Medical Pharmacology Chapter 35 Antibacterial Drugs
Penicillins And Others
Beta-lactamase inhibitors
 |
 |
Overview and Mechanism of Action
Relebactam is presently available as I combination product which includes imipenem and cilastatin, used to treat complicated urinary tract infections (UTI's), pyelonephritis, and complicated interabdominal infections in adults.2
![]() According
to FDA labeling, this combination would be indicated for
patients 18 years of age and older who have limited or no
alternative treatment options, for treatment of the
aforementioned infections due to susceptible Gram-negative
bacteria (2019).7
According
to FDA labeling, this combination would be indicated for
patients 18 years of age and older who have limited or no
alternative treatment options, for treatment of the
aforementioned infections due to susceptible Gram-negative
bacteria (2019).7
![]() In June,
2020. The FDA approved Recarbrio for treatment of the adults
with hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated bacterial
pneumonia caused by the following susceptible Gram-negative
bacteria: Citrobacter calcoaceticus-baumanii complex,
Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae,
Klebsiella aerogenes, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae,
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Serratia marcescens.8
In June,
2020. The FDA approved Recarbrio for treatment of the adults
with hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated bacterial
pneumonia caused by the following susceptible Gram-negative
bacteria: Citrobacter calcoaceticus-baumanii complex,
Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae,
Klebsiella aerogenes, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae,
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Serratia marcescens.8
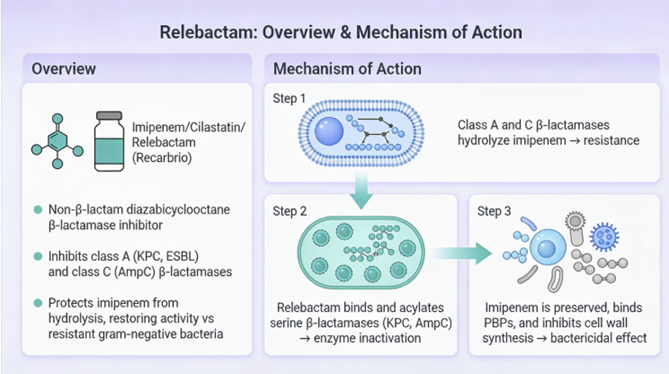
Relebactam is a diazabicyclooctane beta-lactamase inhibitor very closely related to avibactam and is administered in combination with imipenem and cilastatin.4
The triple drug combination, imipenem/cilastatin/relebactam is sold as Recarbrio.3
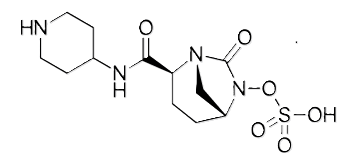
Structurally, it is avibactam with an added piperidine ring, which makes relebactam positively charged at physiological pH.1
Relebactam includes of piperidine rain that reduces transport of the drug out of bacterial cells by producing of positive charge.2,6
This structural change reduces the efflux of the inhibitor from bacteria, thereby increasing its activity against organisms like Pseudomonas that have robust efflux pumps.
Relebactam’s mechanism of action is the same as that noted with avibactamin that it forms a reversible acyl-enzyme complex with serine beta-lactamases, inhibiting the enzyme without being permanently inactivated.1
Thus, in contrast to some other beta-lactamase inhibitors, once relebactam de-acylates from the active site, it can reform the 5 membered ring, regaining capability to bind to target beta-lactamases.2
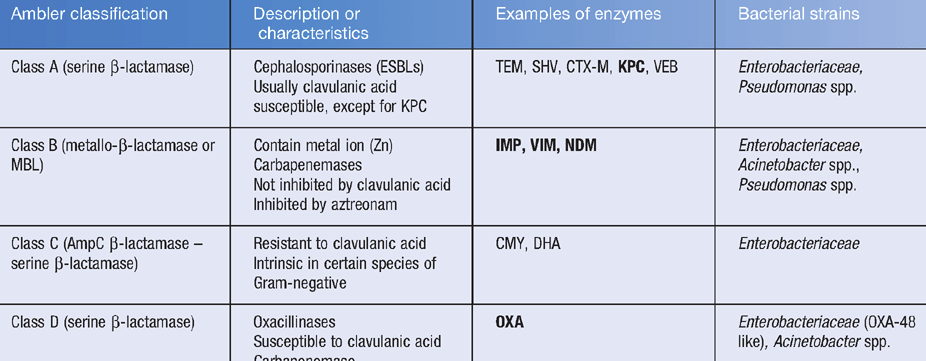
Relebactam is a potent inhibitor of Ambler Class A β-lactamases
(including KPC and ESBLs) and Class C (AmpC) β-lactamases.
