Medical Pharmacology: Renal Pharmacology Practice Questions
Choose the correct answer for each question.
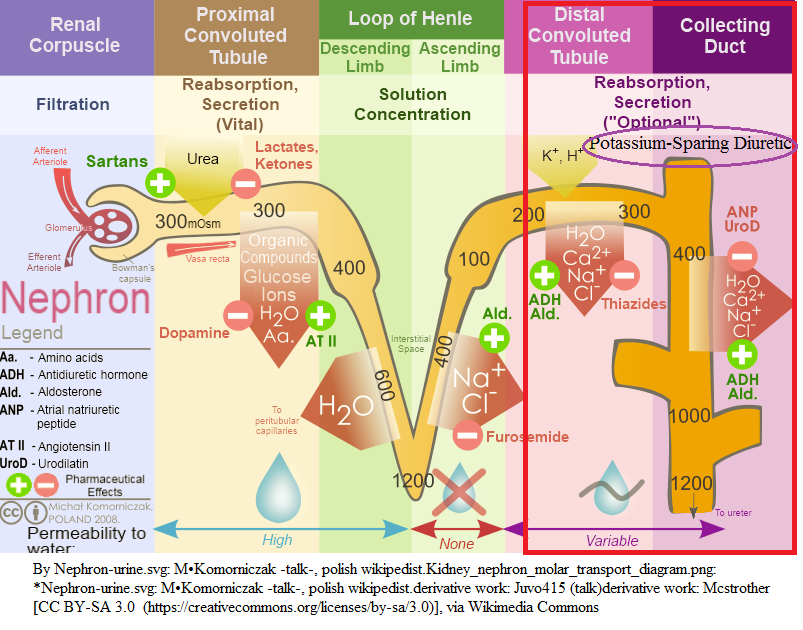
Renal tubule localization(s) of endothelial cells expressing high aldosterone affinity cytosolic mineralocorticoid receptors.
- Collecting duct (epithelial cells)
- Late distal tubule (epithelial cells)
- Both
- Neither
Aldosterone-mineralocorticoids receptor complex induces in the nucleus aldosterone-itis proteins (AIPs)
- True
- False
This/these agents inhibit aldosterone binding to mineralocorticoid receptors.
- Eplerenone
- Spirolactone
- Both
- Neither
Concerning pharmacological effect/effects a mineralocorticoid receptor blockers:
- Urinary excretion effects similar to those caused by epithelial sodium channel inhibitors.
- Clinical effectiveness of mineralocorticoid receptor blockers is dependent on endogenous aldosterone concentrations.
- Both
- Neither
Side effects/effects associated with spirolactone administration include(s):
- Impotence
- Menstrual irregularity
- Gynecomastia
- A & B
- B & C
- A & C
- A, B & C
Mineralocorticoids blockers are often combined with loop diuretics are thiazides in management of high blood pressure and in treating edema.
- True
- False
Use/uses of mineralocorticoids blockers:
- Treating resistant hypertension secondary to primary hyperaldosteronism
- Managing refractory edema due to secondary aldosteronism.
- Both
- Neither
In some patients early treatment with mineralocorticoid blockers decrease mortality following myocardial infarction with systolic dysfunction.
- True
- False
Principal risk associated with mineralocorticoids receptor blockers: hyperkalemia
- True
- False
Adverse effect(s) associated with spirolactone administration:
- Peptic ulcer
- Gastritis
- Both
- Neither
|
If you wish to return to the Table of Contents
in ENGLISH, press the RETURN button above. |
|
Otherwise, if the text is NOT displayed in
English and you are ready to leave this page,
Press here
to return to the Table of Contents
 |