|
|
|
Anesthesia Pharmacology Chapter 4: Physics and Anesthesiology
Increase in Alveolar fractional concentration (FA)
Inspiratory capacity (IC) = 3500 ml
7Functional reserve capacity would be approximately 2300 ml; definition: volume remaining in lungs at resting expiratory levels: equivalent to alveolar volume (A) consisting of respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts (30%-40%); and alveoli: (60%-70%). Normal range is about 1800 ml to 3400 ml.
Factors that increase FRC include: emphysema, aging, asthma, peribronchial asthma.
Factors the decrease FRC include: age, obesity, supine posture, sedation
Vital capacity = 4600 ml
Total lung capacity = 5800 ml
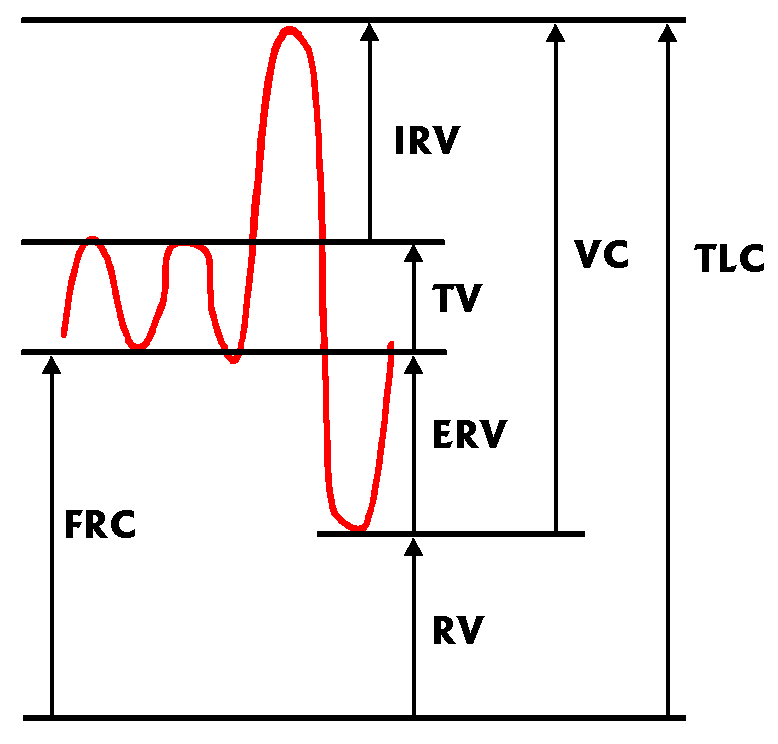
Figure above from reference 8:
![]() FRC = Functional Reserve Capacity
FRC = Functional Reserve Capacity
TV = Tidal volume
VC = Vital capacity
RV = Residual Volume
TLC = Total Lung Capacity
ERV = Expiratory Reserve Volume
IRV = Inspiratory Reserve Volume
![]() Minute ventilation (Respiratory rate x Tidal volume,
(0.5 L): Adult range 5-10 L/minute; neonatal range = 200-300
ml/kg/min
Minute ventilation (Respiratory rate x Tidal volume,
(0.5 L): Adult range 5-10 L/minute; neonatal range = 200-300
ml/kg/min
|
|
Male |
Female |
|
Tidal Volume |
500 |
500 |
|
Inspiratory Reserve Volume |
3100 |
1900 |
|
Expiratory Reserve Volume |
1200 |
800 |
|
Total Lung Capacity |
6000 |
4200 |
|
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC) |
2400 |
1800 |
|
Inspiratory Capacity |
3600 |
2400 |
|
Vital Capacity |
4800 |
3200 |
|
Respiratory Rate |
10-16 breaths/min |
|
Minute Volume |
5-8 L/min |
|
Alveolar Ventilation/min |
3-5 L/min |
|
Maximum voluntary Ventilation |
90-125 L/min (Male); 74-95 L/min (Female) |
9Definitions:
Functional reserve capacity (FRC) = "the amount of gas left in the lungs after normal (unforced) exhalation" .
FRC = ERV + RV, where ERV = expiratory reserve volume which is the "maximum volume of gas that can be forcefully exhaled after a normal exhalation" & RV = residual volume-"the amount of gas left in the lungs after a maximum exhalation"
![]()
6The rate of rise of alveolar anesthetic concentration is analogous to earlier consideration of the rate rise of the inspired concentration.
In the latter example, the dilutional step had to do with the anesthetic circuit volume and how the magnitude of that volume would causes dilution of the anesthetic concentration as measured at the outflow point of the anesthesia machine.
