Anesthesia Pharmacology: Physics and Anesthesiology
Anesthetic Circuitry
The initial phase of equilibration between the anesthetic leaving the vaporizer and ultimately being delivered for inspiration must take into account the dilution factor dependent on the volume of the anesthetic circuit. Complicating this analysis is that variation would be expected based on the use of rebreathing or nonrebreathing systems. Generally, FI (inspired anesthetic concentration) will be dependent on the anesthetic concentration as delivered from the vaporizer, the extent of dilution by the circuit, and ultimately the loss of anesthetic from the circuit because of uptake.
Anesthetic emerging from the vaporizer will be diluted in a manner dependent on circuit volume. For the case in which the circuit volume would be about 7 L, which would be accounted for by a 3 L bag, 2L carbon dioxide absorber and about 2L of tubings and fittings, equilibration might occur within about 10 minutes, assuming an inflow rate of about 5L a fresh gas per minute.
|
|
10Some anesthetic molecules can be lost within the breathing circuit.
For example, methoxyflurane, now an obsolete agent, exhibited significant solubility in plastic and rubber components of the breathing circuit.
Presently, some absorption may occur for halothane (Fluothane) isoflurane (Forane) although nitrous oxide, desflurane (Suprane) or sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) are not significantly absorbed.
10Another aspect has to do with CO2 absorbents, which can degrade sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) and halothane (Fluothane), requiring somewhat higher concentrations.
This degradation process involves removal of hydrogen fluoride and subsequent generation of unsaturated compounds which may be toxic.
Principal examples would be compound A generated by sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) with attendant possible nephrotoxicity in long cases.
The above analysis considers moist (13%-15% water) adsorbents; moreover, dessicated agents will degrade potent inhale anesthetics sufficient to require additional anesthetic gas for sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane).
Furthermore, if Baralyme is dehydrated, more compound A will be produced (opposite seen with dehydrated soda lime).
The dessicated absorbents will degrade those agents containing the CHF2-O- functional group [enflurane (Ethrane), desflurane (Suprane), isoflurane (Forane)] and the degradation product of principal interest is carbon monoxide.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enflurane (Ethrane) |
Desflurane (Suprane) |
Isoflurane (Forane) |
In rebreathing systems, the patient will be breathing in both fresh gas and gas that was previously exhaled.
The inspired anesthetic concentration will then be diluted somewhat, in a manner proportional to the extent of rebreathing.
The effect tends to be greater for a more highly soluble agent compared to an anesthetic with limited solubility.
For a poorly soluble agent, significant agent remains within the alveolar volume such that the decrease in anesthetic tension upon mixing with fresh agent will be relatively limited.
By contrast, a highly blood soluble agent will exhibit significant transfer to blood, thus lowering the anesthetic alveolar concentration and resulting in a more substantial lowering of the inspired gas tension due to mixing.
Rebreathing effects are essentially limited in a manner proportional to the fresh gas inflow rate -- at high flow rates (e.g. 5 L/min) rebreathing effects are essentially eliminated.
High flow rates while eliminating the problem of rebreathing and anesthetic dilution and while having the advantage of a more predictable anesthetic alveolar gas concentration at delivery, there are other problems.
One obvious factor is that, since more volatile agent is used, expense is increased.
Accordingly, other methods, so-called "low-flow" or "closed-circuit" anesthetic techniques have been developed.
![]()
10Low-flow and Closed-Circuit anesthesia methods: Introduction
The earlier considerations dealt with a nonrebreathing system which uses a specific and fixed inspired anesthetic concentration; however, other approaches maybe now more common in practice, although the principles established earlier still apply.
Contemporary approaches are based on an awareness of economical issues which lead to a lower fresh gas flow and the use of a "constant" alveolar compared to inspired anesthetic concentration.
The alveolar concentration is thought to more appropriately reflect the depth of anesthesia.
Low-flow approaches would be associated with disadvantages and advantages.
The clear advantages that less anesthetic agent would be used in accordingly less cost incurred.
Flow rates typically less than 3L/min. (half minute volume) characterize low flow methods.
