Medical Pharmacology Chapter 35 Antibacterial Drugs
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
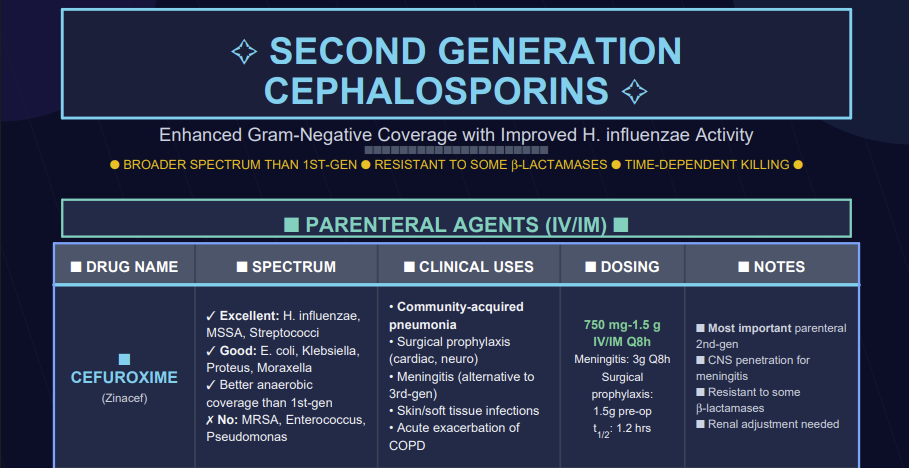
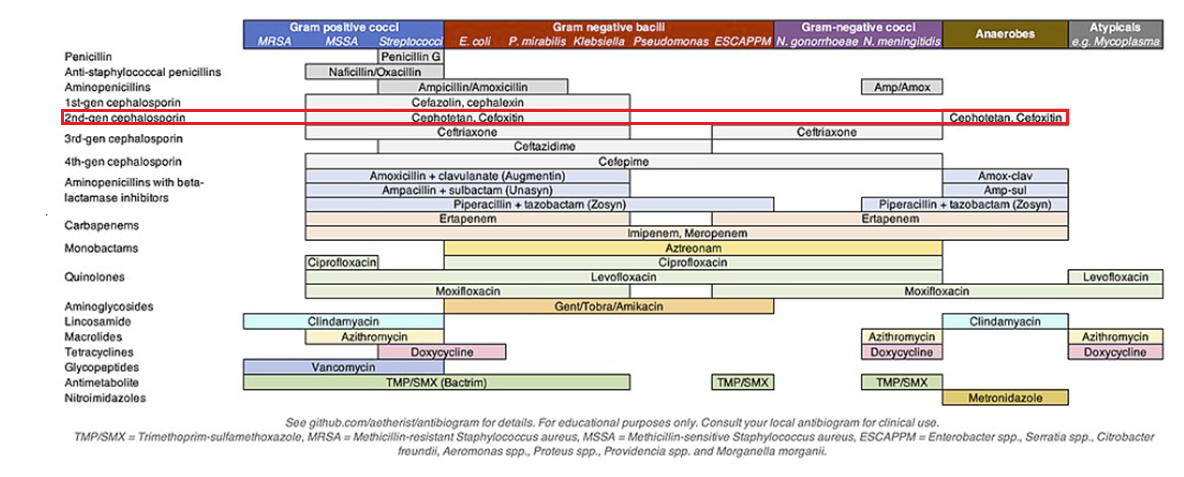
Cefoxitin is a parenteral cephamycin typically grouped with second-generation cephalosporins.2,3
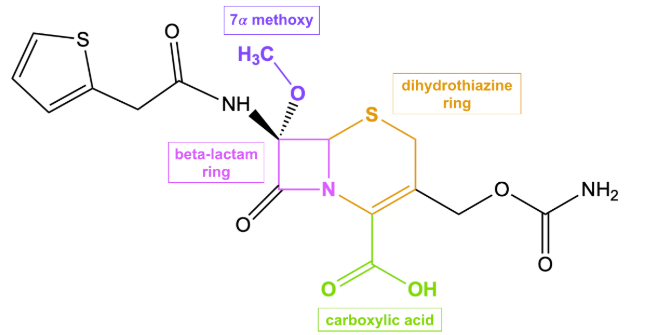
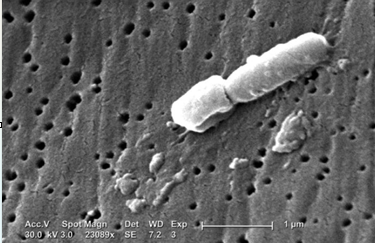
Cefoxitin is derived from cephamycin C and is characterized by a 7-α-methoxy group on the β-lactam ring, which confers enhanced stability against many plasmid-encoded β-lactamases and explains much of its anaerobic and Gram-negative activity.
