the drug.16
-
-
-
Cytochrome P450 Isoenzymes (Isoforms)
-
Important CYP isoenzymes include CYP3A4/5, CYP2D6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP1A2, among others.5
-
Of these, CYP3A4 is the most abundant isoform in the liver, accounting for ~50% of drug metabolism.17
-
-

-
Attribution:
-
The figure above corresponds to figure 1 of reference 17.
-
Sychev D Ashraf G Svistunov A Maksimov M Tarasov V Chubarev V Otdelenov B Denisenko N Barreto G Alieve G The cytochrome P450 isoenzyme-some new opportunities for the prediction of negative drug interactions in vivo. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 May 8;12:1147-1156. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5951216/ (17)
-
-
-
-
-
Oxidation reactions are the most common Phase I processes.
-
Oxidation reactions usually involve inserting an oxygen atom or removing electrons/hydrogens from the drug.18
-
The CYP450 enzymes catalyze oxidation via a complex cycle requiring NADPH and O2 .
-
Overall, Phase I reaction using the CYP450 system includes both an oxidative and reductive step using NADPH and not ATP.5
-
Drug + O2+ NADPH → Drug*+ H20 + NADP+.5
-
-
-
Examples
-
Metoprolol19 (a β-adrenergic receptor antagonist) and omeprazole21 (a proton pump inhibitor) are oxidatively metabolized by CYP2D6 and CYP2C19, respectively.19,21
-
Enzyme polymorphism can result in markedly different drug levels in patients (poor vs. ultrarapid metabolizers).20,21
-
-
Codeine is a classic example of an activation via a Phase I reaction.
-
Codeine is a prodrug that is oxidatively O-demethylated by CYP2D6 into morphine, which is the active opioid.
-
Patients who are CYP2D6 poor metabolizers derive little analgesic effect from codeine.
-
By contrast, ultrarapid metabolizers convert codeine to morphine quickly and abundantly, risking morphine toxicity (e.g. excessive CNS depression) even at standard doses.22
-
Explanation:23
-
A patient with two nonfunctional alleles of the CYP2D6 subfamily would be expected to exhibit limited drug metabolism.
-
An individual with one or two functional alleles would exhibit extensive codeine metabolism.
-
Further, someone exhibiting duplicated or amplified active CYP2D6 genes would be classified as having ultrarapid metabolism.
-
Reduced activity of CYP3A4 (e.g. by other medications or reduced renal function) which contribute to codeine toxicity.
-
"Metabolic pathways of Codeine Biotransformation"23 
-
Attribution:
-
"The conversion of codeine into norcodeine by CYP3A4 and into codeine-6-glucuronide usually represents 80% of codeine clearance, and conversion of codeine into morphine by CYP2D6 represents only 10% of codeine clearance (Blue arrows).
-
"Morphine is further metabolized into morphine-6-glucuronide and into morphine-3-glucuronide. Morphine and morphine-6-glucuronide have opioid activity. (Green arrows).
-
"Glucuronides are eliminated by the kidney and are thus susceptible to accumulation cases acute renal failure.
-
"The patient (Red arrows) had ultrarapid CYP2D6 metabolism, inhibition of CYP3A4 as result of treatment with clarithromycin and voriconazole, and glucuronide accumulation due to acute renal failure.
-
Red arrows with dotted lines indicate low levels of drug conversion or elimination, green arrows with dotted lines indicates low levels of brain penetration, and thick arrows indicate high levels." Figure 1 from Reference 23
-
Gasche Y Daali Y Fathi M Chiappe A Cottini S Dayer P Desmeules J Codeine Intoxication Associated with Ultrarapid CYP2D6 Metabolism .N. Eng J Med 2004;351: 2827- 2031. https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa041888 (Reference 23)
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Another example is the antiplatelet prodrug clopidogrel, which requires CYP2C19-mediated oxidation to form its active thiol metabolite.
-
Individuals with loss-of-function CYP2C19 alleles (≈2% of Caucasians, up to 15–20% of Asians) are “poor metabolizers” who activate clopidogrel poorly.
-
These patients will have a reduced antiplatelet effect and are at higher risk of stent thrombosis; the FDA label for clopidogrel carries a warning about diminished efficacy in CYP2C19 poor metabolizers and suggests considering alternative antiplatelet agents in such cases.24
-
-
-
Phase I oxidation can sometimes produce a toxic metabolite
-
The analgesic acetaminophen (paracetamol) is mainly cleared by Phase II conjugation, but about 5–10% of a therapeutic dose is oxidized by CYP2E1 and other CYPs to a reactive intermediate NAPQI (N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine).