Now we will look at another dilutional step which occurs as the anesthetic gas mixes with alveolar gas.
To simplify our consideration will say that there is no blood flow to the lungs which of course adds a complication and we will consider it later. But for now, the form of the relationship between the alveolar concentration of anesthetic and the inspired concentration of anesthetic is similar to what we have observed earlier and takes the form:
FA = FI (1-e-T/
) where FA will be the alveolar anesthetic concentration and FI will be the inspired anesthetic concentration.
As before the alveolar anesthetic concentration will be less than the inspired concentration in accord with the (1-e-T/
) term. In this expression, T is time and
= the time constant corresponding to be functional reserve capacity (FRC) divided by the minute ventilation (
A) OR FRC/
A .
In our example below, the functional residual capacity (FRC) is equal to 2400 ml and the minute volume = 5000 ml/min.
Note how the alveolar anesthetic concentration (FA ) approaches the inspired anesthetic concentration (FI ).
The dependency reflected in the rate of rise of the alveolar anesthetic concentration resides in two variables, the functional reserve capacity and the minute ventilation (
A).
One way to decrease the initial FRC would be to have the patient exhale deeply before applying the mask; as a consequence, the initial FRC will be reduced.
In the graph below we see a single (Red) data point reflecting a decrease to 1200 ml of the FRC initially from 2400 ml as a result of requesting the patient to exhale deeply before the first breath.
A reduction of the FRC will cause an initial jump in alveolar anesthetic concentration which, although not represented in this graph, would translate to an initial boost in blood anesthetic tension.
6Requesting the patient to breathe more frequently will shift the curve in the direction of the increasing more rapidly the alveolar anesthetic concentration:
Solid circles (above), associated with a higher minute volume, represent more rapid increases in alveolar anesthetic concentration compared to the 2% inspired concentration.
Initially faster ventilation rates might be obtained by requesting the patient breathe more rapidly, but ultimately the anesthesiologist would ventilate the patient more rapidly to achieve more rapid induction in the case of a masked induction or more rapid attainment of appropriate CNS volatile anesthetic concentration (i.e. 1.2 MAC) in transition from intravenous agent induction.
6Increase in FA with pulmonary flow:
The situation is more complex than that described above because pulmonary blood flow would clearly influence the rate at which the alveolar partial pressure increases.
Actually, FA is not simply equilibrating with FI as a single variable, but is influenced significantly by anesthetic molecule flux into the blood compartment.
For anesthetics that are relatively blood soluble, a reduced rate rise of FA/FI will be observed to significant flux of anesthetic molecules from the alveolar volume into the blood volume.
This process retards the attainment of equilibrium.
An example that illustrates this relationship is found by comparing halothane (Fluothane) and desflurane (Suprane) with an assumption that they are only soluble in blood.
This simplifying assumption does not affect our overall analysis and conclusion.
Furthermore, we specify for this hypothetical analysis that the patient will take a single but deep breath of anesthetic gas and hold it.
Let's examine the blood: gas partition coefficients for these agents:
|
Sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) |
Desflurane (Suprane) |
Isoflurane (Forane) |
Enflurane (Ethrane) |
Halothane (Fluothane) |
Nitrous oxide |
|
0.65 |
0.42 |
1.46 |
1.9 |
2.4 |
0.46 |
A blood: gas partition coefficient of 2.4 for halothane means that, in the above hypothetical experiment, about 70.6% (x) of halothane delivered to the alveoli will be transferred to the blood, leaving about 29.4 % (y) remaining in the alveolar space. (70.6/29.4 = 2.4) [the values for x & y result from simultaneously solving x + y = 100 % and x/y = 2.4].
x/y = 2.4
x = 2.4y
x + y = 100% OR
2.4y + y = 100%, i.e.
3.4 y = 100%
y = 29.4%
By contrast, the desflurane (Suprane), which is much less blood soluble, 29.6% of the desflurane (Suprane) molecules will transferred to the blood, leaving 70.4% of the molecules remaining in the alveolar space. The blood:gas partition coefficient for desflurane (Suprane), 0.42 is equal to the ratio 29.6/70.40.
x/y = 0.42
x= 0.42y
x + y = 100% OR
1.42 y = 100%
y = 70.42%
This analysis allows us to appreciate the relationship of the blood: gas partition coefficient with respect to the molecules that on average will either transfer from or be retained in the alveolar volume. Therefore, at equilibrium, the partial pressure halothane (Fluothane) is 29.4% and for desflurane (Suprane) 70.4% relative to the inhaled concentration.
Given that anesthetics exhibit tissue solubility and are administered not as described above but in the continuous manner, a first-order relationship similar to the ones we have described earlier can be applied.