 |
|
Microbiological Characterization
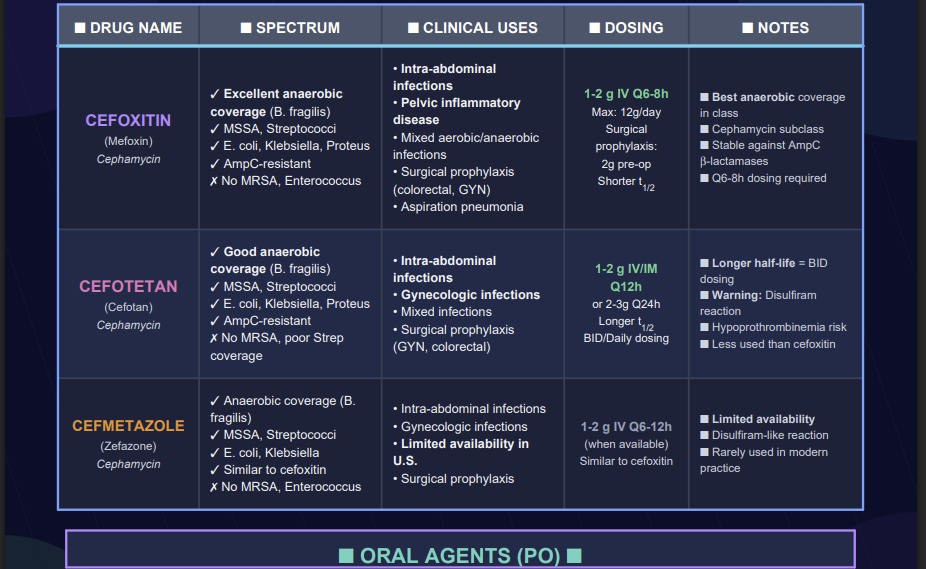
Cefoxitin exhibits broad gram-negative in anaerobic activity, its β-lactamase stability.
These characteristics allow cefoxitin to be viewed as a bridge between cephalosporins and later broad-spectrum β-lactams.4
Additional studies Describe cefoxitin exhibiting strong activity versus many cephalothin-resistant Enterobacterales and good coverage of Bacteroides fragilis.5
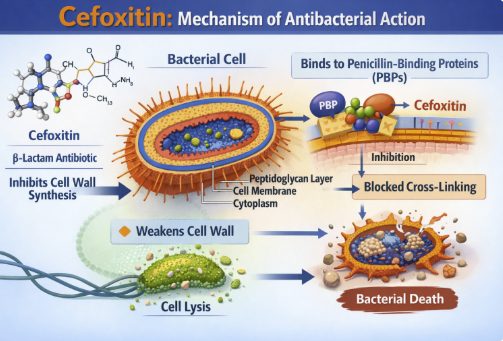
Cefoxitin is a β-lactam that inhibits cell-wall synthesis by binding to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) (transpeptidases).
This activity the final cross-linking steps of peptidoglycan, leading to structurally fragile cell walls and ultimately bacterial lysis.6,7
Points of emphasis include:
Bactericidal PBP-binding mechanism
Relative stability to many penicillinases and cephalosporinases.
Potent activity against anaerobes in the spectrum of Gram-negative rods.
 |
Major considerations
![]() Gram-positive
aerobes (MSSA, streptococci)6,7
Gram-positive
aerobes (MSSA, streptococci)6,7
Active against methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus and various streptococci (S. pyogenes, S. pneumoniae, S. agalactiae)
![]() MRSA and enterococci are intrinsically resistant.
MRSA and enterococci are intrinsically resistant.
Gram-negative anaerobes
![]() Cefoxitin
exhibits good activity activity against many E. coli,
Klebsiella spp., Proteus mirabilis,
Proteus vulgaris, Morganella morganii, Providencia
spp., Haemophilus influenzae, and Neisseria
gonorrhoeae.
Cefoxitin
exhibits good activity activity against many E. coli,
Klebsiella spp., Proteus mirabilis,
Proteus vulgaris, Morganella morganii, Providencia
spp., Haemophilus influenzae, and Neisseria
gonorrhoeae.
![]() Poor activity with cefoxitin has been noted for: Pseudomonas
aeruginosa and many Enterobacter, Serratia,
Citrobacter (especially AmpC-producers).
Poor activity with cefoxitin has been noted for: Pseudomonas
aeruginosa and many Enterobacter, Serratia,
Citrobacter (especially AmpC-producers).
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
Anaerobes
Cefoxitin exhibits excellent activity vs Bacteroides spp., including B. fragilis, Clostridium spp., Peptostreptococcus, and related anaerobes.
Accordingly, this antibiotic is
especially attractive for intra-abdominal and pelvic
infections.6,8
|
|
This Web-based pharmacology and disease-based integrated teaching site is based on reference materials, that are believed reliable and consistent with standards accepted at the time of development. Possibility of human error and on-going research and development in medical sciences do not allow assurance that the information contained herein is in every respect accurate or complete. Users should confirm the information contained herein with other sources. This site should only be considered as a teaching aid for undergraduate and graduate biomedical education and is intended only as a teaching site. Information contained here should not be used for patient management and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with practicing medical professionals. Users of this website should check the product information sheet included in the package of any drug they plan to administer to be certain that the information contained in this site is accurate and that changes have not been made in the recommended dose or in the contraindications for administration. Advertisements that appear on this site are not reviewed for content accuracy and it is the responsibility of users of this website to make individual assessments concerning this information. Medical or other information thus obtained should not be used as a substitute for consultation with practicing medical or scientific or other professionals. |