-
NAPQI is normally detoxified by conjugation with glutathione.
-
In acetaminophen overdose, however, the primary sulfation and glucuronidation pathways saturate and more drug undergoes Phase I oxidation.
-
 Excessive NAPQI is generated, which depletes hepatic
glutathione and then covalently binds to liver proteins,
causing hepatocellular necrosis.25
Excessive NAPQI is generated, which depletes hepatic
glutathione and then covalently binds to liver proteins,
causing hepatocellular necrosis.25
-
Administering (N-acetylcysteine) Increases cellular glutathione levels which in turn promotes NAPQI conjugation that reduces toxicity.26
-
-
-
-
-
-
-

-
Attribution:
-
The figure above corresponds to figure 1 of reference 17.
-
Sychev D Ashraf G Svistunov A Maksimov M Tarasov V Chubarev V Otdelenov B Denisenko N Barreto G Alieve G The cytochrome P450 isoenzyme-some new opportunities for the prediction of negative drug interactions in vivo. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 May 8;12:1147-1156. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5951216/ (17)
-
-
-
-
-
Reduction reactions are chemical opposite of oxidation with reduction involves the gain of electrons by the drug molecule.
-
These reactions, often catalyzed by reductases, are more common for compounds containing nitro (-NO2) or azo (-N=N-) groups and tend to occur in environments with low oxygen tension, such as within the anaerobic bacteria of the gut.27
-
The conversion of warfarin, which is the ketone in its structure, to a reduced alcohol metabolite is catalyzed by reductase (cytosolic). The major warfarin pathway is catalyzed by cytochrome P450, forming hydroxywarfarins.28
-
Warfarin Metabolism28 
-
"Hydroxywarfarins are the predominant metabolites of warfarin metabolism that may be cleared through a novel carbonyl reduction pathway.
-
"Warfarin is directly metabolized via major pathway by membrane-bound cytochromes P450 to form hydroxywarfarins and a minor pathway by cytosolic reductases to form warfarin alcohols.
-
"Further reduction of the hydroxywarfarin major metabolites by reductases to form hydroxywarfarin alcohols may also be possible is the secondary reaction."
-
Attribution:
-
Slightly modified from figure 1 of reference 28
-
Pouncey D Barnette D Sinnott R Phillips S Flynn N Hendrickson H Swamidass S Miller G Discovery of Novel Reductive Elimination Pathway for 10-Hydroxywarfarin. Front Pharmacol. 2022 January 13;12: 805133. (National Library of Medicine). https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8793337/ (reference 28)
-
-
-
-
-
-
Attribution:
-
The figure above corresponds to figure 1 of reference 17.
-
Sychev D Ashraf G Svistunov A Maksimov M Tarasov V Chubarev V Otdelenov B Denisenko N Barreto G Alieve G The cytochrome P450 isoenzyme-some new opportunities for the prediction of negative drug interactions in vivo. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 May 8;12:1147-1156. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5951216/ (17)
-
-
-
-
Hydrolysis reactions involve breaking chemical bonds by the addition of water, typically acting on ester or amide bonds.
-
These reactions are often catalyzed by esterases and amidases found in the liver, plasma, and other tissues.
-
Many prodrugs are designed as esterified forms that are hydrolyzed in vivo to release the active drug.
-
Enalapril, an Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, is an inactive ester that is hydrolyzed in the liver to enalaprilat, the active di-acid form.31
-
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is hydrolyzed by esterases to salicylic acid.32
-
Succinylcholine is a neuromuscular antagonist which is inactivated by pseudocholinesterase (an esterase) in plasma.