PA = FA x PB; The partial pressure the anesthetic will be equal to be fractional anesthetic concentration times the barometric pressure. (PA is the alveolar partial pressure; PB is the barometric pressure; FA is the alveolar fractional concentration.)
Further, PBl = PA x (1-e-T/
), where
is a capacity factor, specifically volume of anesthetic that is dissolved in the blood at the desired anesthetic alveolar partial pressure.
Qualitative inspection of this relationship indicates that the larger the capacity factor (
), longer it will take for that anesthetic to saturate a compartment. Let's see if this assertion is true by analysis.
The results (graph below) illustrate that the PBl rises more slowly for a given alvelolar PA (2%) with an increasing capacity factor. The underlying molecular basis for differences in solubility of one anesthetic compared with another, reflected in different blood capacities will be discussed at a later time.
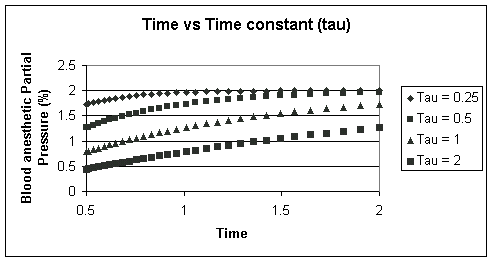
As we have seen, the increase in partial pressures can be described in terms of an equilibration process in which an initial anesthetic concentration is introduced in that is subject to dilution initially, but ultimately approaches a steady-state concentration level e.g. see above for an approach to 2% as a function of time. This analysis may be extended as follows:
6
inspired =anesthetic delivery rate to the alveoli (note the emphasis on rate of delivery).
We are interested in the rate of delivery because of its importance in determining the rate of rise of anesthetic partial pressure in the blood.
Furthermore, the rate of rise, dependent on the anesthetic delivery rate, will be proportional to the alveolar ventilation rate,
A ; it would seem intuitively clear that the number of times per minute we can fill the alveoli with anesthetic-containing gas would be an important factor in the ultimate delivery of anesthetic to the blood.
The last factor would of course be the concentration of gas in the inspired volume which would be the inspired anesthetic fraction, FI .
The equation relating these above factors is:
inspired = FI x
A .
6This relationship (
inspired = FI x
A ) does not consider that some anesthetic gas flow is not exchanged with the bloodstream.
Therefore, the difference between the rate of movement of anesthetic molecules into the alveoli minus the rate of anesthetic uptake into the blood defines the anesthetic flow which is expired or
expired =
inspired -
B; where
B is the rate of anesthetic uptake into the blood.
We are describing some of the various places that the anesthetic molecules can go, given that they have freedom to move across the alveolar membrane into the blood, freedom to never leave the alveolar volume and be removed during exhalation, or even move into the blood and then immediately back into the alveolar space.
It is important to remember that it is the net flux, representing the overall probability of movement in one direction or another that is important.
This analysis is consistent with our earlier discussion of random molecular motions in space.
Once an anesthetic molecule has diffused across the alveolar membrane into the blood, the likelihood of that particular anesthetic molecule diffusing back the other way is rendered less probable because pulmonary flow removes the molecule from the vicinity of the alveolar membrane.
This consideration of course is important in understanding the net flux of anesthetic in the general direction of alveolar volume to blood.
Factors influencing FA/FI: If the inspired anesthetic fraction is FI, then the alveolar anesthetic fraction FA will be affected by the rates of alveolar anesthetic delivery as well as the magnitude of the anesthetic flow that does not participate in gas-blood exchange. This relationship is represented as: FA / FI =
expired /
inspired . Rearranging we have FA =
expired x FI /
inspired.
Qualitatively, it makes sense that the alveolar anesthetic fraction might be increased by
increasing the FI
and/or increasing the anesthetic flow to the alveoli (
inspired)
and/or decreasing the anesthetic flow not available for blood exchange (
expired ).
By example, if 20 ml of anesthetic were inspired and 10 ml of anesthetic expired (with 10 ml transferred to the blood), then the alveolar fractional concentration (FA) would be 50% of the inspired fraction (FI) given that 50% of the anesthetic is transferred to the blood. We noted earlier than since
expired =
inspired -
B, we can substitute
inspired -
B for
expired , obtaining:
FA/FI = (
inspired -
B )/
inspired = (
inspired /
inspired -
B /
inspired ) = 1 - (
B )/
inspired
We can make another substitution by recognizing that :
inspired = FI x
A so FA/FI = 1 - (
B )/(FI x
A).
6
FA/FI = 1 - (
B )/(FI x
A) is a very interesting equation!