In the case of closed-circuit anesthesia delivery of gas is provided in just the quantity required to replace that which is removed from the circuit by the patient, prominently oxygen in the anesthetic agent itself.
Advantages of the low flow/closed-circuit technique include:
Reduced expense
Decreased in heat loss
Reduced anesthetic gas release (environmental issue)
Improved humidification.
Disadvantages, however, are significant, including:
Concern that the patient is receiving sufficient oxygen
Possible increased carbon monoxide concentrations
Rebreathing of toxic substances associated with breakdown of anesthetics.
Concerns about oxygen levels is especially prominent where nitrous oxide is used, given that additional nitrogen is contributed by the body and can somewhat reduce inspired oxygen.
The principal disadvantage of low-flow or more particularly closed circuit systems is a reduced level of anesthesia control.
![]()
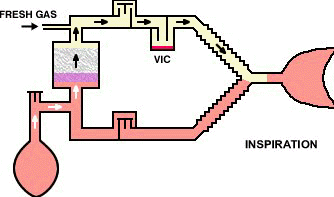
The circle-absorber system noted above can be configured as a closed system, depending on the position of the pressure relief valve.
In that configuration no gas (in principle) would escape from the system such that all the carbon dioxide produced will be absorbed; all of the oxygen consumed by patient metabolism will be replaced; although the anesthetic gas absorbed would be replaced.
If the above system is configured as "semi-closed" then being pressure relief valve can be opened if needed to allow access gas to escape from the system.
Closed systems are typically not really completely closed since sampling is required to determine oxygen, carbon dioxide as well as anesthetic levels. Sampling for analytical analysis may require about 200 ml/minute quantities.
The closed circuit system is problematic because the difficulties in matching anesthetic delivery with alveolar requirements or is noted earlier issues relating to anesthetic control.
We, however, can begin analyzing the closed circuit system and then proceed to evaluate low-flow systems, which are more commonly employed.
10With closed-systems, is noted earlier, it is incumbent on the anesthesiologist to ensure has precisely as possible to replacement of gases consumed and this process focuses on (a) oxygen, (b) nitrous oxide and (c) the volatile anesthetic itself.
10The underlying problems that for any particular estimate of the amount of agent that needs to be replaced there are underlying assumptions and the stability of the values associated with these assumptions ultimately determine the level of difficulty in maintaining correct gas concentrations.
For example, if we choose to set oxygen consumption and apply a certain amount of oxygen input to the system, we recognize that the validity of our choice of oxygen input depends on the stability of the metabolic rate during the intraoperative timeframe.
However, we recognize that sympathetic nervous system discharge will, during this period, cause changes in oxygen requirements following metabolic responses to autonomic tone or changes in body temperature.
By contrast, it appears easier to set the nitrous oxide input requirements, given its relative insolubility and relative constancy concerning rate of gas loss through the skin.
10Significant variability however is associated with the volatile, potent inhalational drugs.
Firstly, we must be concerned with the alveolar agent uptake at a given alveolar agent concentration.
Following Eger, our analysis uses an anesthetic concentration equal to 1 MAC, which would be the anesthetic concentration required to inhibit patient response to painful stimuli (surgical incision) in about 50% of patients. [Given that one does not want to be one of the other 50% of patients either personally or from the point of view of the anesthesiologist, it is not surprising that actual administered anesthetics might be provided at about 1.2-1.3 MAC]
Going back to our problems concerning volatile agent uptake, at 1 MAC, is not surprising that the physical characteristics, i.e. anesthetic solubility would be an important consideration.
Note the figure below in which several agents are compared desflurane (Suprane) (blood gas partition coefficient = 0.45), isoflurane (Forane) (blood gas partition coefficient = 1.4), halothane (Fluothane) (blood gas partition coefficient = 2.5) and sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) (blood gas partition coefficient = 0.65).
|
|
10Remember in looking at the curves above that the agents have different MAC values (in %) as well as different solubilities.
Both factors then have an effect on uptake.
The shape of the curves are similar and are determined by uptake characteristics of major pharmacokinetic compartments.
For example, within the first few minutes, significant anesthetic uptake occurs as organs which have significant blood flow (sometimes called vessel rich groups) contribute prominently.
