Medical Pharmacology Chapter 35 Antibacterial Drugs
Penicillin G and Penicillin V Pharmacology and Therapeutics
Therapeutic uses
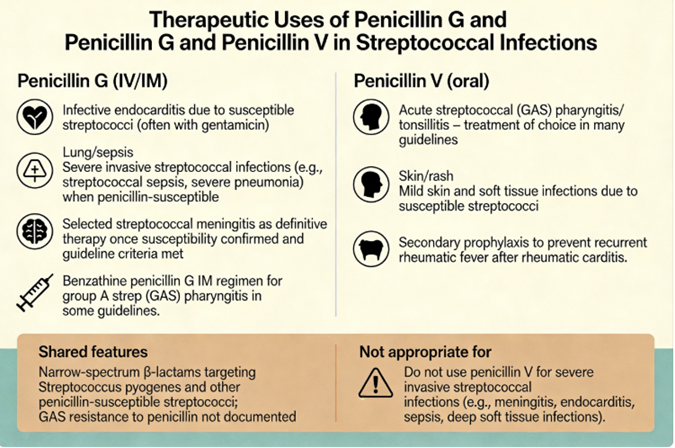 |
Penicillin is the first-line treatment for streptococcal pharyngitis (strep throat) caused by Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A strep).1
Dosing regimens for penicillin as well as amoxicillin have been described.2
Penicillin eradicates S. pyogenes and prevents complications like rheumatic fever.3
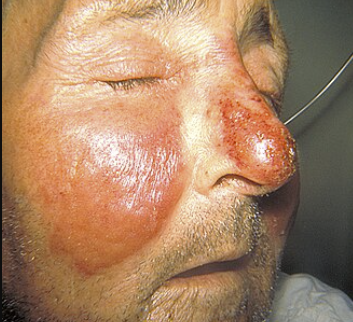
Penicillin V is also used for mild to moderate streptococcal skin infections such as erysipelas or uncomplicated cellulitis.4,5,6
 |
|
Group B Streptococcus (S. agalactiae) infections for example in. neonatal sepsis and prophylaxis in obstetrics may be treated with IV penicillin. In women with penicillin allergy clindamycin may be an alternative.7
Penicillin G (often in combination with gentamicin or another agent) is also a drug of choice for enterococcal endocarditis caused by Enterococcus faecalis (if susceptible), using high-dose IV penicillin G plus an aminoglycoside (gentamicin) for synergy.8
Syphilis and Spirochetal Infections
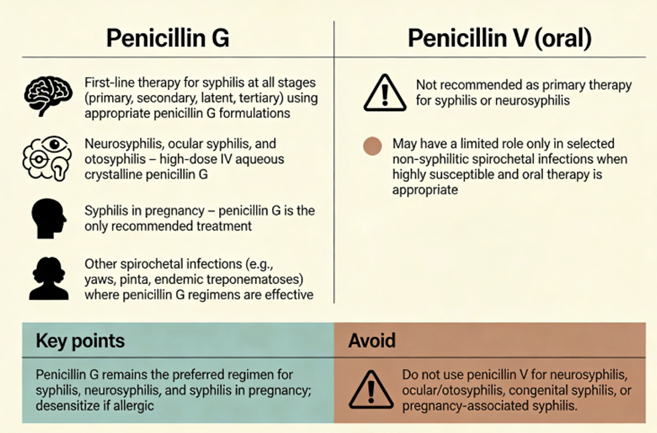 |
Penicillin G is the gold-standard therapy for syphilis, in all stages.9
 |
|
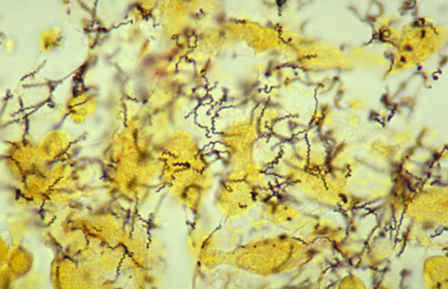
Treponema pallidum is exquisitely sensitive to penicillin G.9
Early syphilis is treated in primary care or infectious disease clinics with a single IM dose of benzathine penicillin G (2.4 million units) to achieve sustained low-level penicillin in the blood.10
Late latent syphilis requires three weekly IM doses, and neurosyphilis or ocular syphilis requires high-dose IV penicillin G for 10–14 days.11,12
Penicillin G (IV) is also recommended for neonatal congenital syphilis13 and, along with azithromycin, for Treponema pertenue infections (yaws).14
Other spirochetal infections treated with penicillin include Leptospirosis (IV penicillin G).15
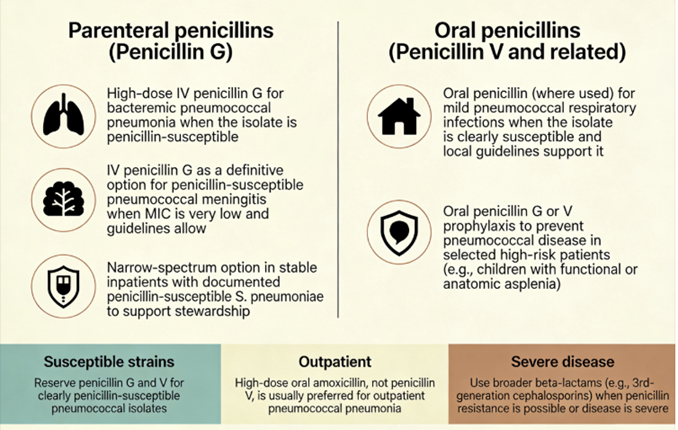 |
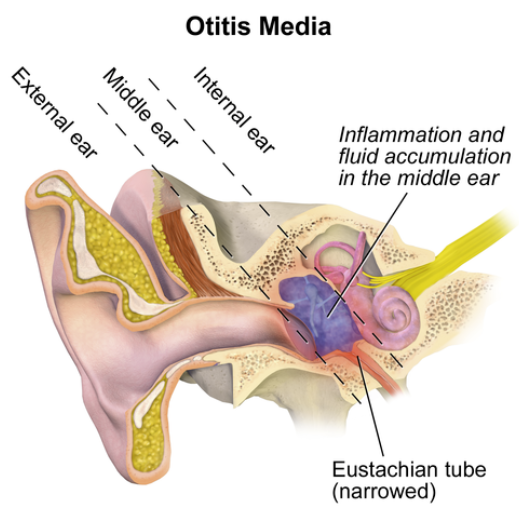
Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) historically was penicillin-sensitive and penicillin G was first-line for pneumococcal pneumonia23, meningitis, and otitis media.
 |
|
![]() Due to
resistance resulting from genetic mutations that alter
penicillin-binding protein structure, management now depends on