Similar to avibactam, relebactam is not active against
Class B (MBL) enzymes or the majority of Class D
carbapenemases like OXA-48.
 |
|
Pharmacokinetics
 |
Absorption
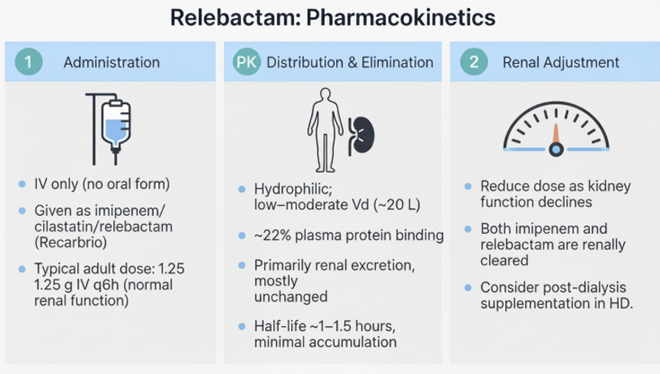
Relebactam is administered intravenously.10
Distribution
Plasma protein binding is modest at approximately 22%, and it
has a volume of distribution of about 19 L.
Metabolism
Relebactam does not undergo significant metabolism and is found
mostly as the unchanged drug in human plasma.
Elimination half-life is approximately 1.2 to 1.8 hours.
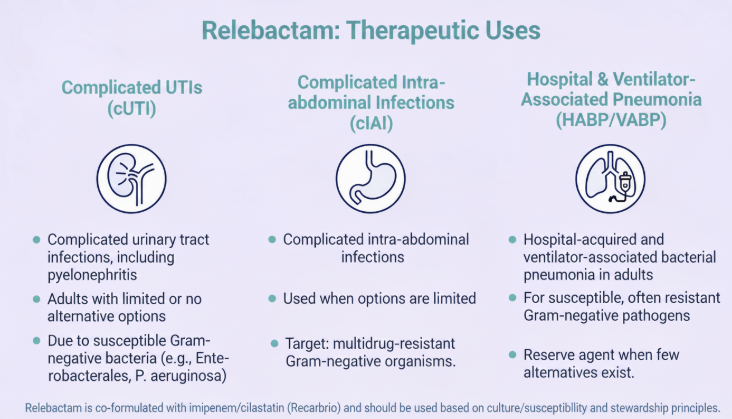 |
Relebactam expands the imipenem spectrum to include many imipenem-resistant Gram-negatives.
Recarbrio is useful in hospital pneumonia due to non-susceptible P. aeruginosa or CRE.
The RESTORE-IMI 1 and 2 trials demonstrated its efficacy in
these settings
August, 2025
|
|
This Web-based pharmacology and disease-based integrated teaching site is based on reference materials, that are believed reliable and consistent with standards accepted at the time of development. Possibility of human error and on-going research and development in medical sciences do not allow assurance that the information contained herein is in every respect accurate or complete. Users should confirm the information contained herein with other sources. This site should only be considered as a teaching aid for undergraduate and graduate biomedical education and is intended only as a teaching site. Information contained here should not be used for patient management and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with practicing medical professionals. Users of this website should check the product information sheet included in the package of any drug they plan to administer to be certain that the information contained in this site is accurate and that changes have not been made in the recommended dose or in the contraindications for administration. Advertisements that appear on this site are not reviewed for content accuracy and it is the responsibility of users of this website to make individual assessments concerning this information. Medical or other information thus obtained should not be used as a substitute for consultation with practicing medical or scientific or other professionals. |