Later, the large muscle group becomes the more important compartment, while finally the relatively poorly perfused adipose tissue compartment dominates at a longer time .
![]() 10The height of
the above curves will be dependent on two major factors: the first
factor is the solubility of the anesthetic; the second factor is the
MAC value
10The height of
the above curves will be dependent on two major factors: the first
factor is the solubility of the anesthetic; the second factor is the
MAC value
|
Anesthetic |
Blood: gas partition coefficient |
MAC |
MAC (vol %) conversion to PMAC1 (mm Hg) |
PMAC1 (mm Hg) |
|
desflurane (Suprane) |
0.45 |
6% |
6.0% x 760 |
45.6 |
|
isoflurane (Forane) |
1.4 |
1.15% |
1.15% x 760 |
8.7 |
|
halothane (Fluothane) |
2.5 |
0.77% |
0.77% x 760 |
5.7 |
|
sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) |
0.65 |
1.7% |
0.17% x 760 |
13 |
![]() 10It turns out that in general solubility and MAC are
related inversely, at least approximately so, so that if the MAC
value is somewhat higher, the blood gas partition coefficient will
be relatively lower.
10It turns out that in general solubility and MAC are
related inversely, at least approximately so, so that if the MAC
value is somewhat higher, the blood gas partition coefficient will
be relatively lower.
An example from the above graph and table can be noted for the comparison of desflurane (Suprane) and isoflurane (Forane). Desflurane (Suprane) has a MAC value about five times higher than for isoflurane (Forane), meaning that many more desflurane (Suprane) molecules are required to achieve one MAC;however, desflurane (Suprane) exhibits lower relative solubility accounting for only a twofold difference in uptake (examine the above curve).
![]() 10There is a "rule" called the
"square-root-of-time rule" which may be considered a
possible approximation, but certainly not a law that may allow
estimation of uptake.10, 24-27 .
10There is a "rule" called the
"square-root-of-time rule" which may be considered a
possible approximation, but certainly not a law that may allow
estimation of uptake.10, 24-27 .
The rule is that anesthetic uptake at some point in time is approximated by taking uptake during the first minute anesthesia and dividing by the square root of time (in minutes).
As we have seen in earlier equations, anesthetic uptake would be anesthetic: blood solubility x cardiac output x the difference in alveolar: venous anesthetic partial pressures (this last factor is sometimes referred to as the "driving force" although we can think of it is merely describing the probability of flux in one direction or the other)
Using estimated values for anesthetic solubility and cardiac output, isoflurane (Forane) uptake in the adult would be the blood: gas partition coefficient of 1.4 times 5400 (cardiac output) times 0.0115 which would be 1 MAC for isoflurane (Forane) represented as a fraction of 1 atmosphere. [If 1 MAC for isoflurane is taken to be 1.15%, then we can convert the value from volume % (that's the 1.15% to the partial pressure at 1 MAC (PMAC1) by multiplying the MAC % 1.15% x 760 mm Hg, giving, for isoflurane 8.7 mm Hg. The number 0.0115 above comes from dividing 8.7 mm Hg / 760 mm Hg, assuming 760 mm Hg represents ambient pressure]
The result of this calculation is 87ml.
According to the equation above, uptake at four minutes would be approximated by 87 divided by the square root of 4 and at nine minutes by 87 divided by the square root of nine.
There is some concern that this approximation tends to overestimate the uptake reduction as a function of time.
10Within the closed-flow system, or one with very low inflow rates {200 ml/min}a concern is how to be confident that adequate amounts of anesthetic available for uptake.
The problem can be appreciated in noting that a maximal outflow of a standard isoflurane (Forane) vaporizer is 5% which, using a 200ml/min flowrate, would correspond to 10 ml of anesthetic introduced per minute -- which would be compared to the 87 mL quantity estimated earlier.
This comparison indicates that initially, even the use of variable bypass (Tec-type) vaporizers that could deliver in an accurate matter anesthetic at low inflow rates would probably not be able to provide adequate the initial anesthesia.
