|
|
Anesthesia Pharmacology: Local Anesthetics
|
|
Overview --Chemical Properties:
Lipophilic component
Connecting chain (ester or amide)
Ionizable group
Racemates/Pure Isomers
Pipecoloxylidide-agents (mepivacaine (Carbocaine), ropivacaine (Naropin))
Chiral agents (asymmetric carbon); left-(S), right-(R)-handed configurations
Mepivacaine (Carbocaine) and bupivacaine (Marcaine) are used clinically as racemates (50:50 mixture) of enantiomers
S enantiomers of mepivacaine (Carbocaine) and bupivacaine (Marcaine): less toxic than racemates
Ropivacaine (Naropin): pure S enantiomer
Pharmacological activity (2 factors--one that considers chemical aspects alone and the second that considers interaction with receptors)
Balance between lipophilic and hydrophilic characteristics
Potency of stereoisomers (e.g.,ropivacaine (Naropin) and mepivacaine (Carbocaine))
Esters: shorter duration of action (compared to local anesthetics with amide linkages)
Properties: Local Anesthetics are weak bases:
Existing as either uncharged base or cation (postiively charged)
Proportions depending on pKa and pH (as described by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation)
log ([cationic form] / [uncharged form]) = pKa - pH
Most local anesthetics have pKa's ranging from 8.0-9.0, therefore at physiological pH, most local anesthetic molecules will be positively charged (cationic form)
Cationic form: probably physiologically active form at the receptor
Uncharged form: important for penetration across biological membranes to reach site of action
Local anesthetic receptor localization internal side of the cell membrane {requiring penetration by uncharged form}
In infected tissue, extracellular pH is lower; more drug in ionized state; less likely to diffuse into the cell; reduced local anesthetic effect
![]() Esters: Cocaine Procaine (Novocain) Benzocaine
(Cetacaine) Tetracaine, Chloroprocaine (Nesacaine)
Esters: Cocaine Procaine (Novocain) Benzocaine
(Cetacaine) Tetracaine, Chloroprocaine (Nesacaine)
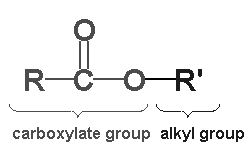
![]() Amides: Lidocaine
(Xylocaine), Mepivacaine (Polocaine/Carbocaine), Etidocaine (Duranest), Bupivacaine
(Marcaine), Prilocaine
Amides: Lidocaine
(Xylocaine), Mepivacaine (Polocaine/Carbocaine), Etidocaine (Duranest), Bupivacaine
(Marcaine), Prilocaine
 ,
,
|
Benzocaine (ester) |
Procaine (ester) |
|
Mepivacaine (Polocaine/Carbocaine) |
Bupivacaine (Marcaine) |