-
Patients with an atypical pseudocholinesterase enzyme (due to a genetic variant) hydrolyze succinylcholine much more slowly, resulting in prolonged paralysis after standard doses – an important pharmacogenetic consideration in anesthesia.33
-
-
-
Clinically Used Drugs Metabolized by Cytochrome P450 isoforms and Factors Influencing Variability.35 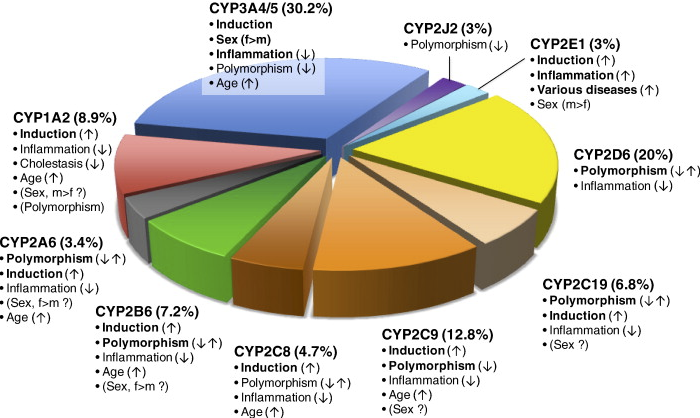
-
"Fraction of clinically used drugs metabolized by P450 isoforms and factors influencing variability.
-
"The total of 248 drug metabolism pathways with known CYP involvement... were analyzed. Each metabolic pathway was counted once for the major contributing CYP isoform.
-
"Important variability factors are indicated by bold type with possible directions of influence indicated (, ↑ increased activity; ↓ decreased activity;↑↓ increased and decreased activity). Factors of controversial significance are shown in parentheses."
-
Attribution:
-
Corresponds to figure 1 of reference (35).
-
Zanger U Schwab M Tochrome P450 enzymes-a drug metabolism: Regulation of gene expression, enzyme activities and impact of genetic variation. Pharmacology & Therapeutics. Volume 138, Issue 1, April 2013, 103-141. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0163725813000065 (Reference 35)
-
-
-
-
-
-
Major Phase I Enzymes and Examples Enzyme35,36 (Location)
Common Substrates
Clinical Notes
CYP3A4/5 (liver, gut)
About 50% of drugs-e.g. midalzolam, statins, cyclosporine, calcium channel blockers (amlodipine), etc.
Abundant enzyme, overlaps with CYP3A5. Induced by rifampin, phenytoin (→faster clearance of substrates); Inhibited by grapefruit juice, azole antifungals, etc. (→higher levels of substrates).5
CYP2D6 (liver)
β-blockers (metoprolol), many antidepressants (SSRIs, tricyclics), codeine → morphine, tramadol, tamoxifen, etc.
Highly polymorphic: 5-10% of Caucasians are poor metabolizers (non-functional CYP2D6) and about 1-2% are ultrarapid (gene duplications). Effects drug efficacy & toxicity (e.g. codeine, ineffective in poor metabolizers, dangerous in ultrarapids)22
CYP2C9 (liver)
Warfarin, phenytoin, NSAIDs (e.g ibuprofen), sulfonylureas (glipizide), losartan (activation)
Genetic variance reduce enzyme activity leading to slower metabolism. Warfarin clearance is significantly reduced by 2/3 as result of genetic variants, so carriers need lower doses; they also have higher risk of bleeding on standard doses. Phenytoin dose should be lower in CYP2C9 slow metabolizers to avoid toxicity.34
CYP2C19 (liver)
Clopidogrel (activation), proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole and others), diazepam, tricyclic antidepressants.
Polymorphisms combinations (about 15% poor metabolizers); poor metabolizers cannot activate clopidogrel well, leading to reduced antiplatelet effect. Ultrarapid metabolizers (CYP2C19*17 allele) clear proton pump inhibitors faster, which can diminish the efficacy of standard doses). Consider alternative therapy or dose adjustments based on genotype for certain drugs.24
CYP1A2 (liver)
Theophylline, caffeine, tizanidine, tricyclic antidepressants, warfarin (minor pathway)
Induced by smoking (polycyclic hydrocarbons induce CYP1A2 - smokers metabolize caffeine/theophylline faster. Inhibited by fluroquinolone antibiotics (ciprofloxacin). Genetic variability exists but less pronounced clinical effect compared to above enzymes.
Esterases (plasma, tissues)
Prodrugs like oseltamivir (Tamiflu), heroin → morphine, local anesthetic esters (procaine), succinylcholine (via pseudocholinesterase).
Non-CYP phase I metabolism. Pseudocholinesterase deficiency (genetic) leads to reduced succinylcholine hydrolysis-most monitored for prolonged apnea. Oseltamivir's activation by hepatic esterases is usually rapid unless liver severely damaged.
