|
|
|
Anesthesia Pharmacology Chapter 4: Physics and Anesthesiology
We have examined hemoglobin which is an example of a relatively complex protein containing several subunits (4) and exhibiting the special properties of positive cooperativity as well as response to allosteric effector molecules.
Other examples include RNA polymerase, consisting of multisubunits, responsible for initiation and RNA synthesis.
54The term to describe higher-order structure for proteins that exhibit multisubunits is quaternary structure.
Stabilization of the complex interactions between subunits occurs as a result of non-covalent interactions.
These complex multisubunit proteins apparently have evolved in a manner that allows functional regulation by binding of small molecules incites other than the principal binding / catalytic site.
Although it is possible to determine the amino acid composition of these complex proteins and even the sequence of the amino acids, most of the interesting functional aspects are revealed only when the higher order, three-dimensional structures are available.
Even beyond that, the specific way that the proteins and moves, transitioning from one state to another, is even more revealing.
Ultimately description of electronic charge position and magnitude changes between the protein moieties within the binding domain and the small molecules that interact there lead to possibly the deepest understanding of complex protein functional dynamics.
54The three-dimensional structure of these complex multisubunit, i.e. oligomeric proteins has been determined for certain oligomers through the use of the technique called x-ray crystallography.
The first protein for which x-ray analysis was performed was hemoglobin.
As might be apparent from the name, globin refers to the protein component, which consists of both alpha and beta chains.
Although we have talked about some other general structural features of hemoglobin we've not talked about dimensional aspects-for example the molecule resembles a sphere and has a diameter about 5.5 nm (1 x 10-9 m).
Oxygen binding sites are located about 2.5 nm (nanometers) apart.
Other aspects of interest include the observation that the major interaction is between alpha & beta chains as opposed to alpha-alpha or beta-beta chains.
![]()
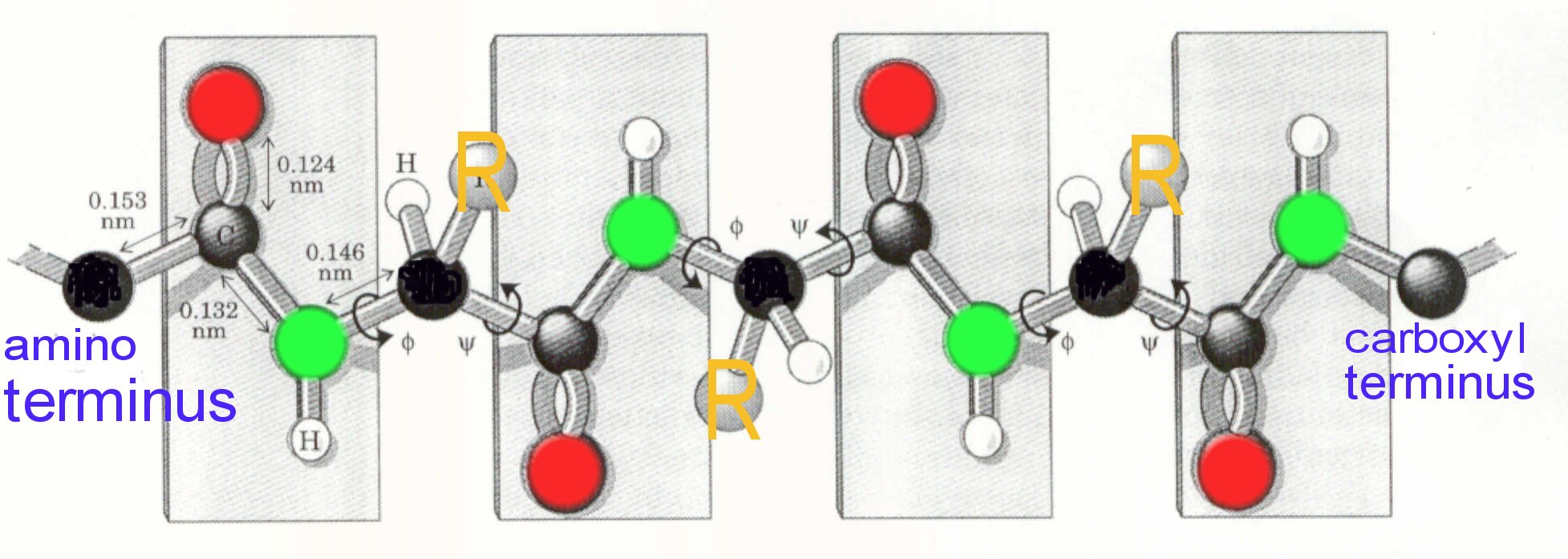
54As we suggested earlier, proteins consist of sequences of amino acids. These sequences define the protein's primary structure. It turns out that a string of these amino acids together form a polypeptide and that the polypeptide may arrange itself in solution to have a preferred three-dimensional conformation. The designation of the confirmation as "preferred" is in reference to a relatively thermodynamically stable structure. A The most common three-dimensional relationship between amino acids was determined to be helical in nature and was called the alpha helix. As a side note, which we will consider in detail later, amino acids differ from one another by having different "R" groups. This point is brought up now only to note that in the alpha helical structure a polypeptide backbone winds around the long axis of the molecule and R groups face outward from the backbone. It is possible to define an aspect of the alpha helix in terms of the longitudinal distance associated with a single turn. The repeating unit distance is about 0.56 nm. The alpha helical structure appears below:
![]()
55The secondary structure must by necessity reference the amino acids themselves and how they bond to one another.
