|
|
|
Anesthesia Pharmacology: Gastrointestinal Drugs
Gastric mucosa and acid secretion
Oxidative phosphorylation dependent secretion by parietal cells.
Parietal cells: found in mucosal glands of the body and fundus of the stomach.
|
|
|
 |
|
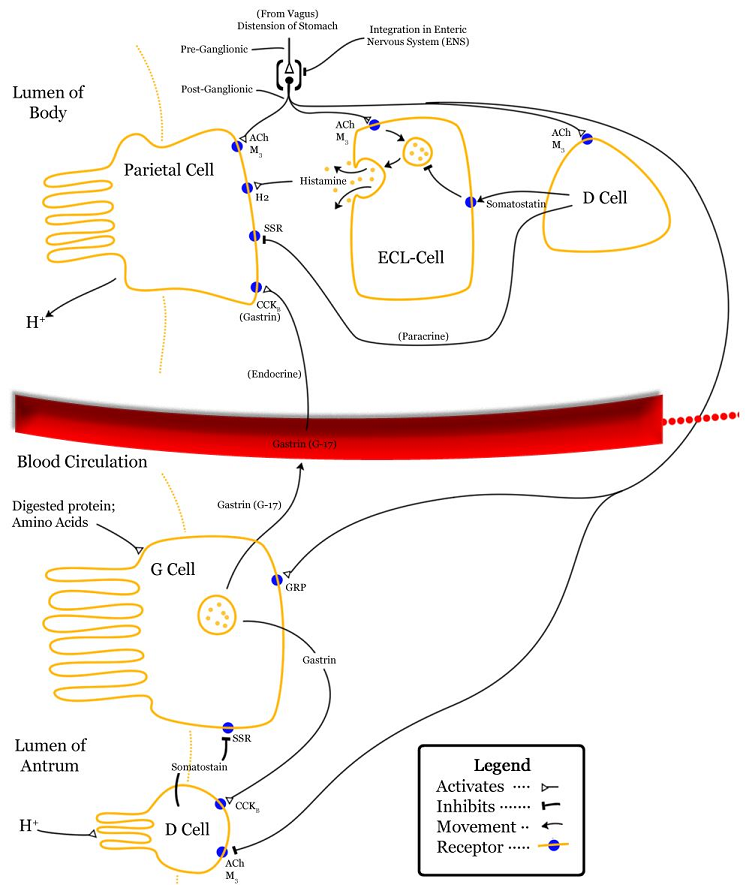
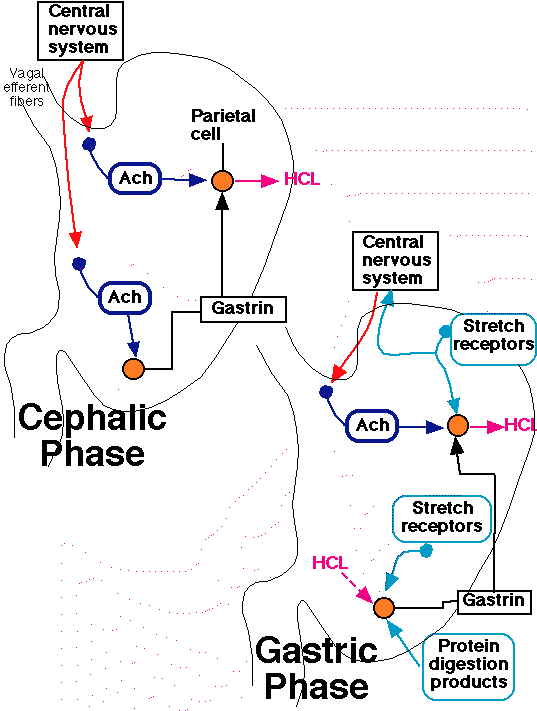
Regulation of gastric acid secretion involves many factors (chemical, neural, hormonal)
Stimulation:
Gastrin-most potent stimulant
Activation of postganglionic vagal fibers (muscarinic cholinergic parietal cells receptor activation)
Gastric mucosa contains large amounts of histamine in:
Mast cell cytoplasmic granules
Enterochromaffin-like cells (ECL)
H2 receptor antagonists competitively inhibit histamine action on H2 receptors, located on:
Gastric parietal cells
Cardiac atrial cells
Uterine smooth muscle cells
H2 receptor antagonists (cimetidine (Tagamet), ranitidine (Zantac), famotidine (Pepcid), nizatidine (Axid)) inhibit:
Basal acid secretion
Secretion in response to feeding, gastrin, histamine, hypoglycemia, or vagal stimulation
Histamine is the most important gastric acid secretion stimulant and is released from enterochromaffin-like cells by gastric and cholinergic activity
Basolateral parietal cells membranes contain receptors for:
Histamine-- stimulation gastric acid secretion
Gastrin-- stimulation gastric acid secretion
Acetylcholine-- stimulation gastric acid secretion
Prostaglandins --inhibition of gastric acid secretion
Somatostatin -- inhibition of gastric acid secretion
 |
|
Friedman, L. S. and Peterson, W.L. Peptic Ulcer and Related Disorders In Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine 14th edition, (Isselbacher, K.J., and Braunwald, E., Wilson, J.D., Martin, J.B., Fauci, A.S. and Kasper, D.L., eds) McGraw-Hill, Inc (Health Professions Division), 1998, pp. 1597-1616.
|
This Web-based pharmacology and disease-based integrated teaching site is based on reference materials, that are believed reliable and consistent with standards accepted at the time of development. Possibility of human error and on-going research and development in medical sciences do not allow assurance that the information contained herein is in every respect accurate or complete. Users should confirm the information contained herein with other sources. This site should only be considered as a teaching aid for undergraduate and graduate biomedical education and is intended only as a teaching site. Information contained here should not be used for patient management and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with practicing medical professionals. Users of this website should check the product information sheet included in the package of any drug they plan to administer to be certain that the information contained in this site is accurate and that changes have not been made in the recommended dose or in the contraindications for administration. Advertisements that appear on this site are not reviewed for content accuracy and it is the responsibility of users of this website to make individual assessments concerning this information. Medical or other information thus obtained should not be used as a substitute for consultation with practicing medical or scientific or other professionals. |