The question becomes whether such a vaporizer, e.g. and isoflurane (Forane) vaporizer, could meet the demand for anesthetic at later time points. The figure below illustrates that at the one-hour., isoflurane (Forane) vaporizers may have difficulty meeting anesthetic demand which leads to the question of how this difficulty can be managed.
|
|
10This figure illustrates the ratio of delivered (FD) to alveolar (FD/FA) anesthetic concentration which would be required to maintain the alveolar anesthetic concentration at the 1 MAC level.
![]() Focusing on the isoflurane (Forane)
curve, note the large difference between the delivered concentration
and alveolar concentration, --The ratio would be the y-axis
value--which reflects the large disparity between the dial setting
on the anesthesia machine vaporizer and what is observed at the
alveolar level.
Focusing on the isoflurane (Forane)
curve, note the large difference between the delivered concentration
and alveolar concentration, --The ratio would be the y-axis
value--which reflects the large disparity between the dial setting
on the anesthesia machine vaporizer and what is observed at the
alveolar level.
Uptake from the alveolar volume is an important consideration and so is the extent of rebreathing.
So for the isoflurane (Forane), which exhibits intermediate solubility (blood: gas = 1.4) difficulty in meeting demand is clear and can be contrasted with the much less soluble anesthetic, desflurane (Suprane) (blood: gas partition coefficient = 0.45).
If we compare these two anesthetics at the ten minute point (first mark on the x-axis), desflurane (Suprane) is fairly close to meeting demand, certainly compared isoflurane (Forane).
If we need to maintain low flow and work within that constraint, then selection of a different anesthetic, i.e. not isoflurane (Forane), would be appropriate in order to position vaporizer outflow capacity in closer accord with physiological requirements.
As already suggested a less soluble agent, such as desflurane (Suprane) would be better-noting that, using the same calculation is before desflurane (Suprane) uptake in the first minute of anesthesia would be about 146 ml [0.45 x 5400 x 0.06].
Still using the 0.2L/min oxygen flow rate and setting the vaporizer to maximum (18% for desflurane (Suprane) vaporizers) one could achieve a 44 ml delivery-lower than required but much closer than for the isoflurane (Forane) case.
![]() 10The general solution to the problem that vaporizers
are not able to provide in many instances sufficient anesthetic to
support uptake rests in the ability to reduce anesthetic
requirement, that is to reduce the MAC value by adding in another
agent.
10The general solution to the problem that vaporizers
are not able to provide in many instances sufficient anesthetic to
support uptake rests in the ability to reduce anesthetic
requirement, that is to reduce the MAC value by adding in another
agent.
For example, if nitrous oxide is used along with the volatile anesthetic, reduced vaporizer requirement results.
Furthermore nitrous oxide will tend to increase total fresh gas flow in order to accommodate significant nitrous oxide uptake.
Remember that in our calculation above we were using a very low flow rate (200 ml/min, i.e. 0.2 L/min), so that by simply increasing flow rate vaporizer outflow would be enhanced.
Before we consider a higher flow rate case, note that in the above example (0.2L/min), the greatest disparity between vaporizer setting (anesthetic input) and alveolar concentration, i.e. the FD/FA ratio will be for the more soluble agent, i.e. isoflurane (Forane) and halothane (Fluothane) [blood: gas partition coefficient for halothane (Fluothane) = 2.5).
10The general problem is flow rate dependent, so that a slight increase in inflow reduces significantly the disparity between the vaporizer setting in the alveolar concentration.
We will consider this and other low-flow anesthetic delivery issues shortly.
Before we do however, note that even the best case for the 0.2L/min inflow rate, after many minutes after initiation, there still is, independent of agent, significant differences between the dialed anesthetic concentration and the alveolar concentration.
This condition contributes to possible variability in the actual alveolar concentration because uptake changes due to transient, variable alterations in cardiac output which influences pulmonary flow can occur without compensation in the absence of changing delivered agent concentration.
In this circumstance even with constant ventilation, the difference between alveolar and inspired anesthetic concentration will change in a manner directly proportional with anesthetic uptake -- more uptake = greater difference between inspired and alveolar anesthetic concentrations.