To introduce this topic, we'll first begin by looking at a two-dimensional representation of the peptide bond geometry, below, (attribution: Ronald C. Beavis, Ph.D. Senior Research Scientist Eli Lilly & Company; David Fenyö, Ph.D. Research Associate, The Rockefeller University.
54Note in the figure above that the "alpha" carbon is separated from the next "alpha" carbon by three covalent bonds (Calpha --C--N--Calpha ).
Again using x-ray crystallographic analysis, it has been determined that the amide bond (C--N) is slightly shorter than that found in an amine that the atoms appeared to be on the same plane, i.e. coplanar.
The finding of coplanarity suggests structural rigidity, consistent with partially electron sharing (2 pairs) between the carbonyl oxygen and the amide nitrogen.
The carbonyl oxygen has a slight negative charge and by contrast the nitrogen has a slight positive charge, resulting in what is called on electric dipole.
The arrangement of the peptide group atoms was thought by Pauline and Corey to configure such that the oxygen of the carbonyl group and the hydrogen atom of the nitrogen are relatively far apart (trans position).
The sharing of the electrons described earlier between the carbonyl oxygen and the amide nitrogen results in a double bond characteristic that resists rotation.
Overall the polypeptide chain can be thought of as consisting of rigid pairs of atoms which are separated by substituted "methylene groups".
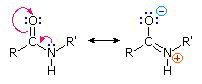 |
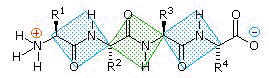 |
These methylene groups (CH-R) and in particular the R substituent confers the individuality associated with different amino acids and beyond that interaction of R groups are important in the folding of the initial polypeptide chain ultimately resulting in higher order protein structures in which the special protein function can be found.
One end of the polypeptide chain will consist of an amine group, while the other end consists of a carboxyl group; the amine end is referred to as having an amino terminus (N terminal) and the opposite end is designated as having a carboxy terminal (C terminus).
Although we specified rigidity for the C--N bond, rotation can occur about N--Calpha and the Calpha --C within limits defined by spatial interference between atoms in the backbone and atoms comprising the amino acid site chains i.e. the R groups.
By convention, certain symbols are used to describe bond rotation: N-C bond rotational angle is defined as phi (
); the Calpha -C bond rotation is defined by psi (
). A plot of allowable conformations, defined by values of phi (
) and psi (
) is represented in a Ramachandran plot.
The series of amino acids that describe the protein is the protein's primary structure.
 |
Black above represents the
carbon
Gray above represents the carbonyl carbon
Green above represents nitrogen
Red above represents oxygen
"R" represents the amino acid side chain
![]()
Alanine |
Serine |
|
|
carbonyl group |
carboxyl group |
| alpha carbon (hydrogen attached) | amino group | carboxylic group | side chain (R group) |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
. |
![]()
|
|
 |
 |
* attribution for these images from Chemistry 641 course by Professors Bahnson & Mueller (http://www.udel.edu/chem/mueller/pages/chem641/chem641.html)
Citations
54Lehninger, AL, Nelson, DL, Cox, MM, "The Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins" in Principles of Biochemistry with an Extended Discussion of Oxygen-Binding Proteins, Chapter 7, , 160-187, Worth Publishers, New York, 1993.
55Ronald C. Beavis, Ph.D. Senior Research Scientist Eli Lilly & Company and David Fenyö, Ph.D. Research Associate,The Rockefeller University.(http://prowl.rockefeller.edu/aainfo/contents.htm)
56attribution for these images from Chemistry 641 course by Professors Bahnson & Mueller (http://www.udel.edu/chem/mueller/pages/chem641/chem641.html)
57attribution: Michigan State University: Virtual Text (http://www.cem.msu.edu/~reusch/OrgPage/VirtualText/protein2.htm)