-
 Phase I
reactions
and
clinical implications
Phase I
reactions
and
clinical implications
-
If a patient is taking two drugs that are substrates of the same CYP enzyme, competition for metabolism can occur; one drug may raise the blood level of the other.
-
One drug may inhibit a CYP enzyme that metabolizes another drug (leading to increased levels/toxicity of the second drug), or induce the enzyme’s expression (leading to faster clearance and reduced effect of the second drug
.5
-
-
-
The anticonvulsant phenytoin induces CYP3A4 and other enzymes, which can reduce the efficacy of co-administered drugs like oral contraceptives or corticosteroids.
-
Conversely, itraconazole (an azole antifungal) inhibits CYP3A4, so taking it with a CYP3A4 substrate like simvastatin can precipitate statin toxicity (rhabdomyolysis).
-
Recognizing Phase I enzyme involvement helps avoid adverse drug–drug interactions and guides dosing (e.g. starting warfarin at a lower dose in a patient known to have CYP2C9 reduced-function alleles.34
-
-
-
 Phase I metabolism tends to
decline with age
and in liver disease, so drugs dependent on extensive Phase I
clearance (e.g. diazepam) may have prolonged half-lives in the
elderly, whereas drugs primarily undergoing Phase II may be less
affected by aging.15
Phase I metabolism tends to
decline with age
and in liver disease, so drugs dependent on extensive Phase I
clearance (e.g. diazepam) may have prolonged half-lives in the
elderly, whereas drugs primarily undergoing Phase II may be less
affected by aging.15
-

References
-
Gonzalez F Coughtrie M Chapter 5 Drug Metabolism In Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (Brunton LL Knollman BC eds) McGraw Hill LLC (2023).
Correia M Drug Biotransformation Chapter 4 in Katzung's Basic & Clinical Pharmacology (Vanderah TW, ed) 16e McGraw Hill 2023.
Ritter J Flower R Henderson G Loke Y MacEway D Robinson E Fullerton M Rang & Dale's Pharmacology Chapter 10 Drug Metabolism and Elimiantion Elsevier 2024.
Vaja R Rana M Anesthesia an Intensive Care Medicine. 2020 September 22;21(10): 517-523. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7508170/
Phang-Lyn S Llerena V Biochemistry, Biotransformation. StatPearls. National Library of Medicine Bookshelf. (Last update: August 14, 2023). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544353/
IU PHAR Pharmacology Education Project: Drug metabolism. https://www.pharmacologyeducation.org/pharmacology/drug-metabolism
McDonnell A Dang C Basic Review of the Cytochrome P450 System. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2013 July 1;4(4): 263-268. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4093435/
Yartzev A Phase I and phase II biotransformation reactions. Deranged Physiology: Pharmacokinetics. (Last updated December 18, 2023). https://derangedphysiology.com/main/cicm-primary-exam/pharmacokinetics/Chapter-3355/phase-i-and-phase-ii-biotransformation-reactions
Nazi, Y The Role of Phase I and Phase II Metabolic pathways in Pharmacokinetics. J Pharma Reports, 8: 225. September 23, 2024. https://www.longdom.org/open-access-pdfs/the-role-of-phase-i-and-phase-ii-metabolic-pathways-in-pharmacokinetics.pdf
de Araujo E Wright T Saqib B Keillor J Gunning P An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry & Molecular Recognition. 1.5: Drug Metabolism (2024. LibreTexts (Chemistry).*
Romano F Non-Cytochrome P450 Enzymes in Drug Metabolism: Emerging Roles. International Journal of Pharmaceutical, Chemical and Biological Sciences (2024) Volume 14, Issue 3. https://www.ijpcbs.com/articles/noncytochrome-p450-enzymes-in-drug-metabolism-emerging-roles-110654.html
Cerny M Prevalence of Non-Cytochrome P450-Mediated Metabolism in Food and Drug Administration-Approved capital oral and Intravenous Drugs: 2006-2015. Drug Metabolism and Disposition. Volume 44, Issue 8, August 2016, 1246-1252. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0090955624113670
D'Onofrio G Santagelo A Riva A Striano P Genetic polymorphisms of drug-metabolizing enzymes in older and newer anti-seizure medications. Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology. Volume 20, Issue 6, 2024. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/17425255.2024.2362190
Konstandi M Johnson E Age-related modifications in CYP-dependent drug metabolism: role of stress. Frontiers in Endocrinology. Volume 14, May 23, 2023. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/endocrinology/articles/10.3389/fendo.2023.1143835/full
Klotz U Pharmacokinetics and drug metabolism and the elderly. Drug Metab Rev. 2009;41(2): 67-76. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19514965/