An additional complication is that rebreathing results in inspired concentration varying in an inverse matter with uptake. Both effects contributed to intrinsic instabilities of alveolar concentration associated with closed circuit systems.
![]()
As just noted, essentially closed systems associated with high FD/FA ratios are also predictive of relative alveolar anesthetic concentration variability. Therefore, it is of interest to reduce such variability while at the same time minimize fresh gas flow. The middle ground is to use low-flow which correspond to < 50% of minute ventilation.
By way of review, low flow systems should be more economical, reduce air pollution while facilitating humidification and maintenance of temperature -- all compared to open systems.
Low flow systems will also minimize the sensitivity of alveolar anesthetic concentrations to changing physiological parameters as well as concerns about relative concentrations of carbon monoxide, toxic anesthetic derivatives which may build up in a closed system, oxygen, and anesthetic levels.
10The two factors that govern the FD/FA ratio, as we have seen, or anesthetic solubility as well as inflow anesthetic gas rate. The effective increasing inflow rate on FD/FA is an inverse effect, that is as the flow rate goes up, the ratio goes down. This conclusion seems reasonable since alveolar uptake would have a less of an effect on alveolar anesthetic concentration in the face of high replenishment flow rates and this effect is shown in the graphs below:10
Moreover, the increase in inflow rate decreases FD/FA because it decreases rebreathing. Note that uptake of anesthetic reduces its concentration in rebreathed gas; therefore, increased flow allows delivery of fresh anesthetic gas that replaces this anesthetic lost by rebreathing. Also, with higher inflow rates, there is less rebreathing anyway so the degree of compensation needed is reduced.
The solubility issue is such that the more soluble the agent is the more the higher the FD/FA will be since FA will be lower relative to less soluble agents since the more soluble agent will be readily transferred to the blood compartment. As expected, FD/FA is greatest early and then decreases as the venous partial pressure increases concurrent with equilibration of agent with vessel rich group compartments.
|
|
|
10First the graph on the left, recognizing a very low flow rate simulating a closed-circuit system.
By contrast, the inflow rate for the graph on the right is twenty times higher (4 :L/min).
Although the shapes of the curves are similar, the big difference is in the FD/FA ratio --y-axis values.
At the very high flow rate, the FD/FA ratio is fairly low even at early time points. Increasing the flow rate does not result in a proportional decrease in FD/FA .
As is observed by comparing the grafts below, there's not a great deal of difference between a 2L/min and a 4 L/min flow rate.
|
|
|
10Choice of the anesthetic agent (solubility & potency considerations), vaporizer capacity, and gas flow are important in obtaining an optimal FD/FA ratio, defined as a ratio which doesn't make the alveolar gas concentration exceedingly sensitive to physiological changes on one hand while still operating in a relatively low-flow environment.
The availability of agent-specific analyzers in the circuit is also an important consideration because these instruments analytically determine the actual gas concentration.
In their absence, there would be a tendency possibly to rely on vaporizer dial settings to indicate pulmonary anesthetic concentration which essentially assumes FD = FA .
Whereas the concentration of anesthetic in the lung must be proportional to the dial setting the actual correlation may not be very strong.
The correlation between the dial setting on the vaporizer and the anesthetic concentration in the lung will always be low early in anesthesia and questionable later in anesthesia when one is dealing with a closed circuit system or a system which approximates a closed circuit by having low gas inflow rates.
Also, if one focuses on the more soluble agents including the commonly used isoflurane (Forane) anesthetic, the correlation will remain poor even later.
By contrast, with relatively poorly soluble agents (sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) or desflurane (Suprane) above left figure), after about 45 minutes, the FD/FA ratio is fairly low, about 1.2.
10One reasonable approach to try to preserve economic benefits while obtaining relatively low FD/FA ratios would combining an initial high flow rate when anesthesia uptake is greatest and then tapering off to lower flows transitioning from 4-6 L/min (initially) to 2-4 L/min (5-15 min) and ultimately to 2 L/min.
