Medical Pharmacology Chapter 35 Antibacterial Drugs
Cefazolin: Therapeutic Uses and Clinical Applications
![]() Cefazolin
is a drug of choice for prophylaxis in many/most clean and
clean-contaminated surgical procedures.2,3
Cefazolin
is a drug of choice for prophylaxis in many/most clean and
clean-contaminated surgical procedures.2,3
Rationale4
Cefazolin covers the most common skin flora (S. aureus, S. epidermidis) and enteric organisms (E. coli) likely to contaminate surgical sites.
The 1.8-hour half-life allows for protection throughout most short-to-medium duration surgeries with a single dose, and its narrow spectrum minimizes collateral damage to the patient's microbiome which, for example reduces C. difficile risk compared to broad-spectrum agents like ceftriaxone or carbapenems.
![]() Surgical
Procedures
Surgical
Procedures
Cardiothoracic: primary agent for coronary artery bypass graft (CABG), valve replacement, and insertion of pacemakers.
Orthopedic: principal agent for joint arthroplasty, fracture fixation as well as spinal surgery.
General Surgery: gastroduodenal, biliary and hernia repair.
OB/GYN: C-sections and hysterectomies.
Head and Neck Surgeries:
![]() Clean-contaminated procedures. (A "clean-contaminated" wound
describes the surgery when respiratory, digestive or
genitourinary tracks are entered under controlled conditions.
This approach is associated with the higher infection risk
compared to clean wounds.)
Clean-contaminated procedures. (A "clean-contaminated" wound
describes the surgery when respiratory, digestive or
genitourinary tracks are entered under controlled conditions.
This approach is associated with the higher infection risk
compared to clean wounds.)
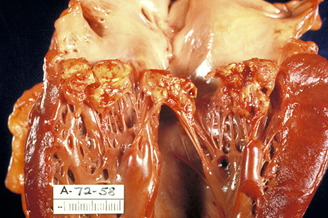
Infective Endocarditis
 |
|
For Methicillin-Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (MSSA endocarditis, cefazolin has evolved from an "alternative" to a "preferred" agent for many clinicians, particularly for patients with penicillin allergies or those who cannot tolerate the adverse effects of anti-staphylococcal penicillins (ASPs).
Native Valve Endocarditis (MSSA)
Regimen: Vefazolin IV every 8 hours for 6 weeks
Rationale: Studies and meta-analyses suggest cefazolin has similar cure rates to nafcillin for MSSA bacteremia and endocarditis, with significantly lower rates of nephrotoxicity.5,6
Special consideration
For severe, life-threatening endocarditis with large vegetations, some experienced clinicians still prefer nafcillin due to possible risk of the inoculum effect with cefazolin.7,8
Prosthetic Valve Endocarditis9
Used in combination with Rifampin (for biofilm penetration) and Gentamicin (for initial synergy), typically for 6 weeks.
This protocol mimics the nafcillin protocol of Cefazolin + Rifampin + Gentamicin.
Dosing10
Cefazolin is highly effective for cellulitis11, erysipelas12, and abscesses caused by MSSA and Group A Streptococcus.12
Osteomyelitis and Septic Arthritis
Cephalothin exhibits both good bone penetration and reliable activity against S. aureus.
Accordingly, cefazolin is effective for treating osteomyelitis.13
Culture and sensitivity testing from the infective site in form the selection of the most appropriate antimicrobial for management of osteomyelitis.14,15
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Cefazolin effectively treats uncomplicated UTIs (cystitis, pyelonephritis) caused by susceptible E. coli, P. mirabilis, and Klebsiella.16
Surrogate Testing
Clinical microbiology laboratories often use cefazolin susceptibility as a surrogate marker to predict susceptibility to oral cephalosporins (like cephalexin) for uncomplicated UTIs.16
Pregnancy
![]() Cefazolin
appears to be a safe option for treating pyelonephritis in
pregnant women, avoiding the risks of fluoroquinolones or
aminoglycosides.17
Cefazolin
appears to be a safe option for treating pyelonephritis in
pregnant women, avoiding the risks of fluoroquinolones or
aminoglycosides.17
![]() Cefazolin is categorized (AU TGA pregnancy category B1): "Drugs
which have been taken by only limited number of pregnant women
in women of childbearing age, without an increase in the
frequency of malformation or other direct or indirect harmful
effects on the human fetus having been observed. Studies in
animals have not shown evidence of an increased occurrence of
fetal damage."18
Cefazolin is categorized (AU TGA pregnancy category B1): "Drugs
which have been taken by only limited number of pregnant women
in women of childbearing age, without an increase in the
frequency of malformation or other direct or indirect harmful
effects on the human fetus having been observed. Studies in
animals have not shown evidence of an increased occurrence of
fetal damage."18
![]() Cefazolin is categorized (US FDA pregnancy category: B) "Animal
reproduction studies have failed to demonstrate risk to the
fetus and there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in
pregnant women."18
Cefazolin is categorized (US FDA pregnancy category: B) "Animal
reproduction studies have failed to demonstrate risk to the
fetus and there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in
pregnant women."18
Bacteremia (Bloodstream Infections)
Cefazolin appears appropriate for use for uncomplicated and complicated MSSA bacteremia.19
Cefazolin: Adverse Reactions and Safety Profile20
Similar to other beta-lactams, cefazolin is generally well-tolerated.
The most common adverse reactions are hypersensitivity reactions, which range from mild skin rashes and urticaria to severe anaphylaxis.
Other potential adverse effects include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea and diarrhea, transient elevations in liver enzymes, leukopenia, neutropenia, and, rarely, renal toxicity.
Prolonged use can, as with other broad-spectrum antibiotics, predispose to superinfections such as Clostridioides difficile–associated diarrhea.
December 2025
|
|
This Web-based pharmacology and disease-based integrated teaching site is based on reference materials, that are believed reliable and consistent with standards accepted at the time of development. Possibility of human error and on-going research and development in medical sciences do not allow assurance that the information contained herein is in every respect accurate or complete. Users should confirm the information contained herein with other sources. This site should only be considered as a teaching aid for undergraduate and graduate biomedical education and is intended only as a teaching site. Information contained here should not be used for patient management and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with practicing medical professionals. Users of this website should check the product information sheet included in the package of any drug they plan to administer to be certain that the information contained in this site is accurate and that changes have not been made in the recommended dose or in the contraindications for administration. Advertisements that appear on this site are not reviewed for content accuracy and it is the responsibility of users of this website to make individual assessments concerning this information. Medical or other information thus obtained should not be used as a substitute for consultation with practicing medical or scientific or other professionals. |