Firstly, let's look at the ratio on the left, FA/FI : Before we introduce anesthetic gas into the circuit this ratio must be zero, but the increase in the ratio, at least a significant increase, does not depend only on the inspired anesthetic fraction, FI , but also on what's going on as described on the right side of the equation.
So, if FA/FI is 0 and starts to increase as inhaled agent reaches the alveolar volume from the anesthetic circuit but uptake of anesthetic in the pulmonary blood
B nearly equals its delivery to the alveoli (FI x
A), then FA/FI will not rise.
For example, if (
B ) = (FI x
A) then (
B ) / (FI x
A) equals 1 and FA/FI would still be equal to 0 since 1 - (
B )/(FI x
A) would be equal to 0.
Now, how could this happen?
Suppose that as we first administer the anesthetic gas, and there is a buildup of anesthetic gas molecules in the alveoli, there is a high probability of net transfer of anesthetic molecules from the alveoli to blood.
Recall initially, there are no anesthetic molecules in the blood and this condition favors transfer, but in addition to that, there is a constant pulmonary blood flow such that initially, they're very few anesthetic molecules remaining near the alveolar membrane-a requirement for diffusion back from blood to the alveolar volume.
Consequently, at the beginning almost all of the gas delivery to the alveoli (FI x
A) is transferred to the blood (
B ) accounting for a limited initial rise in alveolar anesthetic fraction FA compared to the inspired anesthetic concentration FI.
6So the question is what changes as a function of time.
As gas molecules continue to be primarily transferred from the alveolar volume to blood, the concentration, let's say, the number of anesthetic molecules in the blood increases and with that comes an increased likelihood that movement of anesthetic molecules in the blood back across the alveolar membrane will occur.
This process results in a slow increase in alveolar anesthetic concentration since molecules begin overall exhibiting bidirectional movement, alveoli to blood and blood to alveoli.
6This recognition forces us to consider the factors that determine the rate of anesthetic uptake into blood or
B .
First, let's consider roughly what should affect the rate of anesthetic uptake in the blood.
One factor would be the intrinsic tendency for a given anesthetic gas to dissolve in blood. This factor or tendency is described by the blood-gas partition coefficient [we have not consider the molecular basis for this number] and is represented by
b/g.
Another factor would be the amount of blood that passes across alveolar membrane in this factor is represented as the cardiac output, Q. The last consideration deals with partial pressure differences between anesthetic gas associated with the alveolar volume PA and that of the mixed venous blood, Pvenous normalized with respect to barometic pressure, Pbarometric. The equation that summarizes these relationships is:
B =
b/g. x Q x ((PA-Pvenous)/Pbarometric. (Later we will see that the form of this equation is consistent with Fick's law for diffusion)
6By combining
FA/FI = 1 - (
B )/(FI x
A) with
B =
b/g. x Q x ((PA-Pvenous)/Pbarometric) and recalling that
b/g =
blood where
is solubility, we obtain
FA/FI = 1 - (
B/FI)(Q/
A) x ((PA-Pvenous)/Pbarometric)
6The rate of rise of alveolar with respect to inspired anesthetic concentration is defined rather completely by the above equation.
For example, the partial pressure gradient between the alveoli and pulmonary compartments is reflected in (PA-Pvenous), where PA is the alveolar anesthetic partial pressure.
Before induction, Pvenous, would of course be zero and PA climbs with the first inspiration containing anesthetic gas.
The increase in PA is more initially substantial compared to Pvenous taking into account dilution into the venous pool associated with circulation and tissue uptake from the blood compartment.
Eventually, the blood compartment will become saturated and is this process goes forward Pvenous increases and the "transport driving force", i.e.Palveolar -Pvenous declines.
Examining our earlier figure, we note the initial rapid rise of FA/FI which occurs when the venous blood compartment is relatively unsaturated.
Furthermore, following significant transfer of inhaled anesthetic from the alveolar volume to the blood volume, the partial anesthetic pressure in blood begins to increase and the rate of increase in the FA/FI ratio declines.
This change is noted at the first inflection point in the curve associated with the significant changes slope.
During the initial phase, the blood: gas partition coefficient is particularly important as it will determine for molecular reasons the number of anesthetic molecules required to significantly increased the anesthetic blood tension.
Factors that tend to increase the rate of rise of FA/FI include:
relatively low blood: gas partition coefficients for the anesthetic (low
B)
low cardiac output (low Q), high VA (higher minute ventilation)
high (PA-Pvenous), i.e. relatively higher "driving force".
