Medical Pharmacology Chapter 35 Antibacterial Drugs
Second Generation Cephalosporins: Cefuroxime
| Oral Administration |
Pharyngitis and Tonsillitis (Oral Cefuroxime Axetil)2,3,4
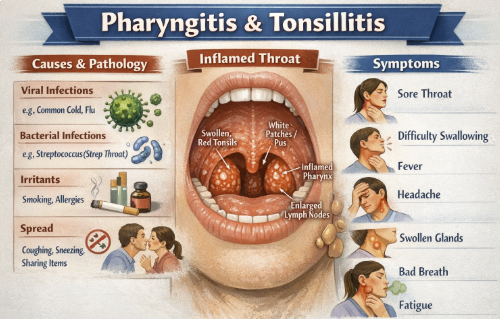 |
Cefuroxime axetil administration may be appropriate for treatment of mild-to-moderate strep throat (pharyngitis/tonsillitis) caused by Streptococcus pyogenes in patients ≥13 years old.
Cefuroxime is essentially a second-line option for strep throat in adolescents or adults who cannot take penicillins.
Cefuroxime may be used in children (certain age groups).5
Acute Otitis Media (Oral Cefuroxime Axetil)
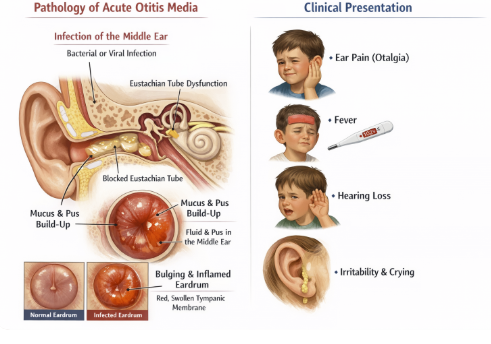 |
Treatment of acute otitis media in children (and adults) due to S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis, or S. pyogenes (including β-lactamase producing strains of Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis).2
Treating acute otitis media is an important pediatric of cefuroxime due to its effectiveness against the major acute otitis media pathogens.6,7,8
If a child has an ear infection not responding to amoxicillin (perhaps due to a β-lactamase producing H. influenzae), switching to cefuroxime axetil or amoxicillin-clavulanate may be appropriate.
Acute Bacterial Sinusitis (Oral Cefuroxime Axetil)2,910
Treatment of acute bacterial maxillary sinusitis in adults or adolescents (≥13) caused by susceptible S. pneumoniae or non-β-lactamase-producing H. influenzae.
Cefuroxime axetil is indeed used for sinusitis, including in children, especially when organisms like M. catarrhalis or H. flu (which often elaborate β-lactamase) are suspected.
Cefuroxime is effective in this context given its resistance to beta-lactamases associated with these bacteria.
Acute Bacterial Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis (Oral Cefuroxime Axetil)2,11,12
In adults (and adolescents ≥13), oral cefuroxime is indicated for acute bacterial exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, caused by susceptible strains of S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae (β-lactamase–negative), or H. parainfluenzae.
This treatment may be targeted for COPD patients or smokers with chronic bronchitis who get a secondary bacterial infection.
Many of those infections involve β-lactamase–producing strains, against which cefuroxime would still be effective (except that some H. influenzae with certain β-lactamases or other resistance may require a stronger agent).
Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections (Oral Cefuroxime Axetil)2,4,13,14
Oral cefuroxime (in patients ≥13) is indicated for uncomplicated UTIs (like simple cystitis) due to E. coli or Klebsiella.
Oral cefuroxime is often reserved for cases where first-line oral agents can not be used.
Cefuroxime remains an effective oral option for UTIs caused by susceptible organisms, including some that produce narrow-spectrum β-lactamases given that cefuroxime will remain active whereas amoxicillin might not.
Uncomplicated Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (Oral Cefuroxime Axetil)2
Oral cefuroxime is indicated in patients ≥13 for uncomplicated skin infections (impetigo, cellulitis) due to MSSA or S. pyogenes.
Pediatric impetigo (often staph or strep) can also be treated with cefuroxime suspension as an alternative to first-generation cephalosporins or anti-Staphylococcal penicillins, especially if broader gram-negative coverage is desired to address possible mixed infection.
|
Early Lyme Disease (Oral Cefuroxime Axetil)2
Cefuroxime axetil is FDA-approved for early Lyme disease (erythema
migrans stage) in adults and children ≥13.21,22
Cefuroxime is one of the first-line oral options for Lyme
borreliosis caused by Borrelia burgdorferi.
Cefuroxime efficacy in this setting is particularly important
for patients who cannot take doxycycline notably pregnant women
or young children.
Joint guidelines by the IDSA, American Academy of Neurology, and
American College of Radiology identifies cefuroxime as an
equivalent alternative to doxycycline or amoxicillin for
treating early Lyme disease.2
![]() Doxycycline is contraindicated in pregnancy and in children <8
due to effects on teeth/bone, so cefuroxime is an excellent
substitute in those cases.
Doxycycline is contraindicated in pregnancy and in children <8
due to effects on teeth/bone, so cefuroxime is an excellent
substitute in those cases.
February, 2026
|
|
This Web-based pharmacology and disease-based integrated teaching site is based on reference materials, that are believed reliable and consistent with standards accepted at the time of development. Possibility of human error and on-going research and development in medical sciences do not allow assurance that the information contained herein is in every respect accurate or complete. Users should confirm the information contained herein with other sources. This site should only be considered as a teaching aid for undergraduate and graduate biomedical education and is intended only as a teaching site. Information contained here should not be used for patient management and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with practicing medical professionals. Users of this website should check the product information sheet included in the package of any drug they plan to administer to be certain that the information contained in this site is accurate and that changes have not been made in the recommended dose or in the contraindications for administration. Advertisements that appear on this site are not reviewed for content accuracy and it is the responsibility of users of this website to make individual assessments concerning this information. Medical or other information thus obtained should not be used as a substitute for consultation with practicing medical or scientific or other professionals. |