Concerning the amount of anesthetic that would be required during a one-hour procedure, such calculations are possible by using constants for the inhaled agents as well as gas laws and specific gravities of the drugs. Eger10,28 has provided in tabular form the results obtained from using these relationships, considering halothane (Fluothane), isoflurane (Forane), sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane), and desflurane (Suprane).
|
Anesthetic agent |
0.2 L/min |
1.0 L/min |
2.0 L/min |
4.0 L/min |
6.0 L/min |
blood: gas solubility |
MAC |
|
halothane (Fluothane) |
4.6 ml |
6.5 ml |
9.0 ml |
13.9 ml |
18.8 ml |
2.5 |
0.77% |
|
isoflurane (Forane) |
6.3 ml |
9.6 ml |
13.9 ml |
22.3 ml |
30.7 ml |
1.4 |
1.15% |
|
sevoflurane (Sevorane, Ultane) |
4.9 ml |
10.9 ml |
18.2 ml |
33 ml |
47.8 ml |
0.65 |
1.7% |
|
desflurane (Suprane) |
10.1 ml |
26.1 ml |
46 ml |
85.8 ml |
126 ml |
0.45 |
6.0% |
If we focus on the 2.0 L/min inflow rate, we note the range of from 9 ml consumed for halothane (Fluothane) to 46 ml required for desflurane (Suprane).
This range reflects a fivefold difference; whereas, the potency range reflected in the MAC values shows and eightfold difference.
The amount of anesthetic delivered takes into consideration not only potency differences (given the constant 1 MAC reference point), but also anesthetic uptake and loss (for example through overflow valves).
Less soluble agents exhibit reduced relative uptake and losses, accounting for the disparity between the MAC range and the 9 ml - 46 ml range.10
Citations
10Eger II, E.I., "Uptake and Distribution" in Anesthesia 5th edition vol. 1 (Miller, R.D. editor; Cucchiara, R.F., Miller, Jr., E.D., Reves, J.G., Roizen, M.F. and Savarese, J.J., consulting editors) Churchill Livingstone, Philadelphia, 2000, pp 74-95.
11Eger, II, E.I., "Concentration and Second Gas Effects" in Anesthetic Uptake and Action, The Williams & Wilkins Company, Baltimore, Maryland, Chapter 6, pp 113-121, 1974
12Eger, II, E.I., "Ventilation, Circulation and Uptake" in Anesthetic Uptake and Action, The Williams & Wilkins Company, Baltimore, Maryland, Chapter 7, p. 131, 1974.
13Color illustrations and design: from Lecture 8. Lung Dynamics by M. Ludwig, McGill University (http://www.mmi.mcgill.ca/Unit2/Ludwig/lect21ventilationperfusion.htm)
14Eiger, E II, Severinghaus. JW: Effect of uneven pulmonary distribution o fblood and gas on induction with inhalation anesthetics. Anesthesiology 25: 620-626, 1964.
15Stoelting,.R.K., Longnecker, D.E. Effects of right-to-left shunt on rate of increase in arterial anesthetic concentration. Anesthesiology 6: 352-356, 1972.
16Diagrammatic representation of pneumothorax: http://bio.bio.rpi.edu/.../Lectures/ L17NEWPVent/L17hpneumo.html
17Chest Teaching File, Wayne State University
18Tension pneumothorax, Michael L. Richardson, M.D., University of Washington
19T Katzenmeyer, K, Friedman, N, Quinn Jr., F.B.Tympanoplasty, Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology; June 9, 1999 (http://www.utmb.edu/otoref/Grnds/Tplasty-9906/Tplasty-9906.htm)
20Ko, JCH, "Airway Management and Ventilation, http://www.cvm.okstate.edu/courses/vmed5412/Lect22.asp
21Klide, A & Teichner, J, Rebreathing System-Parts of the Circle System: Carbon Dioxide Absorber University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine
22Anesthesia Service and Equipment, http://asevet.com/index.htm
23Goldberg, M.E., Cantillo, J, Gratz, I, Deal, E, Vekeman, D, McDougall, R, Afshar, M, Zafeiridis, A and Larijani, G. Dose of Compound A, Not Sevoflurane, Determines Changes in the Biochemical Markers of Renal Injury in Healthy Volunteers, Anesth Analg 1999; 88: 437.