local susceptibility.16,17
Due to
resistance resulting from genetic mutations that alter
penicillin-binding protein structure, management now depends on
local susceptibility.16,17
Penicillin G IV is still used for pneumococcal meningitis (Streptococcus pneumoniae) if the isolate is susceptible (MIC ≤0.06 μg/mL for meningitis); otherwise, third-generation cephalosporins, such as cefotaxime or ceftriaxone, may be appropriate.18
For pneumococcal pneumonia, penicillin G IM or IV can be used if the strain is confirmed sensitive.19
In outpatient primary care, amoxicillin (an oral aminopenicillin) has often replaced penicillin V for empiric treatment of community-acquired pneumonia, noting that Streptococcus pneumoniae is the bacteria most frequently isolated.20
Amoxicillin remains an antibiotic of preference in treating acute otitis media.22
 |
|
Second-line alternatives in case of treatment failure include oral cefuroxime or amoxicillin-clavulanate.21
August, 2025
|
|
This Web-based pharmacology and disease-based integrated teaching site is based on reference materials, that are believed reliable and consistent with standards accepted at the time of development. Possibility of human error and on-going research and development in medical sciences do not allow assurance that the information contained herein is in every respect accurate or complete. Users should confirm the information contained herein with other sources. This site should only be considered as a teaching aid for undergraduate and graduate biomedical education and is intended only as a teaching site. Information contained here should not be used for patient management and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with practicing medical professionals. Users of this website should check the product information sheet included in the package of any drug they plan to administer to be certain that the information contained in this site is accurate and that changes have not been made in the recommended dose or in the contraindications for administration. Advertisements that appear on this site are not reviewed for content accuracy and it is the responsibility of users of this website to make individual assessments concerning this information. Medical or other information thus obtained should not be used as a substitute for consultation with practicing medical or scientific or other professionals. |