Oong G Tadi P. Chloramphenicol StatPearls. National Library Medicine Bookshelf. (Last update July 3, 2023). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555966/#
Sychev D Ashraf G Svistunov A Maksimov M Tarasov V Chubarev V Otdelenov B Denisenko N Barreto G Alieve G The cytochrome P450 isoenzyme-some new opportunities for the prediction of negative drug interactions in vivo. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 May 8;12:1147-1156. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5951216/
Phase 1 Metabolism University of Nottingham. https://www.nottingham.ac.uk/helmopen/rlos/biological-sciences/gastrointestinal-system/liverdrug/page_three.html
Berger B Bachmann F Duthaler U Krahenbuhl S Haschke M Cytochrome P450 Enzymes Involved in Metoprolol Metabolism and Use of Metoprolol as a CYP2D6 Phenotyping Probe Drug. Front Pharmacol. 2018 July 24;9: 774. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6066528/
Meloche M Khazaka M Kassem I Barhdadi A Dube M-P de Denus S CYP2D6 polymorphism and its impact on the clinical response to metoprolol: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Bt J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 April 5;86(6): 1015/1033. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7256128/
Dean L Kane M Omeprazole Therapy and CYP2C19 Genotype. Medical Genetics Summaries. National Library of Medicine Bookshelf. (Last update February 4, 2021). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK100895/
Crews K Gaedigk A Dunnenberger H Klein T Shen D Callaghan J Kharasch E Skaar T Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guidelines for Codeine Therapy in the context of Cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) Genotype. National Library of Medicine: Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011 December 28;91(2): 321-326. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3289963/
Gasche Y Daali Y Fathi M Chiappe A Cottini S Dayer P Desmeules J Codeine Intoxication Associated with Ultrarapid CYP2D6 Metabolism .N. Eng J Med 2004;351: 2827- 2031. https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa041888
Dean L Kane M Clopidogrel Therapy and CYP2C19 Genotype. Medical Genetics Summaries. National Library Medicine Bookshelf. (Last update: December 1, 2022). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK84114/#
Heldring M Shaw A Beltman J Unraveling the effect of intra- and intercellular processes on acetaminophen-induced liver injury. npi Systems Biology and Applications 8, Article number: 27 (2022). https://www.nature.com/articles/s41540-022-00238-5#
Ershad M NMaji A Patel P Vearrier D N-Acetylcysteine.
StatPearls. National Library of Medicine Bookshelf. (Last update February 29, 2024). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537183/Mastering Phase I Metabolism for Better Drugs: Principles of Phase I Metabolism. NumberAnalytics. https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/mastering-phase-i-metabolism-for-drug-development
Pouncey D Barnette D Sinnott R Phillips S Flynn N Hendrickson H Swamidass S Miller G Discovery of Novel Reductive Elimination Pathway for 10-Hydroxywarfarin .Front Pharmacol. 2022 January 13;12: 805133 . (National Library of Medicine). https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8793337/
Seagall M Payne M Ellis S Tucker G Eddershaw P First principles investigation of singly reduce cytochrome P450. Xenobiotica 29(6): 561-571. July 1999. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/12872174_First_principles_investigation_of_singly_reduced_cytochrome_P450
Cytochrome P450. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytochrome_P450
Faruqi A Patel P Jain A Enalapril. StatPearls. National Library of Medicine Bookshelf. (Last update: February 13, 2024). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557708/
Aspirin. DrugBank. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00945
Hager H Patel P Burns B Succinylcholine chloride. StatPearls. Natl Library of Medicine Bookshelf. (Last update: February 15, 2025). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499984/
Chong K Warfarin Dosing and VKORC1/CYP2C9. Medscape. Updated: January 12, 2021. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1733331-overview#
Zanger U Schwab M Tochrome P450 enzymes-a drug metabolism: Regulation of gene expression, enzyme activities and impact of genetic variation. Pharmacology & Therapeutics. Volume 138, Issue 1, April 2013, 103-141. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0163725813000065
Lynch T Price A The Effect of Cytochrome P450 Metabolism on Drug Response, Interactions, and Adverse Effects. Am Fam Physician. 2007;76(3): 391-396. https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2007/0801/p391.html
-