If we examine the right side of FA/FI = 1 - (
B/FI)(Q/
A) x ((PA-Pvenous)/Pbarometric) which is (
B/FI)(Q/
A) x ((PA-Pvenous)/Pbarometric): (a) low
B, (b) low Q (c) high
A , and (d) high (PA-Pvenous) all tend to decrease (
B/FI)(Q/
A) x ((PA-Pvenous)/Pbarometric), such that 1- (
B/FI)(Q/
A) x ((PA-Pvenous)/Pbarometric) is closer to 1 for a given FI. This effect results in FA/FI to be greater for a given FI. (see table below)
It can be also shown by inspection of the equation that changes of these parameters in the opposite direction cause slower rates of FA/FI rise.
|
Increase Rate of Rise of FA/FI |
Decrease Rate of Rise of FA/FI |
Comment |
|
low |
high |
As the blood solubility decreases, the rate of rise in FA/FI increases. |
|
low Q |
high Q |
The lower the cardiac output, the faster the rate of rise in FA/FI |
|
high
|
low
|
The higher the minute ventilation, the faster the rate of rise in FA/FI |
|
high (PA - PV) |
low (PA - PV) |
"At the beginning of induction, PV is zero but increases rapidly (thus [PA-PV] falls rapidly) and FA/FI increase rapidly. Later during induction and maintenance, PV rises more slowly so FA/FI rises more slowly." |
B : blood solubility; Q = cardiac output;
A = minute ventilation; PA , PV pulmonary alveolar & venous blood partial pressure
Considering this relationship, FA/FI = 1 - (
B/FI)(Q/
A) x ((PA-Pvenous)/Pbarometric), let's look at a few cases.
Case 1: Right at the beginning of a volatile agent induction, PA is high compared to Pv since not enough time has elapsed for significant gas molecules to transfer from the alveolar volume to the blood such that the PV has increased much. Holding fractional inspired gas concentration (FI), cardiac output (Q), minute ventilation (
A) all constant, we would expect that FA/FI would be mainly influenced by the blood:gas partition coefficient which would reflect the likelihood of gas transport (movement) into the blood compartment from the alvelar volume as a function of the molecular characteristics of the particular gas. So, for this case the following graphical representation obtains:
FA / FI ratio vs the Blood Gas Partition Coefficient at low Pvenous conditions
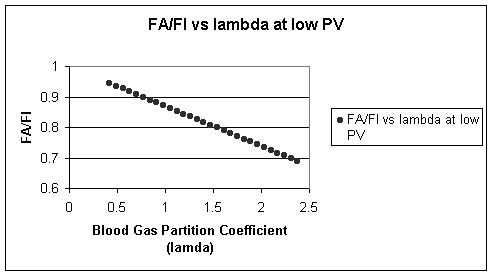
First look at the range of blood:gas partition values; at the left the value is relatively small as seen with desflurane (Suprane, 0.42).
Accordingly, the ratio of the alveolar fractional concentration to that of the inspired anesthetic concentration is closer to 1, since the relatively low tendency of desflurane (Suprane) to partition into blood favorites in a relatively high alveolar concentration.
On the other hand examining higher partition coefficients for example, 2.5 represents the value for halothane (Fluothane), FA/FI is reduced, reflecting greater anesthetic molecule transfer from alveolar volume for a given level of inspired gas concentration. For this case the (PA:Pvenous is 200:1)
Case 2: As transfer continues, the difference between the alveolar partial pressure and the venous partial pressure is reduced as more anesthetic molecules dissolve in the blood [PA-Pvenous is reduced with time assuming continual anesthetic delivery had no other change]. Under the circumstances we might expect the relationship exhibit decreasing sensitivity to the blood gas partition coefficient,
B .For this case the (PA:Pvenous is 4:1)
Case 3: Extending case 2 (For this case the (PA:Pvenous is 200:175), there is very little FA/FI sensitivity to the anesthetic's blood:gas partition coefficient reflecting approach to saturating blood capacity. In this case, there is a higher probability of anesthetic molecules transferring to the alveolar volume from the blood compartment. Of course, as the blood compartment becomes more saturated with anesthetic molecules, there is also increased likelihood of transfer to other compartments in general, including the CNS compartment.
5Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Stoelting, R.K., 3rd edition, Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, 1999, pp 36-37.
6Ebert, T. J. and Schmid III, P. G. "Inhalation Anesthesia" Ch. 15 in Clinical Anesthesia (Barash, P.G., Cullen, B. F., and Stoelting. R.K., eds) 4th Edition, Lippincott Williams& Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp. 377-387, 2001
7Family Practice Notebook
8Lung Function Fundamentals:
9General Biology Laboratory Exercises, Copyright ©2000, Purdue Research Foundation, Clark Gedney